Organ - Lakeland Regional High School
advertisement

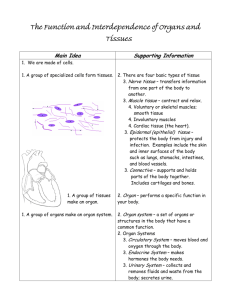
Who? How? Why? When? LIFE What? Where? Develop 10 questions that include the word life in it or any derivatives of the word life. For example: What is life? What is an active class discussion? Okay let’s have an active class discussion! The Meaning of Life Active Reading Activity 1. Answer pre-reading def. 2. Read Title & Skim Article 3. While reading underline important information, jot down notes, ask questions and rephrase important information 4. Answer post-reading questions. The Meaning of Life Active Reading Activity 1. Definitions 2. Reading Comprehension questions Pouring Water Demonstration Planet 1 Planet 2 Planet 3 Planet 4 What will happen when you fill a cup with water and then turn it over? Should we be exploring other planets in search of life? In what ways have we been able to explore other planets/moons? Comparing current methods of exploration: Satellite/Probe Pros Cons Mobile Robot Manned Mission What would be the best way to explore other planets/moon? Journal Question: What can you learn from dissecting a fetal pig? Do you think it is worth it? Explain. To truly explore other planets, we need to be able to interact without barriers. James Cameron’s Avatar Avatar Presented by James Cameron 1. Skim through movie questions. 2. Watch movie and answer questions. 3. Have fun! JQ: Would you choose to be cryogenically preserved (deep freeze after death) if the technology was available? Explain. Avatar Presented by James Cameron 1. Watch movie and answer questions. 2. Have fun! JQ: Is an Avatar living or non-living? How do you construct an Avatar? “Good science is good observation!” What does that mean? Quick Dissection Activity and Data Collection In order to understand how we will survive space exploration, we must understand how our bodies are “put together” To review organ systems thru dissection video: http://www.youtube.com/user/LakelandBiology Levels of Organization Organism Organ System Organ Tissue Cell Organelle Macromolecule Molecule Atom Subatomic Particles How can I remember all eleven organ systems? C DR SMILE RUN Cardiovascular Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Integumentary Lymphatic Endocrine Reproductive Urinary Nervous Circulatory System Function – transports substances throughout the body using heart Organs – heart, arteries/veins & blood Digestive System Function – breaks down food into usable substances & absorption through intestines Organ – esophagus, stomach, and intestines Respiratory System Function – moves air in and out of lungs Organ – trachea, pharynx, bronchi and lungs (diaphragm helps) Skeletal System Function – provides support and structure to the body, site for blood production (red and white cells), Organ – Bones Muscular System Function – allows your body to move through contraction and relaxation Organs– muscles Integumentary System Function – serves as a barrier & protects against infection (1st line of defense) Organ – skin, nails, hair follicles, sweat glands Lymphatic System Function – defend against pathogen and disease with white blood cells (2nd line of defense) Organs –lymph nodes/lymph vessels Endocrine System Function – slowly relays messages that regulate the body (growth and development) Organs – glands Reproductive System Function – production of sperm & egg cells to create offspring. Organs – testes & penis; ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus. Urinary System Function – filters & eliminates waste from the blood Organ – kidneys, bladder Nervous System Function – quickly relays messages to and from brain through cells called neurons that regulate behavior. Organs – brain, spinal cord, sense organs Journal Question: How can you learn about yourself by dissecting the fetal pig? Explain. What are all organ systems working toward? Homeostasis – process by which organisms keep internal conditions relatively constant despite changes in the external environment. Examples: temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, etc. Objectives: -Use technology appropriately in school -Visualize the 11 organ systems - Recognize that by studying the fetal pig you can understand how a human and is constructed. -Visualize and interconnectedness between organs and organ systems. -Develop basic dissecting skills. External Dissection 1. Determining the age of your pig. 2. Identifying the sex of the pig. External Dissection 1. Observing the Integumentary System. 2. Observing Muscular System. Male vs. Female Mouth Dissection A 1. B C Identifying the tongue, soft & hard pallet. 2. Opening of mouth to view epiglottis. D JQ: No Journal Question Today. Instead, put gloves on, your apron on, and have a seat in your desk. Your homework tonight is to complete the Dissection Lab Internal Dissection 1. Re-tie your pig to the dissecting tray. (tape?) 2. Make incisions to expose internal organs. 3. Identify all internal organs and show teacher. 4. When finished, work on Post-lab questions. Clean-up 1. Put the fetal pig into the bag provided. Label bag with you & your partners names. 