14. Late Middle Ages.HWH
advertisement

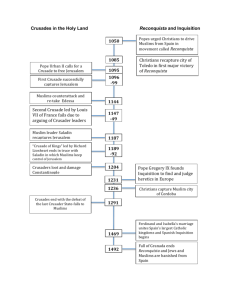
February 27, 2014 • Complete your stations from yesterday (you will have 10 minutes!) • Then, make a list of everything you know about Islam. Origins of Islam 1. The Arabian Peninsula a. Bedouins i. Nomadic Arab people b. Limited Farming c. Trading towns i. Mecca 1. 2. Both a trading and religious center Kaaba a. b. Ancient Building considered sacred Holds what is believed to be a meteorite 2. Muhammad the Messenger a. His Life i. ii. iii. iv. Born about 570 A.D. Married at the age of 25 Judaism and Christianity influenced his thinking 610 A.D., had a dream in which he was commanded by an angel to speak messages, or revelations by God (Allah) v. Would become both a prophet and political leader b. Revelations i. Allah was the one and only true and all-powerful God ii. Began preaching in public 3 years after his dream iii. Criticized the belief in many gods c. Sharing Revelations i. 622- Muhammad move to Medina 1. His journey from Mecca to Medina would become known as the hejyruh or hijra ii. Built up followers and their faith became known as Islam 1. Means “achieving peace through submission to God” iii. Followers became known as Muslim 3. Basic Ideas of Islam a. Followers would later write down Muhammad’s revelations b. This would form the Qur’an i. Sacred text of Islam c. 5 pillars of Islam i. Profession of faith 1. 2. 3. 4. “There is no god but God (Allah) and Muhammad is the messenger of God” Signals acceptance of the faith Denies existence of gods and goddesses Affirms that Muhammad was a man not a deity ii. Performance of five daily prayers 1. Worshipers always face Mecca when they pray iii. Giving of alms, or charity, to the needy and poor 1. Required to give certain amount of their income to charity iv. Required to fast 1. Go without food or water from dawn to dusk during the month of Ramadan v. Journey to Mecca 1. Only if you are financially and physically able 2. Journey called hajj 3. Gather and pray around the city’s mosque a. Building where Muslims worship d. Guidelines for Behavior i. Qur’an provides guidelines for moral behavior 1. 2. 3. Forbidden to eat pork or drink alcoholic beverages Must wash themselves before praying to be pure before God Prohibits murder, lying and stealing ii. Jihad 1. Has several meanings a. Can be translated to mean “Struggle for the Faith” b. Struggle to defend the Muslim community c. Has also been translated as “holy war” e. The Summa and Sharia i. Summa 1. 2. Means “tradition” Provides guidance in many areas a. b. c. Personal relationships Business dealings Religious practice ii. Sharia Law 1. Part of the Muslim legal system 2. Outlines methods of reasoning and arguing legal cases f. The People of the Book i. Islam is monotheistic, like Judaism and Christianity ii. Teach that Allah is the same God in Jewish and Christian traditions iii. Muhammad saw Abraham, Moses and Jesus as messengers from God, but he was the last prophet iv. See the sacred text from Judaism and Christianity as coming from Allah but Qur’an has the greatest authority v. Told to respect Jews and Christianity as “people of the book” 4. Division in Islam a. Sunnis i. Followers of Mu’awiya ii. Name means “followers of Summa” or “way of the prophet” b. Shia i. Formed by those who did not support Mu’awiya ii. Followed Muhammad’s son-in-law, Ali iii. Believed God had blessed Ali’s descendents because they were Muhammad’s true heirs iv. Call each of Ali’s successors Iman c. Sufis i. Seek a mystical, personal connection with God The Family Women Muslim Society Slavery Economy The Family - main social unit - man is head of family - men can have many wives - treat all wives equally Women - women are equal to men before Allah - women can inherit property and seek divorce in some circumstances - go into battle - influence political decisions - few rights during Abbasid rule (veil and hijab) Muslim Society Slavery - slavery common in Muslim lands (from non-Muslim regions) - required slaves to be treated fairly - slaves could buy their own freedom Economy - trade routes - expanded use of coinage, which eased long-distance trade - standardized weights and measurements - trade of goods and ideas Form and Function of a Mosque • Response Groups – Groups of 4 – One presenter per question – Each person will be the presenter once Religions Graphic Organizer • Take out your religions graphic organizer (should be in Unit 1 section) • Complete the graphic organizer for Islam (the last column) The Crusades February 28, 2014 Please turn in your HW from last night (religions graphic organizer) 1. On your web-enabled device, go to m.socrative.com 2. Enter room 779513. 