PowerPoint #3 - Porterville College

PT20E Therapeutic Communications and
Relationships
PowerPoint #3
Course Objective #1
• Define and describe the Psychotherapeutic
Management Model according to the
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, (DSM) current edition.
Psychopathology
• Definition: the systematic study of mental disorders.
Psychotherapeutic Management
Model
• Definition: Nursing care that balances the three (3) primary interventions used in care of
D.D. and Psychiatric patients.
Psychotherapeutic Management
Model
• Three (3) primary interventions:
– Communicated Nurse-Patient Relationship (words)
– Psychopharmacology (drugs)
– Milieu management (environment)
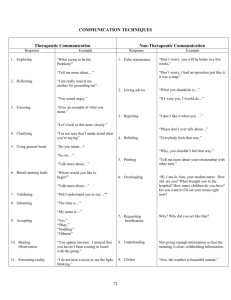
Therapeutic Nurse-Pt. Relationship
• Communication skills
Psychopharmacology
• Psychotropic drugs:
Course Objective #4
• Relate why a psychopharmacolo gic understanding is important for the psychiatric technician
Importance of
Psychopharmacology
• Assess response
• Respond to side effects
• Evaluate for desired results
• Safely dispense
• Teaching
• Idiosyncratic reactions
Milieu Management
• Definition:
Purposeful manipulation of the environment to promote a therapeutic atmosphere.
Course Objective #5
• Define milieu management and its six elemental components
Milieu Management
• Components:
– Safety
– Structure
– Norms
– Setting limits
– Balance
– Environmental modifications
Safety
• Freedom from danger or harm
Structure
• Physical environment
• Regulations
• Schedules
Norms
• Expectations of behavior
• Promote community
• Truths held by a culture
Beliefs
Values
• Deep feelings that determine what is considered good or bad.
• Society accepted rules
Norms
Setting Limits
• Clear & enforceable limitations on behavior
Setting Limits
– Behaviors:
– Physical aggressiveness
– Self-destructive acts
– Lack of compliance
– Use of alcohol or drugs
– Elopement
Setting Limits
• Anticipate behavior!
Balance between Independence vs.
Dependence
• Gradual process
– too fast
– Overwhelmed
Environmental Modifications
• Changing the environment to promote mental health
– Physical arrangement
– safety issues
– orientation features
Course Objective # 2
• Describe the consequences of an imbalance in nursing care
Consequences of an Imbalance in
Nursing Care
• Patient needs & setting
• Utilization
Consequences of an Imbalance in
Nursing Care
• All components must be present if pt’s. are to fully benefit
Consequences of an Imbalance in
Nursing Care
• Imbalance
• compromise tx
Course Objective #3
• Relate the difference between therapy and being therapeutic.
Therapeutic vs. Therapy
Education
• Therapy
– graduate-level psychiatric training
• Therapeutic
– undergraduate-level psychiatric nurses
Therapeutic
Tasks
• Communication
– Respect
– Desire
– Understanding
– Active listening
Therapeutic
• Knowledge/skills
• Each encounter is part therapeutic milieu
Therapeutic
• Real!
– Problems
– Solutions
– Practice situations
Therapeutic
• Consistent
• Spontaneous
• Informal
• Recreational
Therapy
• Cure or manage the course of mental disorder
• Trained
• Selective pt
• Sessions
– Formalized
– On-going
– Specific time, place, & length
• Specialized techniques
Therapy
Therapeutic Nurse-Pt. Relationship
• Definition: A series of goal-directed interactions that focus on the patient
– T, F, B’s
– potential solutions
• Purposeful
• Unique
Therapeutic Nurse-Pt. Relationship
• Client challenges:
– Communicating
– Relating
– Functioning
Role of the Psych. Nurse
• Identify problems
• Discover ways of meeting needs
• Experience relationship
Characteristics of the TxN-PR
• Planned
• Patient centered
• Goal directed
Brief Encounters
• Brief encounters
– Process feelings
– Validation
– Feedback
• Quickly
Course Objective #21 & 22
• List the stages of the therapeutic P.T.—patient relationships.
• Identify and describe the major tasks of each stage of the P.T.—patient relationship
Stages of TxNPR
• Orientation Stage
• Working Stage
• Termination Stage
Orientation stage
• Establishing trust and rapport
• Nurses learns
– Concerns
• Patient learns
– Role of the nurse
Orientation stage
• Create an environment
– Honest
– consistent,
– keeps promises
• Clear, specific communications
• Confidentiality explained
Orientation stage
• Initiating conversations
• Non-confrontational
Orientation stage
• Establish a contract
– Expectation
– responsibilities
Orientation stage
• Gather assessment information
– intake interview
• Needs
• coping strategies
• defense mech.
