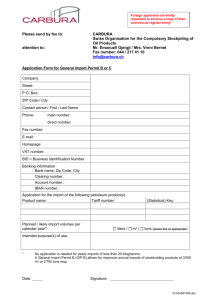
How to Export from Canada to Peru
advertisement

HOW TO IMPORT TO CANADA Jose Zlatar WHAT CAN YOU IMPORT ? WHAT CAN YOU IMPORT ????? Basically there are 2 types of goods you can import into CANADA : 1. NON REGULATED GOOD. Any product that does not need an special permit to be imported 2. REGULATED GOODS. Products subjected to import controls. • WHAT ARE REGULATED GOODS ? • All goods listed as REGULATED by the EXPORTS AND IMPORTS CONTROL BUREAU (EICB) • The EICB administers the EXPORTS AND IMPORTS PERMITS ACT enacted since 1947 to protect vulnerable industries and regulate trade. • The EICB is part of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Trade. REGULATED GOODS REGULATED GOODS Import Controlled : • Textiles and Clothing : check if needs country quota. • Agricultural products : POULTRY, EGGS, DAIRY subject to quotas. • Steel Products • Military equipment, weapons and munitions. Can I bring a Pollito a la brasa from Peru?? REGULATED GOODS REGULATED GOODS Export Controlled : * Sugar, Wheat, Peanut butter • Textiles and Clothing • Military, dual use goods • Nuclear energy materials and technology • Chemical or Biological Goods • Softwood lumber, unprocessed wood • Goods of US origin • All products going to Iran, North Korea and Myanmar and any other country listed on the Control List. HOW TO IMPORT REGULATED GOODS • OBTAIN AN IMPORT PERMIT 1. Register with the Exports and Imports Control Bureau 2. Apply for an Import Permit 3. Buy Import Quota if required from a quota holder ( it is very difficult to obtain a quota in Canada) IMPORTING NON REGULATED GOODS WHO YOU WILL BE DEALING WITH : • Canada Customs and Revenue Agency, to obtain your Business Number. • Canada Border Services Agency for all import documentation and quick release of products. GOODS YOU CAN IMPORT GOODS YOU CAN IMPORT • Commodities : bulk, wholesale or industrial packaging • Consumer Products : Wholesale or Retail packaging • Equipment and Machinery COMMODITIES COMMODITIES • Can be Food Products, Industrial raw materials, usually packed in industrial size packaging. • The only packaging requirement is a clear label on Master Case, Tote, Bag or Drum showing the product name, its country of origin, weight per package, producing plant and registration number : IN BOTH ENGLISH AND FRENCH CONSUMER GOODS CONSUMER GOODS • Packaging size must be approved for import into Canada. • Clear labeling in BOTH ENGLISH AND FRENCH • BAR CODE as per import requirements in size and location • Label has to be approved before entering the country • EQUIPMENT AND MACHINERY • They have to meet safety standards set up by Industry Canada. • Check import duties, if compete with Canadian production might be subject to higher duties. • Operation must meet Canadian standards. It has to be approved by ESA (Electrical Safety Authority) locally before leaving the port of entry if machinery doesn’t have the CSA stamp. IMPORT PROCESS IMPORT PROCESS 1. Pre-import 2. Import 3. Post-import activities Import Pre-Import Post-Import 1. Pre-import Pre-import Basic knowledge needed for international trading: 1. 2. 3. INCOTERMS. You have to have a good command of your Incoterms. Know your purchase and selling terms. SUPPLIER. Who is your supplier and where is located, your purchase and payment terms. Can your supplier provide all needed import docs?? LOGISTICS. Deep understanding of all logistics involved in the exporting process. 1. Pre-import Pre-import 4.DOCUMENTATION. Knowledge of all documentation and legal requirements at your exporting port and at your importing port. Be sure you have all import or export permits. 1.1. INCOTERMS What are INCOTERMS : Terms internationally accepted that provide rules for trading. International Commercial Terms (INCOTERMS) Buying or selling INFORMATION based on : 1. 2. 3. 4. Departure point Main Carriage Unpaid Main Carriage Paid Arrival or Destination Point 1. 2. 3. 4. Departure point : EXW (ex works) Main Carriage Unpaid: FCA (free carrier) FAS (free alongside ship) FOB (free on board) Main Carriage Paid: CFR (cost and freight) CIF (cost, insurance and freight) CPT (carriage paid to) CIP (carriage insurance paid to) Arrival or Destination Port DAP (delivered at place) DAT (delivered at terminal) DDP (delivered duty paid) 1.2. SUPPLIER 1.2. SUPPLIER • Who is your supplier? Where is located? • What are your purchase terms? EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF ? • Clarify all technical specifications at purchasing : quality, packaging, quantity. • After a Purchase Order is issued, all amendments will cost you money. • Specify Payment Terms : COD, CAD, open terms (7,15,30,60, 90 days?), L/C sight or terms? Partial shipments allowed? etc 1.3. LOGISTICS 1.3. LOGISTICS • • • • - All transportation, storage, loading and unloading activities involved from the point in which the product is received from the supplier to the point in which the product is appropriated by the buyer. Main controllable cost, component of your cost structure. Important to coordinate shipping and arrival dates with market situation and payment terms. Main logistics components before the import is done involves: Truck at arrival port to move product to de-stuffing facility - P&D of marine container and de-stuffing facility cost. - Lumpers / laborers needed to unload the container 1.4. DOCUMENTATION 1.4.DOCUMENTATION The main documents needed in most cases are: - BILL OF LADING. Showing you as the consignee or duly endorsed, all 3 originals to secure ownership. Your carrier has to provide the CBSA with the Cargo control Document. - 2 copies of the Commercial Invoice - 2 copies of your B3 import declaration - Packing List with product description. - Certificate of origin - Government Issue certificate : If animal product a zoo sanitary certificate If vegetable product a Phytosanitary certificate. If machinery you need a CSA stamp on the machine and a product description to have an accurate tariff. 2. IMPORTING 2. IMPORTING • 1. 2. 3. If all previous issues before loading the container are covered, the Importing process comes down to the following issues: IMPORT LOGISTICS. Shipping cost from the delivery port to your de-stuffing facility. DOCUMENTATION. As required at exporting and importing. INSURANCE. Be sure your imported products are arriving in good conditions, if not do you have a damage insurance ? 2.3. IMPORT DUTIES 2.3. IMPORT DUTIES These are the IMPORT TAXES you have to pay for Importing Products into Canada. As a norm, if it is not produced in Canada then is duty free : avocados, oranges, camels, etc. You HAVE to consult a Custom Broker to determine the duties you have to pay . 2.3. INSURANCE 2.3. INSURANCE EXTREMELY IMPORTANT when Importing. • You don’t want to find a container full of damaged goods after you paid for it. Or stones instead of product !!! 3. POST IMPORT ACTIVITIES 3. POST IMPORT ACTIVITIES • An import operation is not finish until you are in full control of the imported goods. • Be ready for import problems such us: - Exporter can’t meet shipping time frame (you don’t want Christmas products in February ) - Market jumps up and exporter wants to cancel the order or increase price to fulfill contract. - Goods do not arrived in good conditions. 3. POST IMPORT ACTIVITIES 3. POST IMPORT ACTIVITIES • Your best supplier is one that always ships good products in time, always : • Pay your supplier as per the agreed terms. • Be sure you are buying the right quality and quantity • Always look for an alternative supplier if you have to honor a sale contract with the imported product. (always have a plan B) CANADA PERU FREE TRADE AGREEMENT • 1) Market access: Better market access through elimination of import tariffs. • 2) Service Sector: Better market access for service providers • 3) Investment: Promotion of two-way investment between Canada and Peru • 4) Government Procurement: Better access to Peru’s government procurement contracts by Canadian companies CANADA PERU FREE TRADE AGREEMENT • Peru already eliminated tariffs on 95 % of current Canadian exports, with most remaining tariffs to be eliminated over a five- to ten-year period. • Products that have a duty-free access to Peru include wheat, barley, lentils, peas and now all beef cuts (including bone in), all paper products, machinery and equipment. • Canada immediately eliminated 97% of its tariffs on Peruvian imports. The remainder 3% is being eliminated over a remainder of five years period. Be careful… Extremely careful.. With “Doña Coca” (be sure who is your supplier) Canada Laws 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Customs Act Customs Tariff The excise Tax Act Special Import Measures Act CCRA regulation and policies Legislation Administer by the CCRA on behalf of other government departments in relates to importation CCRA: Canada Customs and Revenue Agency Not everybody knows that: 1. 2. 3. 4. $20 or less Mail or postal Low-value shipments Moving back to Canada Regular Commercial $1,600 or less (“menos papeleo”) Casual goods $1,600 or more Importing Commercial Goods into Canada Es facil: b/l, factura, • • • BASIC DOCUMENTATION : B3 mas otros doc’s y ya! pero en orden!! – Bill of Lading – Invoice – Certificate of Origin Sanitary Certificates or industry certifications if needed Form B3, provided by Customs. AWB Good Luck with your Importing Business Jose Zlatar MBA GREAT LAKES FOOD TRADING INC. Ph. 647-722-2450 Fx. 647-722-2451