Organic Chemistry
advertisement

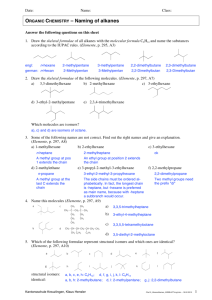
Organic Chemistry Ch. 18 Organic Chemistry • Study of organic molecules: – Hydrocarbons – Alcohols – Acids – Vitamins – Ethers • Naming hydrocarbons • Naming side groups • Formation of polymers Alkane • Saturated Hydrocarbons – Maximum # of H atoms; all single bonded carbon atoms • Can exist as Chains or Rings • Longest chain of carbons is called the Parent Chain • Parent Chain tells you the base name • ALWAYS end in ANE • Rings always include “Cyclo” Properties of Alkanes • Alkanes vary in Parent Chain length and complexity • Longer Parent Chains= higher melting/boiling points • 1-4 carbons gases • 5-16 carbons liquids • +16 carbons solids • Rings burn more uniformly while chains tend to explode • Produce Structural Isomers – Same molecular formula but different structure and therefore different name Writing Compounds • Shorthand: Pentane CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Shows number of Carbon/Hydrogen but no structure • Condensed: CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 • Structural Diagram: Naming Alkanes • Simple Alkanes you follow base name; Side groups make things pentane more complicated • Side group- any carbon chain, alcohol, ether, etc…attached to the parent chain 2-methylbutane • Rules: 1) Parent chain is longest number of carbons 2) Side groups must have the LOWEST position numbers possible 3) Alkane side groups end in “-yl” 4) Multiple side groups use Latin numbers; di, tri, etc… 5) Multiple side groups are alphabetical 2,2-dimethylpropane 4-ethyl-3-methylheptane Practice Naming Alkanes CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 nonane 3-ethylhexane 5-(1-methylpropyl)decane cyclopropylcyclopentane (2,2-dimethylpropyl) cycloheptane Alkenes • Unsaturated Hydrocarbons; missing H atoms due to double bonds • Can exist as Chains or Rings • Longest chain of carbons is called the Parent Chain (contains double bond) • Parent Chain tells you the base name • ALWAYS end in ENE • Rings always include “Cyclo” ethene 3-octene cyclodecene • Rules: Naming Alkenes 1) Double bond must have the lowest position number 2-methyl-3-heptene possible 2) Use di, tri, ect… plus “ene” when there are multiple double bonds 3) If double bond is a side 3,3-dimethyl-1-hexene group add “-yl” to ene 4) Rules for side groups still apply Draw: 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-nonene Properties of Alkenes • Ethene gas is huge part of plastic production • Double bond produces Geometric Isomers – Double bond stops free rotation of atoms – Cis isomers Same side – Trans isomers Opposite side • Trans Alkenes have higher melting points than Cis Alkenes • Alkenes become Alkanes through Hydrogenation – Reacting with H2 gas Cis Trans Practice Naming Alkenes 2-ethlyhexene trans-2-pentene cis-3-(1-methylethyl)-2hexene cyclopentene Aromatic Hydrocarbons • 6 carbon Alkene ring – Benzene • Electrons shared equally in the ring; resistant to Hydrogenation • Give of distinct aromas: – Cinnamaldehyde 肉桂醛 • Cinnamon – Phenylethanol 苯乙醇 • Roses Alkynes • Unsaturated Hydrocarbons • Contain triple bonded carbon atoms • Naming rules are the same for Alkenes • ALWAYS ends in YNE • The longer the Alkyne the higher the boiling/melting points • Made into Alkenes with Hydrogenation propyne 5-ethyl-3-heptyne 5-cyclopropyl-1-hexyne Practice Naming Alkynes 5-methly-2-hexyne 4-methyl-1,5-octadiyne 5-ethyl-2-methyl-3-heptyne 2-methyl-3-hexyne