3. Answer the questions! (You may use your notebook to help you). ** If you do not have a smart phone, please take a quarter-sheet from the front of the room. The Crusades 1. What are they and why did the happen? a. What is a crusade? i. It is a series of religious wars launched by European Christians b. Why did they happen? i. European Christians’ goal was to take back Jerusalem and the area around it called the Holy Land 1. It was under the control of the Muslims ii. Jerusalem and the area around it, were considered holy to Christians, Jews and Muslims 2. Launching the Crusades a. Council of Clermont i. ii. Called by Pope Urban II Purpose of the meeting was to address the Byzantine emperor’s request for help against the Turks iii. Urban called on all Christian warriors to put aside their differences and fight against the Turks 3. Fighting the Crusades a. The First Crusade i. Set out in 1096 ii. Made up of two groups 1. The Peasants a. b. c. Were unskilled While they were passing through Germany some attacked Jewish communities Those who made it to Jerusalem quickly fell to the Seljuk Turks 2. Trained Knights a. Were unprepared for the hardships of their journey i. Will resort to looting towns and farms to get supplies when food and water ran low b. Took 3 years to reach the Holy Land c. Recaptured Jerusalem d. Created 4 states in the Holy Land i. ii. Jerusalem, Edessa, Antioch, and Tripoli were the capitals of these four states They were intended to be Christian strongholds Crusader Fortress in Tripoli Still standing today in Lebanon “It was necessary to pick one’s way over the bodies of men and horses… In the Temple and porch of Solomon, men rode in blood up to their knees and bridle reins… The city was filled with corpses and blood.” —Raymond d’Aguilers, History of the Franks Who Captured Jerusalem b. Second Crusade i. 1144, Muslims recaptured Edessa ii. European leaders will call for a second crusade in response to this iii. It was a failure c. Third Crusade i. Saladin 1. 2. New leader of the Muslims Will drive the Crusaders out of Jerusalem ii. Loss of Jerusalem starts the Third Crusade 1. 2. Known as the Kings Crusade Richard the Lion-hearted was the only king to fight in the Holy Land a. b. Had respect for Saladin He won several battles against the Muslims; was unable to drive them out of the Holy Land or retake Jerusalem d. Fourth and later Crusades i. Fourth Crusade began in 1201 1. 2. Crusaders could not pay the Venetians for transport Agreed to attack the city of Zara, which had once belong to the Venetians, as payment a. 3. 4. 5. The city was held by the Christian king of Hungary Pope will excommunicate the crusaders for their actions Crusaders will continue to the Holy Land; on the way the attack Constantinople Disorganization and a lack of strong leadership made the Fourth Crusade a failure ii. There were five more crusades that followed after the Fourth, none were successful iii. By 1291, Muslims had driven the Christians out of the Holy Land 4. Effects of the Crusades a. Economic Changes i. The Crusaders enhanced existing trade ii. Increase in trade added to the changing European economy of the Middle Ages b. Political Changes i. Kings will take control of unoccupied land ii. Will give kings more power c. Social Changes i. Brought knowledge of Muslim culture to Europe ii. Christians who participated in crusades came to respect other cultures; those who did not became more intolerant iii. Many Europeans began to view all nonChristians as enemies Kingdom of Heaven Art and Culture of the Middle Ages 1. Visual Arts a. Gothic architecture i. Greatest examples of religious feelings were found in churches ii. Built in the Gothic style 1. Churches were taller and brighter than earlier churches iii. Advances in engineering 1. Flying Buttress a. Most important advance b. New type of support c. Supported church