2. With soap and water clean tools and tray, return to cart. 3. Wipe down table and sink with wet sponge. 4. Return to seat. Testing your skills – Name that Organ System 1. Serves as a barrier & protects against infection. 2. Quickly relays messages from one part of the body to another. 3. Breaks down food into simple molecules that can be used by cells. 4. Brings oxygen in and carbon dioxide out. 5. Filters and removes waste from the blood. 6. Produces gametes (sperm and egg) cells. 7. Provides support and is a site for blood cell formation. 8. Allows the body to move. 9. Transports substances throughout your body 10.Slowly regulates the body’s functions. 11. Protects the body from disease. Testing your skills – Name that Organ System Answers 1. Integumentary System 2. Nervous System 3. Digestive System 4. Respiratory System 5. Excretory or Urinary System 6. Reproductive System 7. Skeletal System 8. Muscular System 9. Circulatory System 10.Endocrine System 11. Lymphatic System Testing your skills – Name as many Organs as you can for each system: 1. Cardiovascular System 2. Digestive System 3. Respiratory System 4. Skeletal System 5. Muscular System 6. Integumentary System 7. Lymphatic System 8. Endocrine System 9. Reproductive System 10.Urinary System 11.Nervous System Testing your skills – Name that Organ Answers 1. Cardiovascular System – heart, blood vessels 2. Digestive System – esophagus, stomach intestines, pancreas 3. Respiratory System – nose, mouth, trachea, bronchi, lungs 4. Skeletal System – bones, ligaments, cartilage 5. Muscular System – muscles 6. Integumentary System – skin, nails, hair 7. Lymphatic System – lymph nodes 8. Endocrine System – glands, pancreas 9. Reproductive System – testis, uterus, penis, ovaries, breasts 10. Urinary System – kidneys, bladder 11. Nervous System – brain, spinal cord Spend the remaining time answering the post-lab questions. They are application questions, so you will need to really think in order to answer them completely. Skills Test: Removing a Selected Organ System Choose one of the following organ systems to remove: 1. Respiratory System 2. Digestive System 3. Urinary System Going Further: Remove the Brain The organ system and brain must be intact in order to receive full credit for it. Clean-up 1. Put any extra parts in the bag provided and bring up front. 2. With soap and water clean tools and tray, return to cart. 3. Wipe down table and sink with wet sponge. 4. Return to seat. JQ: Did the fetal pig dissection meet your expectations? Elaborate. Take out your lab. You need your textbook tomorrow. 1. Fontanelles are the “soft spots” on a young human, or pig’s skull. What would be the benefit of having spaces between the sections of the skull? Explain. 2. Humans, like the pig, have cartilidge rings holding their trachea (windpipe) open. Why do they need these rings? 1. When most organs/tissues swell, they grow bigger until the damage is fixed. What restricts the brain from swelling, and what could happen if the brain swells too much? 2. In many mammals, the lungs are late to develop. Why would they develop later than many other organs? Fetal Pig Dissection Write-up 1. What was the purpose of the fetal pig dissection? 2. Compare and contrast the organs/organ systems of the fetal pig and the avatar. 3. Why are the anatomy and physiology different between the fetal pig and the avatar? Explain JQ: What do you see? Welcome to Name that Image! How are these pictures possible? Microscopes Instruments that magnifies images that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Light Microscopes Passes light rays through an object, and up through two lens to form an image. Can magnify small living or nonliving objects 1000x its normal size. Total Magnification Magnification Magnificati Total Objectives of Objective on Magnification of Eyepiece Low Power Med. Power High Power Microscope Drawings Always draw what you see. Name of Object Total Magnification Length of Object JQ: Would you rather have the ability to grow to the size of a tree, or shrink to the size of a pinhead? JQ: No Journal Question today. Study for today’s quiz! Tissues = group of similar cells working together. Lines and protects body surfaces. Example: Skin & Lining of Organs Connects, supports and insulates body. Example: Blood, fat, bone. Contracts & relaxes to produce movement. Example: walls of intestines, heart Carries info. to all parts of the body. Example: neurons JQ: If you can’t see something, does that mean it doesn’t exist? Explain. Adipose Tissue Skeletal Muscle Multipolar Neuron Smear JQ: Would you rather have the ability to grow to the size of a tree, or shrink to the size of a pinhead? Sticky Cells Activity 1. Cut a square of sticky tape, place the sticky side of the tape on the inside of your forearm, and let sit for 15 minutes. JQ: Why does Jake say a prayer for the Hexapede after killing it? JQ: Would you trade your human nervous system for an avatar nervous system? JQ: What is an Avatar? Explain. Why do humans need an Avatar to interact on Pandora?