D170 W15 Orientation and Imaging Williams Define the following
advertisement

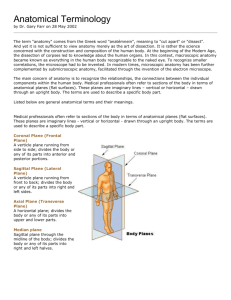
D170 W15 Orientation and Imaging Williams Define the following sub-disciplines of anatomy: Gross anatomy – Regional anatomy – Systemic anatomy – Surface anatomy – Microscopic anatomy (histology) – Describe the hierarchy of structural organization, noting the following levels. Give an example at each level. Chemical level – Cellular level – Tissue level – Organ level – Organ system level – Organismal level – What are the 12 systems of the human body? (Figure 1.2) Describe what a human looks like when standing in the anatomical position. What is the difference between the axial and appendicular regions of the body? Know the regions listed in Figure 1.3 Explain how to use the following terms to describe relationships between parts of the human body. Give an example for each. (Table 1.1) Superior (cranial) – Inferior (caudal) – Medial – Lateral – Proximal – Distal – Ipsilateral – Contrallateral – Anterior (ventral) – Posterior (dorsal) – Superficial (external) – Deep (internal) – Describe the following types of planes that cut through the body. Use regional terms to describe how the body is sectioned (cut) by these planes. Frontal (coronal) plane – Transverse (horizontal) plane – Sagittal plane – Midsagittal (median) plane – Parasagittal planes – Oblique sections – Describe the six basic features of the human body plan. Fill out the following table for the cavities of the body. Cavity name Dorsal Cranial Vertebral Ventral Thoracic Mediastinum Pleural Pericardial Abdominopelvic Abdominal Pelvic Contains what sub-cavities? Part of what larger cavity? Organs included in this cavity What is a serous cavity? Describe the structure of a serous cavity and give an example. Label quadrants and superficial organs Complete the following table regarding imaging methods. Imaging method How it works What it can view well Light microscopy Uses a beam of light Electron Uses a beam of microscopy electrons Scanning electron Uses a beam of microscopy electrons X-rays Computed tomography (CT) or CAT X-rays are absorbed by certain tissues X-rays taken around a person Strengths Weaknesses Positron emission topography (PET) Sonography Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Detects radioactive isotopes Sound waves reflect off of tissues Magnetic field detection Vocabulary Tissue Organ Organ system Anatomical position Axial region Appendicular region Superior (cranial) Inferior (caudal) Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Ipsilateral Contralateral Anterior (ventral) Posterior (dorsal) Superficial (external) Deep (internal) Frontal (coronal) plane Transverse (horizontal plane) Cross section Sagittal plane Median (midsagittal plane) Parasagittal plane Oblique section Dorsal body cavity Ventral body cavity Viscera Thoracic cavity Abdominopelvic cavity Pleural cavity Mediastinum Pericardial cavity Abdominal cavity Pelvic cavity Peritoneal cavity Serous membrane (serosa) Light microscopy Electron microscopy Scanning electron microscopy Artifacts X-ray imaging CT CAT Angiography PET Sonography (ultrasound) MRI Plus all terms on Figure 1.3