was from outside i. ii. Allowed for higher ceilings Will give church a more airy feeling d. Allowed for larger windows i. ii. Churches hire artists to create stain glass windows Showed scenes from the Bible or depicted lives of the saints iv. Churches were decorated inside and out 1. Exterior a. b. Had statues of saints, kings and figures of the old testament Gargoyles i. Craved in the likeness of hideous beasts and served as water spouts to drain water from the roof 2. Interiors a. Number of decorative elements i. ii. Murals were used to depict religious scenes Candleholders, crosses and statues were decorated with gold and precious stones b. Illumination i. Process of decorating manuscripts with pictures and designs 1. One common technique was to decorate the first letter on the page c. Tapestry i. Large woven hangings ii. Hung in castles to prevent drafts iii. Showed scenes of daily life or fantastic creatures like dragons or unicorns 2. Literature a. Religious Texts i. ii. Create all sorts of works, from sermons about how people should live to interpretations of passages from the Bible Hildegard of Bingen 1. 2. 3. A nun and medieval poet Wrote dozens of poems and music to accompany them Wrote in Latin b. Epics and Romances i. Long poems that tell stories of heroes and villains ii. Works differ in their subject matter iii. Often performed by wandering singers called troubadours iv. These poems were written in the vernacular (common language) c. Major Works i. Geoffrey Chaucer 1. He wrote the Canterbury Tales a. b. c. Characters come from a wide rage of social backgrounds His descriptions help historians know what life was like for people during the middle ages Wrote in English and help spread the language in England ii. Dante Alighieri 1. He wrote The Devine Comedy a. b. c. d. Book is composed of three parts: Inferno, Purgatory, and Paradise Tells the story of the magical trip he made through the afterlife The poet Virgil acts as his guide for part of the trip His writing led to the increase of Italian 3. Thinking and Learning a. Alchemy i. People began to conduct experiments ii. Practiced an early form of chemistry called alchemy iii. Gained practical experience in chemical reactions b. Universities i. Helped increase the flow of Greek learning into Europe ii. Liberal arts 1. Study of Latin grammar, rhetoric, logic, geometry, arithmetic, astronomy and music iii. Also taught theology, medicine and law c. Thomas Aquinas i. Taught at the University of Paris ii. Argued that both reason and faith were necessary for understanding truth iii. His approach was called Scholasticism 1. Tried to show that Christian teachings were also knowable and provable through the use of logic http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/ancient/buildin g-gothic-cathedrals.html Trade and Towns 1. Growth of Towns a. Italian Trade Cities i. First of medieval Europeans to build a thriving trade economy ii. Venice was the most important of the early trade cities 1. 2. 3. Protected by powerful warships Traded with both the Byzantine empire and Muslim lands Goods were very expensive and very profitable iii. Italians will control almost all trade in southern Europe b. Hanseatic League i. A group of northern German cities that worked together to promote and protect trade ii. Controlled most of the trade between Europe, Russia and the Baltic region c. Trade Fairs and Markets i. Trade fairs 1. 2. 3. 4. Place where buyers and sellers would meet Held in towns and drew in large crowds Merchants offered a great variety of goods: fabrics, spices, trained animals…etc. Held once a year at a specific location ii. For everyday needs people went to local markets d. Money and Credit i. Cities will begin minting their own coins 1. 2. Will be used as payment Also used to pay taxes to the lord ii. Some would allow customers to buy goods on credit 1. 