BHS 150.2 Biochemistry Date: 02/08/13, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
advertisement

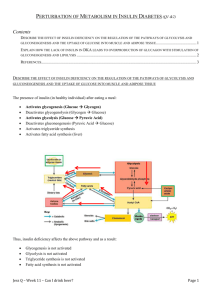
BHS 150.2 Biochemistry Notetaker: Laurel Hammang Date: 02/08/13, 1st hour Page1 HW #4 distributed Q1: Receptor mechanism of action for glucagon and insulin. Know mechanisms for final exam. Q2: Think about glycogen synthetase, glycogen phosphatase, pyruvate kinase, and the effects of high levels of insulin. Insulin activates a phosphatase, which removes a phosphate group. Activates things to store glucose. Pyruvate kinase is important to convert it to acetyl coA. *Remember that adding/removing phosphate only changes activity level of enzymes. Think logically. *See table at end of homework for summary of pathways Q3: Early into fasting period. Glucagon levels are starting to increase, and glycogen is starting to be broken down. Gluconeogenesis isn’t really starting yet because there’s still glycogen available and it’s less energy intensive to use that as a fuel source first. Q4: Not quite into starvation mode yet. Gluconeogenesis is really “kicking in” now, and muscles are being broken down for amino acids, so are lactate and glycerol to make glucose. *Process of changing between different types of metabolism is a gradual change, none of the pathways have a definite start/stop point. *Know which primary sources of energy are used for muscle and brain. What are cells using in each of the three states? What’s increasing, what’s decreasing? *Know main enzymes in glycogen *Know 4 bypass enzymes for gluconeogenesis *Be familiar with names of enzymes they’re bypassing, too. REVIEW FOR FINAL 100 Questions Saturday at 9 am Covers pages 201-370 All eye-related things are tested as if it were new material Aqueous, Trabecular Meshwork (TM), Ciliary Body Tested as if new material Substances found in aqueous-what do they mean? What’s their function? See chart pg 202 Production: pumps and channels TM-function of structural components (ie what do GAGs do?) Drugs: alpha-agonists, beta antagonists, etc Diabetes-related Lens Tested as if new material Proteins: location and function Metabolism: location, what do pathways provide for the lens? Accommodation What are the problems leading to presbyopia? Treatments (?) Development: growth factors, Rb protein, changes at equator (differentiation) Molecular p225-297 Describe processes for replication, transcription, translation Know major players, basics Coding vs. template strand Less ordering of events, comparing processes, more of what is the point of each process? # of base pairs: characteristics (melting temps, can you id how many base pairs? Etc) Direction: copied/read? synthesized? Mutations Sunlight (XP) and smoking damage: nucleotide excision repair Regulation of growth: oncogenes, proto-oncogenes Crystallins, cataracts, diabetes Tested as if new material Vitreous Structural components: functions of Changes with age and development diabetes Function of lactate, ascorbic acid, glucose: what does it mean if any of these are present? Retina Rod pathways and connections Metabolism Pathways into brain P and M cells, simple and complex cells Phototransduction Neurotransmitters, production Liver Glycogen and its structure (alpha 1,4 and 1,6) major enzymes and regulation Structure Insulin and glucogon Gluconeogenesis Major enzymes (4) Regulation against glycolysis *nothing on the amount of energy needed to make glucose Integration of Metabolism See table at end of homework and Questions 2-4 Diabetes-anything eye-related Low Insulin and high glucose