Introduction_to_A&P

What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationship of its parts
Anatomists learn about the structure of the human body through dissection
Physiology is concerned with the functions of living organisms and their parts
Pathology is the scientific study of disease
From the perspective of an anatomist or physiologist, disease results from abnormalities in body structure or function
Structural Levels of Organization
The body is a unit constructed of the following smaller units:
Cells: the smallest “living” structural units; organizations of various chemicals
Tissues: organizations of similar cells that perform a common function (e.g. heart muscle tissue)
Organs: organizations of different kinds of tissues that perform a specific function (e.g. the heart)
Organ Systems: organizations of different kinds of organs that together perform some complex function (e.g. the cardiovascular system)
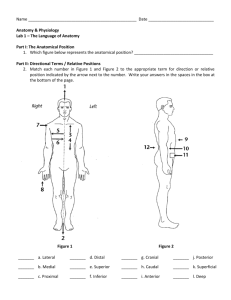
Anatomical Position
Standing erect with the feet slightly apart and arms at the sides with palms turned forward
Anatomical Directions
Superior: toward the head, upper, above
Inferior: toward the feet, lower, below
Anterior: front, in front of
Posterior: back, in back of
Medial: toward the midline of a structure
Lateral: away from the midline or toward the side of a structure
Proximal: toward or nearest the trunk, or nearest the point of origin of a structure
Distal: away from or farthest from the trunk, or farthest from a structure’s point of origin
Superficial: nearer the body surface
Deep: farther away from the body surface
Planes or Body Sections
Sagittal plane: a lengthwise plane that divides a structure into right and left sections
Midsagittal plane: a sagittal plane that divides the body into two equal halves
Frontal (coronal) plane: a lengthwise plane that divides a structure into anterior and posterior sections
Transverse plane: a horizontal plane that divides a structure into upper and lower sections
Body Cavities
Ventral cavity
Thoracic cavity
Mediastinum: the midportion of the thoracic cavity; the heart and trachea are located in the mediastinum
Pleural cavities: the right lung is located in the right pleural cavity, the left lung is in the left pleural cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
The abdominal cavity contains the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen
The pelvic cavity contains the reproductive organs, the urinary bladder, and the lowest part of intestine
Dorsal cavity
The cranial cavity contains the brain
The spinal cavity contains the spinal cord
The Balance of Body Functions
Survival of the individual and of the genes is the body’s most important business
Survival of the genes depends upon reproduction
Survival depends on maintenance or restoration of homeostasis (relative constancy of the internal environment)
The body uses negative feedback loops and, less often, positive feedback loops, to maintain or restore homeostasis
All organs function to maintain homeostasis
Body functions are related to age; peak efficiency is during young adulthood, diminishing efficiency occurs after young adulthood