Feedback Mechanisms & Homeostasis
advertisement

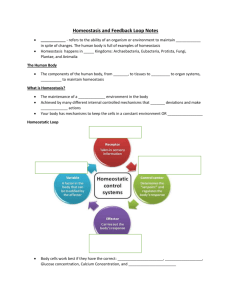
FEEDBACK MECHANISMS & HOMEOSTASIS HOMEOSTASIS • Maintaining the internal environment within a stable range given factors that influence the external environment • Homeostasis controls many aspects of the internal environment, for example: • Body temperature • Blood concentrations of: glucose, hormones, carbon dioxide and ions • Oxygen levels • Blood pH • Blood pressure • Solute concentration (Water balance) FEEDBACK MECHANISMS • Maintain homeostasis by detecting and responding to a stimulus • A non-biology example: NEGATIVE FEEDBACK • Reduces the size of the stimulus to restore homeostasis • Temperature regulation • Blood glucose • Blood pressure • Stimulus effector response NEGATIVE FEEDBACK: HUMANS Protein receptor on cells surface takes up insulin BLOOD PRESSURE NEGATIVE FEEDBACK • A. stimulus – exercise increases blood pressure • B. receptor gets the message to the (C) control center. • D. The effector, the heart, pumps blood slower & E. blood vessels dilate & get wider to allow blood to pass through). • F. Homeostasis is obtained NEGATIVE FEEDBACK: PLANTS POSITIVE FEEDBACK - CHILDBIRTH POSITIVE FEEDBACK • Response increases the original stimulus to restore homeostasis • Rarely used • Only normal when there is a definite end point • Childbirth • Blood clotting