Acids
advertisement

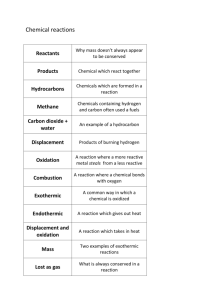
Formation of Hydrogen Gas: The Rate Of a Reaction The rates of reaction between a strong acid and magnesium metal, and a weak acid and magnesium metal to generate hydrogen gas are compared. Purpose • In flask number one was added HCl (strong acid) and in flask number two was added CH3COOH (weak acid) in equal amounts to both flasks. Magnesium metal was then added to each flask which was covered immediately with a balloon. The reaction between the acid and the metal produced hydrogen gas. Demonstration • Flask number two with the strong acid inflated the balloon much faster than flask number one with the weak acid. Concepts • Acids • Oxidation of metals • Hydrogen Acids • An acid is a substance that is able to donate a proton and increase the concentration of ions when it dissolves in water. • A strong acid is an acid that ionizes completely in water. • The most common strong acids are HCl, HBr, HI, HClO3, HClO4, H2SO4 and HNO3. • A weak ccid is an acid that partially ionizes in water. • Many weak acids are organic compounds that are made of carbon, hydrogen and opxygen. • Acetic acid is an organic compound that is found in vinegar. • Acetic acid has the chemical formula CH3COOH Oxidation of Metals • Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses one or more electrons. • In this demonstration the metal is been oxidized by the acid to make a salt and hydrogen gas. • Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H(g) • Mg(s) + CH3COOH(aq) Mg(CH3COO)2(aq) + H2(g) • A piece of iron rusting is a good example of oxidation of a metal. Hydrogen • Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. • It is the first element in the periodic table and has the lowest atomic weight of 1.006. • At room temperature it is a colorless and odorless gas. • Hydrogen gas exists as a diatomic molecule, H2 Conclusions • Stronger acids generate hydrogen gas faster because they are able to donate protons at a faster rate. This is in keeping with the definition and classification of strong acids. Acetic acid, a weak acid, does not react as quickly as a strong acid. Comments • The oxidation of metals is used when small amounts of hydrogen are needed in the laboratory. • For industrial use some other methods are use like reacting methane(natural gas) with steam at 1100C.