• recurring thoughts, feelings, behaviors
• awareness of problems
• ability and motivation to change
Orientation stage
• Gather assessment information
• Defining goals
• Needs
• Coping strategies
• Defense mech.
• Recurring T, F, B
• Motivate to change
– Prioritize
Orientation stage
• Management of emotions:
– Fear of losing control
– Feelings
– Anger
Orientation stage
• Feelings natural
– Expression
• Empathy
– Not alone
– Hope
Orientation stage
• Palliative coping mechanisms
– Rest
– Nutrition
– Exercise
– Meditation
Orientation Stage
• Teaching healthy ways to meet emotional needs
– Coping skills
– Challenging negative self-images
Orientation stage
• Providing support:
– Realistic hope
• Abilities
• Strengths
– Worth
– Non-judgmental
– Dependence independent
Orientation stage
• Providing structure:
• If the pt loses control
– take temporary control
• If the patient is withdrawn
– Spending time
• The major task of providing structure is
– limit-setting
Orientation stage
• Crisis
– Providing support
– Managing emotions
Working Stage
• AKA:
– Learning Stage
– Change Stage
• Problem-solving
– Work toward change
– Stabilization
Working Stage
• Observation:
– Describe the problem
Working Stage
• Observation:
– Describe the problem
– “Participant Observer”
• Nurses relationship
Working Stage
• Analysis:
– Encourages accuracy in pts conclusions
Working Stage
• Interpretation:
– Change is necessary
– Explore solutions
Working Stage
• Planning:
– formulating a plan
– assists pts to solve their own problems
– Encourage short-term, realistic, achievable, daily goals
Working Stage
• Testing out:
– Trying out new behavior or solution in a safe environment first
– Rehearsal
Working Stage
• Role playing
– Practicing behaviors
– Nurse
• plays the role of persons with whom pts are difficulty
• assess communication & behavior
Working Stage
• Evaluation
– assess success
Working Stage
• Feedback
– Constructive
Working Stage
• In-depth data collection:
– Increased knowledge
– Priority issues
Working Stage
• Reality testing:
– Presenting another point of view
Working Stage
• Cognitive restructuring:
– Cope with negative thoughts
– more realistic conclusions
• redefine
• reinterpret
• change perception
Working Stage
• Supportive confrontation:
– Challenging pt’s contradictions,
– It challenges pts to
• Meet their own needs
• Be accountable for their own
– Feelings
– Behaviors
– Decisions
Supportive Confrontation
• Example:
• Pt: “I went out drinking only once last week. At least I’m trying to change.”
• Nurse: “I can appreciate your effort, but you agreed to abstain from alcohol completely.”
Working Stage
• Writing/journaling:
– Tool
– Release emotions
– Objective
• Letters
Working Stage
• Promoting change:
– Pt. initiated change
– Support
• Family & friends
• Groups
– Motivated
Working Stage
• Teaching new skills:
– Desire + Know how
– Small steps
– Practice
– Feedback
Termination Stage
• Evaluation & summary of progress:
– ID changes
– Long-term goals
– Strengths & weaknesses
Termination Stage
• Synthesizing what has occurred:
– Progress
– Indirect outcomes of TxPNR
– Encouraged other relationships
Termination Stage
• Referrals:
– ID community resources
– Written d/c instructions
Termination Stage
• Discussion of termination:
Continuum of Care
• Definition:
– levels of care through which a pt can move depending on needs at the time
Course Objective # 25
• List approaches and precautions to take with the following patient experiencing:
• Potential for violence, Hallucinating,
Delusional, With conflicting values, With incoherent speech, Manipulative, Crying,
That are sexually inappropriate,
Uncooperative or in denial,
Depressed/apathetic, Suspicious,
Hyperactive, Transference
Special Approaches/Precautions
• Brief encounters
Violent Behavior
• Keep your distance
• Do not touch without approval
• Change the topic
• Suggest a “Time Out”
Violent Behavior
• Sit by the door
– DO NOT BLOCK THE DOORWAY!