2. The promise of later payment Customers would sign a document stating when and how payment was made iii. Money and credit would lead to the creation of Europe’s first banks 1. People could deposit money for safe keeping or request loans 2. Most money lenders were Jewish a. Religious laws prevented Christians from charging interest on loans 2. Growth of Towns and Cities a. New Technologies i. Heavy plow 1. Increased the amount of crops people could grow on their land ii. Watermill and windmill 1. These were used to grind wheat into flour iii. Improvements meant that fewer people were needed to work on farms iv. More people will move to the cities and try to build a life for themselves b. Free towns i. Most medieval towns were run by local lords would charge taxes and fees that they wished ii. Merchants appealed to kings for special charters for new towns 1. 2. Allowed merchants to run towns anyway they wanted Paid taxes to the king in exchange c. Guilds i. Developed out of the craftspeople need to organize themselves ii. Created trade organizations called guilds 1. 2. 3. All members of a guild had the same occupation One of the primary functions was to restrict competition Members would set standards and prices for their products iii. Guilds also trained children in their craft 1. Apprentice a. b. c. A child learning a craft Spent several years working with a master craftsperson, learning the basic skills of the craft Most also lived in their master’s house 2. Journeyman 1. After learning the basic skills an apprentice would become a journeyman 2. Some would travel from workshop to workshop learning from different masters 3. Very difficult to become masters due to some guilds restrictions iv. Most guilds were only for men but some accepted female members. Challenges of the Late Middle Ages 1. Religious Crisis a. Hersey i. Beliefs opposing the official teachings of the Church 1. Many were de-emphasizing the role of the clergy and the sacraments ii. The Church tried several methods to stamp this out 1. Inquisitions a. b. Primary method Legal procedures supervised by special judges who tried heretics 2. Christian education a. b. New religious orders were formed to spread Christian teaching Members were called friars i. ii. 3. War Took vows of poverty and obedience Lived among the people b. Papacy Dispute i. ii. 1309, the pope was forced to leave Rome and he went to Avignon, France Pope Gregory XI 1. 2. After70 years of the papacy being in France, he moved it back to Rome He will die a year later iii. Two men will claim papal power 1. One was in Rome and the other was in Avignon iv. Conflict lasted 40 years 2. Wars and Conflict a. Hundred Years’ War i. Cause 1. 2. The king of France will die without an heir in 1328 Two men will claim the right to rule a. b. 3. 4. His nephew King Edward III of England The dead king’s regent The French selected the regent and crowned him King Philip VI of France This decision sparks the war Edward III of England Philip VI of France ii. The War 1. Edward and the English army were winning battle after battle due to superior weapon technology….like the longbow and cannon 2. 1429- The war changed a. Joan of Arc i. Claimed that the saints had told her to lead the French into battle ii. Will defeat the English at the battle of Orleans iii. Will be captured, tried and executed by the English iii. The End 1. War ends in 1453 2. King Charles II of France will help drive the English out b. The War of the Roses i. Causes 1. Two families in England will fight for the throne a. b. The Lancasters- emblem was the red rose The Yorks- emblem was the white rose Lancaster’s Emblem York’s Emblem ii. The War 1. Edward IV will take the throne in 1461, he is a York 2. His brother will become king after his death, he will be Richard III 3. Richard will be killed while trying to prevent a rebellion Edward IV Richard III 4. Henry VII a. From the Tudor family in England b. Related to both families i. ii. Married to Edward IV’s daughter Related to the Lancasters by blood c. His rise ended the war 3. The Black Death a. Origins i. Started in the East in 1346 ii. Carried by rats that had fleas, that came over on the boats from the east iii. By 1351, almost all of Europe was touched by the Black Death b. Course of the Disease i. Disease was almost always fatal ii. Symptoms 1. 2. 3. 4. Large dark splotches on the skin High fever Vomiting Severe headaches iii. Historians estimate that 25 million Europeans or 1/3 of Europe’s total population died during the Black Death c. Effects i. Most believed that God was punishing them for their sins ii. Some blamed the Jews and anti-Semitic feeling increased in Europe iii. The manorial system ended