Naming Ionic Compounds: Chemistry Worksheet
advertisement

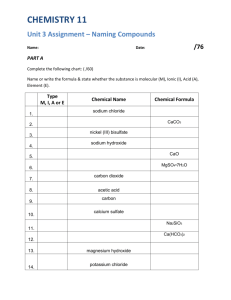
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS There are a few general rules that apply when naming ionic compounds. 1. Most ionic compounds are also called salts. 2. Most ionic compounds exist as solids and many dissolve to form aqueous solutions. 3. An ionic compound is made up of a metal and a nonmetal; metals are located on the left side of the periodic table and nonmetals are on the right side. 4. The cation (positive ion) is written first followed by the anion (negative ion). 5. Before naming compounds, you should first memorize the individual cations and anions. Writing Chemical Formulas 1. The charge of the individual ions in a salt should add up to zero, the overall charge of the compound. For example NaCl is composed of Na+ ions and Cl- ions. For every one sodium ion you need one chloride ion (+1) + (-1) = 0 Ba2+ and N3- : You need 3 (+2 ) Barium ions to cancel out the 2 (-3) nitride ions so the overall charge of the compound is zero. 2. The individual ions should add up to the overall charge of the polyatomic ion. What is the charge of Mn in MnO4-? 1 Mn + 4 O = -1 so 1(Mn) + 4 (-2) = -1 so Mn - 8 = -1 so Mn = +7 Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Symbol Element Root Anion Symbol Anion Name Br Bromine Brom Br- Bromide Cl Chlorine Chlor Cl- Chloride F Fluorine Fluor F- Fluoride H Hydrogen Hydr H- Hydride I Iodine Iod I- Iodide N Nitrogen Nitr N-3 Nitride O Oxygen Ox O-2 Oxide P Phosphorus Phosph P-3 Phosphide S Sulfur Sulf S-2 Sulfide Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Name the metal then the root of the nonmetal + ide ending: NaCl Sodium chloride BaCl2 Barium chloride H2S Hydrogen sulfide Mg3N2 Magnesium nitride NaF Sodium fluoride K2O Potassium oxide Notice that the cation is always mentioned first and then the anion. Notice that the anion always ends in -ide Notice that the number of elements in the compound is not mentioned in the name. Name the following ionic compounds: Na2O K2S CaCl2 AgCl MgBr2 AlN Ba3As2 AlH3 ZnI2 Li3P Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Answers: Na2O = sodium oxide K2S = potassium sulfide MgBr2 = magnesium bromide AlN = aluminum nitride Ba3As2 = barium arsenide CaCl2 = AgCl = silver chloride AlH3 = aluminum hydride ZnI2 = zinc iodide phosphide calcium chloride Li3P = lithium Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Some polyatomic anions that you must know: NO3- = nitrate NO2- = nitrite SO4 2 - = sulfate SO32- = sulfite PO43- = phosphate PO33- = phosphite CO32- = carbonate HCO31- = hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate OH- = hydroxide CN- = cyanide C2H3O2- = acetate C2O42- = oxalate Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Naming salts composed of the polyatomic ions is the same as with the monatomic anions. Metal name then polyatomic name. NaOH sodium hydroxide H2SO4 hydrogen sulfate Ba(NO3)2 barium nitrate CsNO2 cesium nitrite Sometimes there is a common name: KHCO3 potassium hydrogen carbonate or potassium bicarbonate Note: the polyatomic anions must be memorized. Name the following ionic compounds: NaHCO3 K2SO3 MgSO4 Ca(OH)2 NH4NO3 Zn(NO3)2 KCN Li3PO4 H3PO4 HNO3 Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Answers: NaHCO3 = sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate K2SO3 = potassium sulfite MgSO4 = magnesium sulfate KCN = potassium cyanide H2PO4 = hydrogen phosphate Ca(OH)2 = calcium hydroxide NH4NO3 = ammonium nitrate Zn(NO3)2 = zinc nitrate Li3PO4 = lithium phosphate HNO3 = hydrogen nitrate Early Names of Elements Present Name Symbol Former Name Antimony Sb Stibium Copper Cu Cuprum Gold Au Aurum Iron Fe Ferrum Lead Pb Plumbum Mercury Hg Hydrargyrum Potassium K Kalium Silver Ag Argentum Sodium Na Natrium Tin Sn Stannum Tungsten W Wolfram Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds The previous examples only named type 1 or “fixed oxidation state” cations. When naming type 2 or “variable oxidation state” cations the rules change. CuOH copper(I) hydroxide Fe(NO3)3 iron(III) nitrate CuSO4 copper(II) sulfate Sn(NO2)4 tin(IV) nitrite Sometimes a common name exists: CuOH cuprous hydroxide Fe(NO3)3 ferric nitrate When naming type 2 cations, the systematic method (IUPAC) requires the use of roman numerals after the elemental name to represent the oxidation state of the cation. The common name uses the –ic ending for the higher oxidation state and –ous ending for the lower oxidation state. Many times the old latin or greek name is used as the root. Name the following ionic compounds: CuHCO3 FeSO3 CuSO4 Cr(CN)3 Cr(PO4)2 Sn(OH)2 W(NO2)5 Ti(CO3)2 CoPO4 PbCl2 Nomenclature of binary ionic compounds Answers: CuHCO3 = copper(I) hydrogen carbonate or cuprous bicarbonate FeSO3 = iron(II) sulfite or ferrous sulfite CuSO4 = copper(II) sulfate or cupric sulfate Cr(CN)3 = chromium(III) cyanide Cr(PO4)2 = chromium (VI) phosphate Sn(OH)2 = tin(II) hydroxide or stannous hydroxide W(NO2)5 = tungsten(V) nitrite Ti(CO3)2 = titanium(IV) carbonate CoPO4 PbCl2 = cobalt(III) phosphate or cobaltic phosphate = lead(II) chloride or plumbous chloride PRACTICE PROBLEMS # 9a Below the formula, give the systematic name for the following compounds. If a common name exist, write it below the systematic name. 1. KBr potassium bromide 2. BaO 3. Na2O Sodium oxide Barium oxide 4. BiF3 5. Cr2S3 Bismuth (III) fluoride Chromium (III) sulfide 6. Ti(NO3)4 Titanium (IV) nitrate or titanic nitrate The problem set continues on the next page. GROUP STUDY PROBLEM # 9a Below the formula, give the systematic name for the following compounds. If a common name exist, write it below the systematic name. 1. CaI2 2. Cs2S 3. Al2S3 4. CdI2 5. SnCl2 6. Zn(NO3)2 7. Fe2O3 8. Fe(OH)2 9. PbSO4 The problem set continues on the next page. PRACTICE PROBLEMS #9b Below the name, write the formula for the following compounds. Lithium chloride b) Aluminum sulfide e) Copper(II) oxide Li Al3+ S2f) + Cl - LiCl Iron(III) chloride i) FeCl3 Potassium nitrite KNO2 Ammonium carbonates s (NH4)2CO3 CuO Al2S3 Calcium bicarbonate l Ca(HCO3)2 Potassium perchlorate KClO4 )Iron(II) phosphate w) Fe3(PO4)2 GROUP STUDY PROBLEM #9b Below the name, write the formula for the following compounds. a) Barium oxide b) Sodium bromide c) Copper(I) oxide d) Iron(II) chloride e) Potassium nitrite f) Calcium hydroxide g) Silver nitrate h) Ammonium chloride i) Lithium phosphate j) Sodium nitrite k) Sodium bicarbonate l) Calcium Carbonate m) Sodium sulfate n) Iron(III) hydroxide o) Copper(II) hypochlorite p) Sodium sulfite