• Do not go into a room alone
• Leave temporarily
– Be aware of self-injury potential
• Call for assistance
Hallucinations
• 1 st
– Comment
– Assess the content
• Powerlessness
• Hatred
• Guilt
• Loneliness
Hallucinations
• Do not focus on the hallucination
– Activities &encounters
• “Do Not to act on commands”
• “Tell staff”
Delusions
• A fixed, false belief
• not consistent with the person’s intelligence and culture
• unamenable to reason
Delusions
• 1 st
– Clarify the meaning
– Rarely discussed
• Do not arguing
• Monitoring
Conflicting Values
• Nurses vs. patients
• Examine the effects of beliefs
• Perspective
Incoherent Speech
• Clarify
• Repeated questions anxiety
• Frequent, brief support
Manipulation
• Means to gain attention, sympathy, control & dependence
• 1 st
– Address
– Limit-setting
– Help pts. to directly express their needs
Crying
• Allowed & encouraged
– Nrs – quite
• Stopped
– Offer opportunity to talk
Sexual Innuendos or
• Correct
Inappropriate Touch
• Discuss
• If continue
– Limit-setting
– Reassignments
Lack of Cooperation/Denial
• ID the cause
– Disturbances in thought process
– Lack of insight
– Disagreement
– Fear
Lack of Cooperation/Denial
• Discussed directly
• Trust
• Patience
Depressed
Affect/Apathy/Psychomotor
Retardation
• Acknowledge feelings but discourage rumination
• Encourage
– personal care
• Postpone major decisions
Depressed Affect/Apathy/Psychomotor
Retardation
• Patience
• Frequent contact
• Empathy
Suspiciousness
• Underlying
– Fear
• Communicate
– Clearly & simple
– Avoid arguments
– Rational
• Encourage participation
– Do not force
Hyperactivity
• Decrease stimulation
• Physical activity
• Remain calm
• PRN meds?
Course objective #26
• Compare and contrast transference and counter-transference
Transference (pt)
• Unconscious emotional reaction
• Patient Nurse
• Based on past experiences
Transference (pt)
• Positive
– if pts view the nurses as helpful and caring
• Negative
– interfere with treatment
Countertransference (nurse)
• Unconscious emotional reactions
– Nurse patient
– based on the nurse’s past experiences
– sympathetic
– unable to confront the pt appropriately
Interventions
• 1 st
– Recognize
• 2 nd
– Discuss
– Gently & directly
Course Objective #27
• Relate the nursing process to psychiatric nursing
What are the 5 steps of the nursing process?
• Assessment
• Diagnosis
• Planning
• Implementation
• Evaluation
Nursing process in psychiatric nursing…
• Patient centered
• Individualized
Course objective #29 & 30
• Define and describe the following: Intake interview, Brief psychiatric rating scale,
Nursing care plan, Process recording
• Define and give examples SOAP and narrative progress notes
• Proof
• Law
Documentation
Types of Documentation
• Progress Notes:
– Assessing and analyzing communication skills, identifying pt themes, and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions
Types of Documentation
• S.O.A.P. Notes:
– General narrative of basic nursing care provided to the pt
SOAP Charting
• S:
• Subjective Data:
– What the pt says: “___”
– Reported
SOAP Charting
• O:
• Objective Data:
– Direct observation
SOAP Charting
• A:
• Assessment/Analysis:
– interpretation
– Conclusions
– responses
SOAP Charting
• P:
• Plan:
– Actions / treatments
Types of Documentation
• Problem-oriented Recording (POR)
– description of a specific intervention, used for a specific problem and evaluates the pts response
P.I.E.
Problem-oriented Charting
• P
– Problem
• I
– Intervention
• E
– Evaluation
Types of Documentation
• Pt Care Plan:
– Formal, written plan
– Guides pt care
• Diagnosis
• Goals
• Interventions
Types of Documentation
• Special Procedures Documentation:
– Interventions implemented
– Timely
– Expected level of care
Intake Interview
• Systematic
• Mental Status Exam (MSE)
• Assessments include:
– Motivation to change
– Coping strategies
– Defense mechanisms
– Recurring T, F, B’s
Course Objective #28
• List key members for a psychiatric treatment team.
Treatment Team
• Psychiatrist:
– MD
– Specializes in psychiatry
– Lead
– Writes medical orders
Treatment Team
• Psychologist:
– PhD in psychology
– psychological testing
– individual therapy
Treatment Team
• Clinical Social Worker:
– D/C planning/placement
– individual therapy
– licensed
Treatment Team
• MFT’s:
– Marriage and family therapists
– Run groups
– Individual therapy
Treatment Team
• Nursing Staff:
– RN’s, LVN’s, PT’s:
– manage the milieu
– administer meds
Treatment Team
• Activity Therapists:
– Leisure skill
– Activity therapy groups
Treatment Team
• Occupational Therapists:
– Training for work skills
– ADL’s
Treatment Team
• Patient:
– Participate
Encouraging Description of Perceptions
• Perceptions are unique so it is important to learn how each person perceives a feeling or interprets situations and events.