IIC.30 MLA Citation and Format Presentation
advertisement

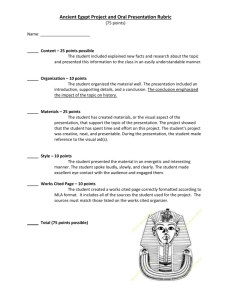
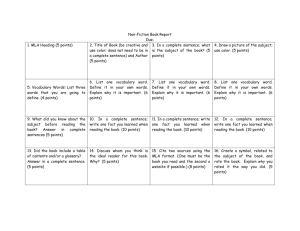
An Introduction to MLA Citation & Format Clovis Community College Center Table of Contents What is MLA? Why Use Documentation? Comparing Other Styles The Basic Format Cover Page Work Cited In-text Citations for Print and Electronic Sources Work Cited Books Magazines Websites Databases What is MLA? MLA is the Modern Language Association’s standardized method for citing sources for research as well as a method for formatting papers. MLA format is typically used for English and Humanities. Why Use Documentation? It helps a writer support a thesis. It helps integrate quotations and other source material. It provides your reader with research information on your topic. And most importantly, it helps avoid plagiarism. Comparing Other Styles APA – American Psychological Association standard for documenting sources and formatting papers. This style is typically used for Social Sciences. Chicago Style – This is yet another method of documentation which is typically used for Humanities and Social Sciences. Don’t confuse these with MLA; see the guidelines specific to this style. The Basic Format In-text Citations for Print and Electronic Sources After the borrowed phrase, put the author’s last name in parentheses along with the page number. E.g. Estimates of the number of accidents caused by distracted drivers vary because little evidence is being collected (Smith 2). On electronic sources with no page number, simply put the last name. The Work Cited Page Work Cited Format for a Book For most books, arrange the information into three units, each followed by a period and one space. Start with the author’s name, last name first. The title and subtitle, italicized. The place of publication, the publisher, and the date The medium of publication (print or web) E.g. Tan, Amy. The Bonesetter’s Daughter. New York: Putnam, 2001. Print. Work Cited Format for a Magazine List in order, separated by periods. The The The The author’s name title of the article, in quotation marks title of the magazine, italicized date and the page numbers, separated by a colon The medium of publication (print or web) E.g. Kaplan, Robert D. “History Moving North.” Atlantic Monthly. Feb.1997: 21+. Web. Work Cited Format for Websites For websites include these elements: Author’s name Title of the work in quotation marks Title of the site, italicized Date of publication or last update Sponsor of the site (if not named as the author or given as the title of the site) Date that you accessed the source The URL in angle brackets (optional) The medium of publication E.g. Shiva, Vandana. “Bioethics: A third world issue.” Native Web. 15 Sept. 2001.<http://www.nativeweb.org/pages/legal/ shiva. html>. Web. Work Cited Format for an Online Database For databases include these elements: Publication information for the source The name of the database, italicized The name of the service The name and location of the library where you retrieved the article The date you accessed the source The URL of the service (optional) The medium of publication Common Misconceptions About MLA MLA does not require a cover sheet as some may think; cover sheets are used only for APA and Chicago. All sources listed on the works cited page must be in alphabetical order. All paraphrases & quotations must be cited even if you’ve cited the source earlier in the essay. Double space everything, but do not include an extra space between paragraphs. For more assistance, visit the Writing Center in the open computer lab Hours: Monday 9:00-2:00 Tuesday 10:00-3:00 Wednesday 9:00-2:00 Thursday 10:00-3:00 Phone number 325-5248 Call or stop by to make an appointment with a tutor!