Lead (Pb) Awareness - Hettrick, Cyr & Associates, Inc.
advertisement

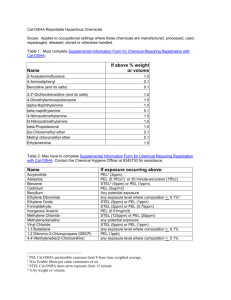
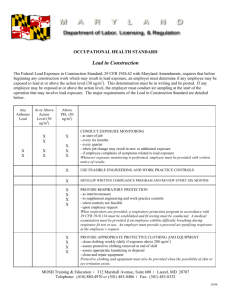
<Insert Company Name Here>. EXPOSURE TO LEAD IN CONSTRUCTION 29 CFR 1296.62 LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Purpose: The purpose of the Company’s Lead Safety Program is to protect both our employees and the environment from lead contamination. The intent of out program is to be in full compliance with OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1926.62 and all other local, State, and Federal Requirements. A copy of 29 CFR 1926.62 can be obtained from the Corporate Safety Director. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM What is Lead: Discovered by: - Known since ancient times Origin name – From the Latin word “plumbum,” meaning liquid silver Period Symbol – Pb Lead is a bluish-white lustrous metal. It is very soft, highly malleable, ductile, and a relatively poor conductor of electricity. It is very resistant to corrosion but tarnishes upon exposure to air. It is believed that Lead Poisoning contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire: The Romans used lead to make drinking chalices,to line the city water supply system, and for drainage rings in their bathtubs. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Common Uses of Lead (Metal & Dioxides): Storage batteries Cable covering Plumbing Ammunition Gasoline (phased out) Sound absorber Radiation shields around X-ray equipment and nuclear reactors Paints (phased out) Production of fine "crystal glass" and "flint glass“ Solder Pewter LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Key Definitions: Action Level: means employee exposure, without regard to the use of respirators, to an airborne concentration of lead of 30 micrograms per cubic meter of air (30 ug/m3) calculated as an 8-hour time weighted average (TWA). Competent Person: means one who is capable of identifying existing and predictable lead hazards in the surroundings or working conditions and who has authorization to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them. Lead: means metallic lead, all inorganic lead compounds, and organic lead soaps. Excluded for this definition are all other organic lead compounds Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL): (1) the employer shall assure that no employee is exposed to lead at concentrations greater than 50 ug/m3 TWA: (2) If the employee is exposed to lead for more than eight hours in any work day, the employees’ allowable exposure, as a TWA for that day shall recalculated. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM What are different types of lead exposure: 1 - Welding 2 – Cutting 3 – Abrasive Blasting 4 – Torch Burning 5 - Grinding 6 - Chipping 78910 - LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Safety Director Responsibilities: Entire lead safety program, including revisions and updates to reflect the current status of the program Engineering & administrative controls for lead exposure Employee training and awareness Medical surveillance program Respiratory protection program Lead disposal program Housekeeping program Protective clothing issue, storage, and disposal LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Superintendent / Foreman Responsibilities: Provide effective and continuous control of all lead operations Immediately report any deficiencies in engineering or administrative controls Conduct routine assigned inspections and monitoring Provide immediate on-the-spot training for any employee who shows lack of knowledge of lead safety requirements Ensure all employees are properly trained before commencing any operation that may contribute to lead exposure LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Employee Responsibilities: Follow all operational and lead safety procedures Seek immediate assistance to resolve questions Conduct operations in accordance with company provided training Immediately report to a superintendent, foreman, or safety director any deficiency in engineering or administrative controls Properly use, store, and dispose of issued and assigned personal protective clothing. Maintain hygiene facilities in a neat and orderly manner LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: Pure Lead (Pb) is a heavy metal at room temperature and pressure and is a basic chemical element. Lead can be combined with various other substances to form numerous lead compounds. When heat is provided, Lead will produce Lead Fumes. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM ROUTES OF ENTRY: INHALATION – When Lead is scattered in the air as dust, fume, or mist it can be inhaled and absorbed into the lungs and upper respiratory tract. ABSORBATION – Lead can also be absorbed through the digestive system if swallowed. Handling food, cigarettes, chewing tobacco, or make-up which have lead contamination or handling these items with hands contaminated with lead, will contribute to ingestion. Lead cannot be absorbed through the skin LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM HEALTH HAZARDS: A significant portion of inhaled or ingested Lead goes directly into the blood stream. Once in the blood stream, Lead is circulated throughout the body and stored in various organs and body tissue. Some of the Lead is quickly filtered out of the body and excreted, but some remains in the blood and other tissues. As exposure to Lead continues, the amount stored in the body will increase. LEAD stored in the body tissue can cause irreversible damage, first to individual cells, then to organs and whole body systems. