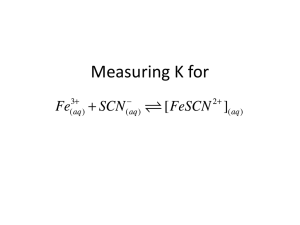Exp 2 Beer's Law
advertisement

EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT DETERMINATION Fe3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq) ⇆ FeSCN2+ (aq) (blood red) A darker color means a higher concentration of the colored component The “darkness” can be determined by measuring the amount of light absorbed by the solution, called its ABSORBANCE EX2-1 (of 21) COLORED SOLUTIONS A solution will appear a certain color if it absorbs its complementary color from the color wheel EX2-2 (of 21) COLORED SOLUTIONS If a solution appears red, it is primarily absorbing its complimentary color, green EX2-3 (of 21) SPECTROPHOTOMETER – A device that measures the amount of light absorbed by a sample A light bulb emits white light A diffraction grating separates the colors of light Light passes through a slit to form a narrow beam EX2-4 (of 21) Light passes through the sample Another slit allows just one color to pass A detector measures the final amount of light Incident 100 photons Light Transmitted 10 photons Light I0 It TRANSMITTANCE (T) – the fraction of the incident light that passes through the sample T = It /I0 T = 10 photons _________________ 100 photons EX2-5 (of 21) = 0.1 100 photons 10 photons I0 It ABSORBANCE (A) – negative logarithm of the transmittance A = -log (T) A = -log (0.1) = 1 EX2-6 (of 21) 100 photons 1 photon I0 It ABSORBANCE (A) – negative logarithm of the transmittance A = -log (T) A = -log (0.01) = 2 EX2-7 (of 21) PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION 10.00 mL 0.200 M Fe(NO3)3 EX2-8 (of 21) 3.00 mL 0.00200 M KSCN 17.00 mL 0.5 M HNO3 PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION Concentration of Fe(NO3)3 in the Stock Solution: MCVC = MDVD MC = 0.200 M MD = ? M VC = 10.00 mL VD = 30.00 mL MCVC = MD = (0.200 M)(10.00 mL) = 0.0667 M Fe(NO3)3 _______ ________________________ VD (30.00 mL) EX2-9 (of 21) PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION Concentration of KSCN in the Stock Solution: MCVC = MDVD MC = 0.00200 M MD = ? M VC = 3.00 mL VD = 30.00 mL MCVC = MD = (0.00200 M)(3.00 mL) _______ VD EX2-10 (of 21) ___________________________ (30.00 mL) = 0.000200 M KSCN PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION Concentration of Fe3+ in the Stock Solution: 0.0667 M Fe(NO3)3 x 1 = 0.0667 M Fe3+ Concentration of SCN- in the Stock Solution: 0.000200 M KSCN x 1 EX2-11 (of 21) = 0.000200 M SCN- PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION Concentration of FeSCN2+ in the Stock Solution: Fe3+ (aq) Initial M’s Change in M’s Equilibrium M’s 0.0667 -x 0.0667 - x + SCN- (aq) 0.000200 -x 0.000200 - x ⇆ FeSCN2+ (aq) 0 +x x We will assume all of the SCN- is converted to FeSCN2+ at equilibrium EX2-12 (of 21) PART A – Preparing the STOCK SOLUTION Concentration of FeSCN2+ in the Stock Solution: Fe3+ (aq) Initial M’s + 0.0667 - 0.000200 Change in M’s Equilibrium M’s 0.0667 – 0.000200 SCN- (aq) ⇆ 0.000200 -0.000200 0.000200 – 0.000200 FeSCN2+ (aq) 0 + 0.000200 0.000200 We will assume all of the SCN- is converted to FeSCN2+ at equilibrium the [FeSCN2+] = 0.000200 M EX2-13 (of 21) PART B – Preparing the STANDARD SOLUTIONS Must calculate the concentration of FeSCN2+ in each standard solution Solution 0: 0 M FeSCN2+ Solution 1: 0.000200 M FeSCN2+ Solutions 2-5: MCVC = MDVD EX2-14 (of 21) PART C – Determining the Absorbances of the STANDARD SOLUTIONS ABSORBANCE SPECTRUM – A graph of the absorbance of a solution at different wavelengths EX2-15 (of 21) PART C – Determining the Absorbances of the STANDARD SOLUTIONS LAMBDA MAX (λmax) – The wavelength of maximum absorbance When measuring the absorbance of solutions, it is most accurate to measure the absorbance at λmax EX2-16 (of 21) PART C – Determining the Absorbances of the STANDARD SOLUTIONS Absorbance Measure the absorbance of FeSCN2+ solutions of known concentrations at the peak wavelength, and plot absorbance vs. concentration C: 0.25 M A: 0.241 Concentration of FeSCN2+ EX2-17 (of 21) 0.50 M 0.478 0.75 M 0.722 1.00 M 0.961 BEER’S LAW – The mathematical relationship between concentration and absorbance A = ɛbc A = absorbance ɛ = extinction coefficient (a constant for a given solute at a given wavelength) b = width of the cuvet holding the sample (for our cuvets it is 1.00 cm) c = concentration (in our lab it’s in “M FeSCN2+”) EX2-18 (of 21) b = 1.00 cm A = ɛbc A = kc y = mx + b This means a graph of A vs. c will produce a straight line slope = ɛb EX2-19 (of 21) Beer's Law Graph 1.2 Absorbance 1 A-546.0 = mx + b m(slope): 3425 b(y-intercept): - 0.021 0.8 C: 0.25 M A: 0.241 0.50 M 0.478 0.75 M 0.722 1.00 M 0.961 0.6 0.4 A = ɛbc A = (3425 M-1)c – 0.021 0.2 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 M 0.8 1 1.2 FeSCN2+ This is called a CALIBRATION LINE m = Δy = Δ Absorbance = no units ____ _____________________ ____________ Δx Δ Concentration M EX2-20 (of 21) = M-1 Beer's Law Graph 1.2 Absorbance 1 A-546.0 = mx + b m(slope): 3425 b(y-intercept): - 0.021 0.8 C: 0.25 M A: 0.241 0.50 M 0.478 0.75 M 0.722 1.00 M 0.961 0.6 0.4 A = ɛbc A = (3425 M-1)c – 0.021 0.2 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 M 0.8 1 1.2 FeSCN2+ If an unknown solution has an absorbance of 0.351, find its concentration 0.351 = (3425 M-1)c – 0.021 0.372 = (3425 M-1)c 0.372 = c ___________ 3425 M-1 EX2-21 (of 21) = 0.000109 M