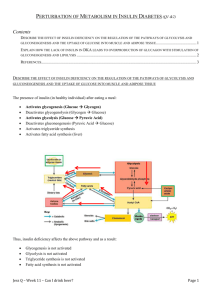
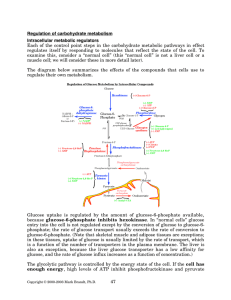
Document
advertisement

Regulation of Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 19 Regulation by Compartmentalization • Form of reciprocal regulation • Degradation vs biosynthesis • Requires transporters Specialization of organs Fuel Storage • Total amounts • Availability at time of need Liver: Tissue Specific • • • • • Gluconeogenesis ketogenesis Urea production Lactate recycling Alanine recycling Liver: Fed state • Glucose uptake • Glycogen synthesis • Convert excess sugar, amino acids to fatty acid • Make, transport TAG Liver: Fast state • Glycogen breakdown • Maintain blood sugar level • Catabolize glucogenic amino acids to maintain glucose and citric acid cycle • Catabolize fats and ketogenic amino acids for ketone body Muscle • Glucose trapped as glycogen (no blood sugar regulation) • Source of energy in starvation Muscle: Active State • Immediate ATP/creatine • Anaerobic muscle glycogen • Aerobic muscle glycogen • Aerobic liver glycogen • Adipose fatty acids Adipose • Fed state: uptake of fats AND glucose (why?) • Fast state: release of fats by hormone sensitive lipase (HSL) Kidney • Elimination of waste • Maintenance of pH • With liver, carries out gluconeogenesis Cori Cycle Alanine-Glucose Cycle Chemical Regulation • Local allosteric regulation • Hormone mediated allosteric regulation • Covalent modification Major points of Regulation Urea: Local Regulation • Role of citrate in multiple pathways • Regulation by energy charge (ATP, AMP ratio) – [ATP] does not change much • AMP-dependent protein Kinase (AMPK) acts as energy sensor – High [AMP] activates kinase to switch off anabolism and switch on catabolism Hormone Regulation: Insulin • • • • Small protein hormome Released at high [glucose] Pancreatic b cells Release probably triggered by glucose metabolism, not cell surface glucose receptor – May be mitochondrial difference, explaining why diabetes changes with age – May be difference between hexokinase and glucokinase isozyme in pancreas Hexokinase • Most tissues except pancreas and liver • First irreversible reaction • Linked to glucose uptake – Locks glucose in cell • Many isozymes – Most inhibited by glucose6-phosphate – Product inhibition Glucokinase • Isozyme in liver and pancreas • Higher Km – Hexokinase always saturated, but glucokinase sensitive to [glucose] • Not inhibited by glucose-6-P – Why? Liver serves to modulate blood sugar Isozyme kinetics • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose Insulin Signal Transduction Glucose Entry into Cells • Tissues have unique function • Isozymes of glucose transporter, GLUT – Insulin dependent in muscle – Higher [glucose] required for liver uptake Covalent modification • Signal transdution leads to phosphatase and/or kinase activity • Covalent modification • Glycogen phosphorylase – Phosphatase inactivates (b form) – Kinase activates (a form) Insulin Regulation of Glycogen Insulin Glucagon and Epinephrine • Glucagon released with low blood sugar (pancreas a cells) • Epinephrine released by adrenal glands • Oppose insulin – Activates glycogen breakdown – Activates gluconeogenesis – Activates hormone sensitive lipase Glucagon Regulation of Glycogen Glucagon Obesity • Hereditary, age, and environmental • Set-point • Leptin – Appetite suppressant – Made in adipose • Brown fat Diabetes • Type 1 (Juvenile onset) – Insulin dependent • Type 2 – Insulin resistance • Body feels like a fast – Gluconeogenesis increase – Lower fat storage – Increase in fat utilization • ketogenesis Hyperglycemia • Non-enzymatic glycosylation • Sorbitol production leads to tissue damage • Drugs aimed at undoing metabolic problems • Metformin – Activates AMPK » Suppress gluconeogenesis – Actuvates glucose and fatty acid uptake in muscle Review • Central molecules – Relate to reactions • Enzyme classes • Cofactors • Basic reactions – Redox – Decarboxylation – energetics • Reaction motifs Central Molecules Enzyme classes Problem 6.14. Propose a name for the enzyme, and indicate metabolic purpose of reaciton. Cofactors Problem 12.26-27 • Identify the metabolic pathway. Indicate which redox cofactor is necessary. Problem 33: • Identify the necessary cofactors Reaction Motifs