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Lead Health Hazard Information for Employees Prevention of adverse health effects for most workers from exposed to lead throughout a working lifetime requires that workers blood lead (PbB) levels be maintained at or below 40 micrograms per 100 grams of whole blood (40ug/100g) The blood lead levels of workers (both male & female) who intend to have children should be maintained below 30 ug/100g to minimize adverse reproductive health affects to the parents and to the developing fetus. Once your blood lead level climbs above 40 ug/100g, your risk of diseases increases. Your blood lead level will not indicate the amount of lead stored inside your body tissue, only the amount circulating in your blood stream. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM SHORT-TERM (ACUTE) EFFECTS OF OVEREXPOSURE TO LEAD: Lead is a potent, systemic poison Taken in large enough doses, lead can kill in a matter of days Acute brain conditions may develop quickly to seizures, coma, and death from cardio respiratory arrest. Lead adversely affects numerous body systems, and causes forms of health impairment and disease which arise after periods of exposure as short as days or as long as several years LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Long-term (Chronic) Effects of Overexposure to lead: Chronic overexposure to lead may result in severe damage to blood-forming, nervous, urinary, and reproductive systems. Some common symptoms of chronic overexposure include: Loss of appetite – Metallic taste in the mouth – Anxiety – Constipation Nausea – Excessive Tiredness – Weakness – Insomnia – Headache Nervous irritability – Muscle & joint pain or soreness – Fine tremors Numbness – Dizziness – Hyperactivity - Colic In lead colic there may be severe abdominal pain LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Monitoring: The company will make an “initial determination” of lead work tasks and exposure levels. The company will make subsequent “initial determinations” in the event of changes to hazard control methods or operational processes that affect employee or environmental exposure. Initial Determinations shall be conducted to determine if any employee may be exposed to lead at or above the action level of 30 micrograms per cubic meter of air (30 ug/m3) averaged over an eight (8) hour period. Where documentation is made that no employee is exposed to airborne concentrations of lead at or above the action level, the company shall maintain a written record. The record shall include quantitative sampling data, date of determination, location of the worksite, and the name and social security number of each employee monitored. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Monitoring Requirements: Where a determination shows the possibility of any employee exposure at or above the action level, the company shall conduct monitoring which is representative of the exposure for each employee in the workplace or process area who is exposed to lead. For the purpose of monitoring requirements, employee exposure is that exposure which would occur if the employee were not using a respirator. Monitoring and sample collection shall cover full shift (for at least 7 continuous hours) personal samples including at least one sample for each shift of each job classification in each work area. Full shift personal samples must be representative of the monitored employee’s regular, daily exposure to lead. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Monitoring Frequency: At or above the Action Level and Below PEL: Every six months if the initial determination or subsequent monitoring reveals employee exposure at or above the action level and below the permissible exposure limit (PEL) This monitoring frequency will continue until at least two consecutive measurements, taken at least seven days apart, are below the action level. Above the PEL: If the initial monitoring reveals that employee exposure is above the PEL the company will repeat monitoring every three months Quarterly monitoring will continue until at least two consecutive measurements, taken at least seven days apart, are below the PEL but at or above the action level. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Additional Monitoring: Whenever there has been a production, process, control or personnel change which may result in new or additional exposure to lead, or whenever any other reason to suspect a change which may result in new or additional exposures to lead, additional monitoring will be conducted. