Zac Epstein Jessica Hudson 1763-1776 1763 Pontiac's Rebellion
advertisement

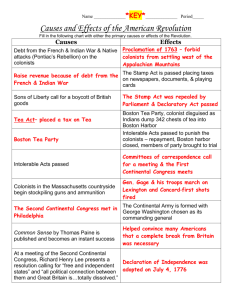
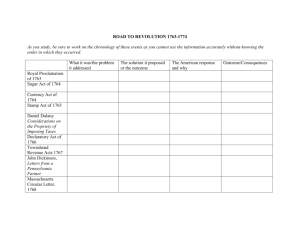
Zac Epstein Jessica Hudson 1763-1776 1763 Pontiac’s Rebellion: multiple Indian tribes came together under Pontiac to rebel against British Proclamation Line of 1763: Limited white settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains Treaty of Paris: ended the Great War for Empire, a war in Europe in which British fought Paxton Boys massacre: a group of Scots-Irish men living on western frontier (called Paxton Boys) killed twenty of Conestoga tribe, a peaceful one 1764 Currency Act of 1764: banned paper money in America Sugar Act of 1764: replaces Molasses Act of 1733; raised price of French molasses, encouraged colonists to buy products from England, hurt those who thrived off importing cheap molasses 1765 Stamp Act of 1765: direct tax put on printed documents Quartering Act: required colonists provide food and shelter for British troops First American boycott of British goods 1766 Stamp Act repealed Declaratory Act passed 1767 Townshend Act of 1767: meant to raise money from colonists Revenue Act of 1767: meant to “strengthen imperial power” New Yorkers refused to comply by Quartering Act, etc., ends in Restraining Act (New York assemblies suspended) 1768 Second American boycott: British goods boycotted in NY, MA; spreads to VA, PA development of Daughters of Liberty (women take part in boycott, make own cloth, etc.) 1769 British army occupies Boston 1770 Partial repeal of Townshend Act Boston “Massacre”: seven civilians killed; intensified by colonist reporters, political cartoonists to gain resistance to British 1773 Tea Act: gave East India Company government loan, making English tea cheaper than smuggled tea from the Netherlands Boston Tea Party: December 16, 1773: artisans and laborers tired of being taken out of economy, dressed up as Indians and threw 342 tea chests into harbor (about $900,000 today) 1774 Coercive Acts: passed by Parliament, made MA pay for the tea wasted (closed Boston Harbor to shipping, suspended town meetings, new Quartering Act) Justice Act: allowed trials to be moved to other colonies and Britain Quebec Act: Roman Catholicism allowed in Quebec First Continental Congress (September, Philidelphia): Declaration of Rights and Grievances passed, asked for King to repeal Coercive Acts; decided to stop accepting British goods in December 1774, if by September of 1775 Parliament hadn’t repealed acts, vowed to stop exports to Britain and affiliates 1775 Second Continental Congress: created a Continental army 1776 Thomas Paine’s Common Sense published, rapidly gains popularity, mocked British government Zac Epstein Jessica Hudson Declaration of Independence: signed on July 4, 1776; written by Thomas Jefferson, who established the new nation’s political views