Exercise Science
advertisement

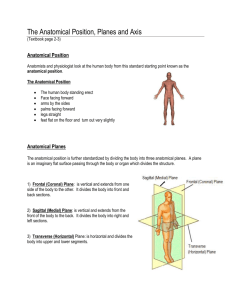
Exercise Science Grade 12 Principles and Terminology 1 week Basis of the entire course Get off to a good start and remember the terminology Course Terms Exercise Physiology: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Why? Concerned with maximizing athletic performance and exercise potential Terminology Anatomical Position Is used as a standard starting position ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ Anatomical Planes The anatomical position can be standardized by dividing the body into three anatomical planes These planes relate to positions in space and are at right angles to one another Anatomical Planes Frontal (Coronal) Plane: ______ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Sagittal (median) plane: _____ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Transverse (horizontal) plane: ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Anatomical Axes In addition to anatomical planes, the human body is also divided into anatomical axes Anatomical axes are used to describe the direction of movement at joints Anatomical Axes Horizontal Axis: ____________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Longitudinal axis: ___________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Antero-posterior axis: _______ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Combining Anatomical Axes and Planes The body can be described by: The anatomical plane through which the movement occurs and The anatomical axis around which it rotates Example Bicep Curl Bending of a joint that reduces the angle between two bones (Flexion) Happens on the horizontal axis and through the sagittal plane Joint is the elbow (axis) Range of motion (plane) front/back Relationships b/w Axes and Planes 0f Movement Axis of Rotation Plane of Motion Example Horizontal Sagittal Flexion, extension Longitudinal Transverse Rotation of extremities, axial rotation Antero-posterior Frontal Abduction adduction Joint Movements Flexion: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Example? Extension: ___________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Occurs in the sagittal plane Example? Joint Movements Abduction: ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Occurs in the frontal plane Example? Adduction: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Occurs in the frontal plane Example? Joint Movements Internal Rotation ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Occurs in the transverse plane plane Example? External Rotation: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Occurs in the transverse plane Example? Joint Movements Elevation ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Occurs in the frontal plane plane Example? Depression: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Occurs in the frontal plane Example? Joint Movements Supination: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Think soup Example? Pronation: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Think pouring of something Example? Joint Movements Circumduction: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Compound movement happening in both the frontal and sagittal planes Joint Movements Dorsiflexion: Movement of ankle to decrease angle between foot and lower leg Occurs in the sagittal plane Example? Plantar Flexion: Movement of ankle to increase angle between foot and lower leg Occurs in the sagittal plane Example? Joint Movements Inversion: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ____________ Example? Eversion: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ____________ Example? Joint Movements Opposition: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ____________ Example? Reposition: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ____________ Example? Joint Movements Protraction: Movement in an anterior direction Forward Example? Retraction: Movement in a posterior direction Backward Example? Video of Joint Movements Joint Movements http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Wf7mmecaWE Directional Terms The following terms will allow you to explain body position and movement There are 10 terms 5 ideas with opposites Directional Terms Anterior Refers to the front of the body Can also refer to relationships within the body Example The sternum is anterior to the heart Posterior Refers to the back of the body Can also refer to relationships within the body Example The heart is posterior to the sternum Dorsal means towards the back and ventral means toward the front (anterior and posterior or more common terms) Directional Terms Directional Terms Superior Refers to upward surfaces Inferior Refers to downward surfaces Medial Means toward the midline or sagittal plane Lateral Means away from the midline or sagittal plane Directional Terms Proximal Means toward the point of attachment of the limb to the body Distal Means farther away from the point of attachment Superficial Mean on, or close to, the surface of the body Deep Means farther away from the surface of the body Directional Terms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-GAw9w1XNEI Joint Movements http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Wf7mmecaWE