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Employee Notification of Monitoring Results: Within five working days after the receipt of monitoring results, each employee will be notified in writing of the results which represent that employee’s exposure Whenever the results indicate that the representative employee exposure, without regard to respiratory protection, exceeds the PEL, the notice will include a statement that the PEL was exceeded and a description of the corrective action taken or to be taken to reduce the exposure to or below the PEL LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Methods to Reduce Overexposure to Lead: Engineering Controls Mechanical Ventilation Non-recirculation of contaminated air Administrative Controls Job rotation schedules Respirators Respirators shall only be utilized to supplement engineering and administrative controls The respiratory program shall be in compliance to 29 CFR 1910.134 LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Protective Clothing & Equipment If an employee is exposed to lead above the PEL, without regard to respiratory protection, or where the possibility of skin irritation exists, the company will provide at no cost to the employee appropriate protective work clothing and equipment such as, but not limited to: Coveralls or similar full-body clothing Gloves, hats, and shoes or disposable shoe coverlets Face shield, vented goggles, or other appropriate protective equipment LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Housekeeping: All surfaces shall be maintained as free as practicable or accumulations of lead Floors and other surfaces where lead accumulates may not be cleaned by the use of compressed air Shoveling, dry, or wet sweeping, and brushing may be used only where vacuuming or other equally effective methods have been tried and found not be effective Where vacuuming methods are used, the vacuums shall be used and emptied in a manner which minimizes the reentry of lead into the workplace. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Hygiene Facilities & Practices: The following requirements pertain to all areas where employees are exposed to lead above the PEL, without regard to the use of respirators No storage or consumption of food or beverages No tobacco product storage or use No personal clothing or articles, except in authorized change areas The following items shall be provided by the company, at no cost to the employee, for any employee who is exposed above the PEL. Change rooms Showers Separate Lavatories LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Safe Work Practices: Any employee who handles lead, or a lead compound material shall wash their hands and face with soap and water, or equivalent: Prior to eating, drinking, smoking, or chewing tobacco At the end of each shift The use of work gloves will not negate the need to wash hands and face prior to handling food, beverages or tobacco products. Food, beverages, and/or tobacco products shall not be stored or consumed in the work area. All employees engaged in lead work activity shall participate in the Lead Monitoring program including: Personal Air Sampling, Hand Wipes, and if required – Medical Monitoring. LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Signs: Proper signs will be posted at the entrance and exits to all lead hazard areas above the PEL. No other signs or statements may appear on or near any lead hazard sign which contradicts or detracts from the meaning of the required sign All lead hazard signs will be kept illuminated and cleaned as necessary to that the legend is readily visible. The signs will contain the following or other appropriate wording/warning: WARNING LEAD WORK AREA POISON NO SMOKING OR EATING LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Employee Training: All affected employees will participate in the company Lead Safety Training program. All affected employees will be trained prior to the time of initial job. All affected employees shall be trained on the specific nature of the operations which could result in exposure to lead above the action level Employee training shall consist of: Specific OSHA requirements contained in: 1926.62 – OSHA Lead Standard 1926.62 – App A – Substance data sheet for occupational exposure to lead 1926.62 – App B – Employee standard Summary LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Medical Surveillance: The company has instituted a medical surveillance program for all employees who are or may be exposed above the action level for more than 30 days per year. This medical surveillance program and all medical examinations and procedures are performed by or under the supervision of a licensed physician. The program functions under the requirements of OSHA Standard 1926.62. Elements of the program include: Biological testing Employee notification Medical examinations and consultants Medical removal protection Medical removal and protection benefits LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM Recordkeeping: All records relating to the company lead safety program are to be maintained for at least 40 years or the duration of employment plus 20 years, whichever is longer. The following records will be established and maintained: Exposure Monitoring Medical Surveillance Medical Removals