CH 2
advertisement

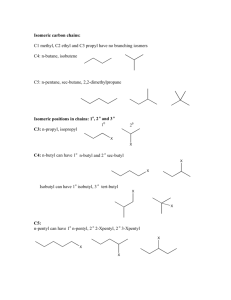
Organic Nomenclature Alkanes SWBAT: Name alkanes with alkyl groups Organic Chemistry The study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (synthesis) of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons and their derivatives Organic Molecules Organic molecules are compounds consisting of nonmetals (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, the halogens, phosphorus, silicon and sulfur) with carbon Due to carbon’s hybrid bonding orbitals, organic molecules have a variety of configurations The types of atoms bonded to the carbon atoms will ultimately determine function and properties of the compound Organic vs. Inorganic General Comparison Organic Compounds Mostly covalent bonding Low boiling pt Low melting pt High flammability Most are nonpolar Not soluble in water unless a polar group is present Do not conduct electricity Inorganic Compounds Many ionic, some covalent High boiling pt High melting pt Low flammability Most are ionic or polar covalent Most are soluble in water unless nonpolar Conduct electricity Hydrocarbons A hydrocarbon chain is a series of carbons bonded together with numerous hydrogen's attached Includes Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Cyclical HC Use certain prefixes for naming to indicate chain length Alkane Formulas and Names Strings, branches of carbons with single bonds between C Essentially many CH4 reacted together Formula rules: CnHn+2 CH2 – methylene unit Names: Prefixes indicate # of C followed by -ane Homologous series of the first 12 linear alkanes Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Heptane Octane Nonane Decane Undecane Dodecane (meth=1) (eth =2) (prop=3) (but=4) (pent=5) (hex=6) (hept=7) (oct=8) (non=9) (dec=10) (undec = 11) (dodec= 12) CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C7H16 C8H18 C9H20 C10H22 C11H24 C12H26 1-10 Alkane Prefix Quiz Just the prefix…not the -ane 1. CH4 6. C6H14 3. C3H8 8. C8H18 2. C2H6 4. C4H10 5. C5H12 7. C7H16 9. C9H20 10.C10H22 Mnemonic for First 8 Prefixes Mrs. Edwards Plays Basketball, Please Hold Her Overcoat Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Heptane Octane CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C7H16 C8H18 Alkane Naming and Drawing 1. Expanded structure 1. Make string of carbons (prefix= # of C) Ex: Butane (but=4) Butane 2. Condensed structure A CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 3. Condensed structure B CH3CH2CH2CH3 4. Condensed structure C CH3(CH2)2CH3 Butane 5. Carbon skeleton: C-C-C-C *all H are understood 6. Kekulé or Line-angle formula (most reduced form) • Each endpoint, every corner symbolizes a C • H are understood Alkanes methane hexane CH4 C6H14 ethane heptane C2H6 C7H16 propane octane C3H8 C8H18 butane nonane C4H10 C9H20 pentane decane C5H12 C10H22 Alkyl Groups Substituent – element or group of elements that branch off parent chain (replace a H) methyl ethyl group group propyl group Alkyl Groups isopropyl butyl groups butyl secbutyl tertbutyl isobutyl Only iso- is alphabetized, tert, sec are not. Haloalkanes Haloalkanes have a halogen that has replaced a hydrogen The halogens are substituent groups treated the same as the alkyl groups. Alpha without prefixes F = fluoro Cl = chloro Br = bromo I = iodo Rules to Naming Hydrocarbon Chains 1. Number the longest continuous chain of carbons 1. 2. 2. Carbons attached to double/triple bonds receive the smallest number possible If no double/triple bonds are present, carbons with groups attached, receive the smallest number possible Use prefixes for repeating groups di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, …. 3. 4. 5. Alphabetize groups without prefixes All lowercase, commas between numbers, dashes between numbers and words Use appropriate ending ane, ene, yne or functional group ending Find The Longest Continuous Chain of Carbons Number the Carbons so that the groups receive the smallest number possible Use prefixes with same multiple substituent groups 7 – ethyl – 3,5 - dimethyl – 6 - tertbutylundecane Naming Hydrocarbon Chains Naming Hydrocarbon Chains Naming Hydrocarbon Chains If more than one type of substituent group, alpha. the groups without prefixes 5 – secbutyl - 3,6 – dimethylnonane 4 – tertbutyl - 5 - ethylnonane Cycloalkanes 1. Start at noon and go clockwise until you get to first carbon with a substituent group this is # 1 2. Go clockwise or counterclockwise so substituent groups receive the smallest number possible Cyclical Alkanes have 2 H less from ring closure cyclopropane C3H6 cyclooctane C8H16 cyclobutane cyclononane C4H8 C9H18 Alkanes cyclodecane C10H20 cycloundecane C11H22 cyclododecane C12H24 Practice methylcyclopentane 1,1-dimethylcyclopentane Practice 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane Practice 2-ethyl,1-methylcyclohexane Practice 2-cyclopropyl-4-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane