Arthropods & Insects: Characteristics, Examples, Dissection
advertisement

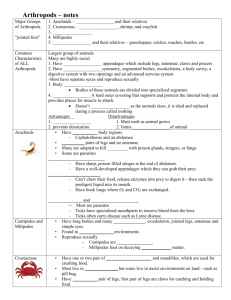
ARTHROPODS Ch. 24 General Characteristics Segmented bodies Jointed appendages Hard external skeleton (exoskeleton made of chitin) General Characteristics Molting Open circulatory system Brain with ganglia Compound eyes General Characteristics Some aquatic arthropods have gills Terrestrial arthropods have trachae (exchange CO2 and O2 change through holes called spiracles). Examples of Arthropods 560 million years old Crustaceans- live in the ocean Crayfish, crabs, lobsters, barnacles Arachnids Spiders, ticks, scorpians, mites Insects Myriapods- many legs Centipedes, millipedes Extinct Arthropods Trilobites **Horseshoe crabs are the only closest living relatives. Eurypterids Review 1) List 3 characteristics of arthropods that unite them as a single large group. 2) Name 1 group of arthropod that is now extinct. Name at least 3 groups still in existence today. INSECTS Keys to Insect Success Ability to fly (1 or 2 pairs of wings) Diverse feeding habits Many types of mouthparts Digestive enzymes to eat unusual food Keys to Insect Success Video clip Metamorphosis- body form changes from juvenile to adult Larva, pupa, adult Impact of Insects Bees & flowers Termites & wood Insect Medicine? Diseases/ pests Entomology- study and classification of insects Insect Collection Some Major Orders of Insects Lubber Grasshopper Dissection Grasshopper Head Compound eyes Simple eyes Mandible Palps Antennae Grasshopper Thorax Tympannic membrane Jumping legs Walking legs 2 pairs of wings Grasshopper Abdomen Spiracles Ovipositor (if female) Grasshopper Internal Anatomy Grasshopper Internal Anatomy