DO NOW - O. Henry Science
advertisement
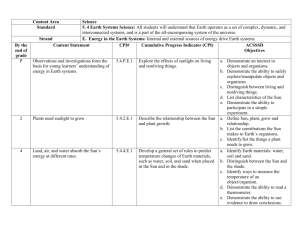
DO NOW Monday Jan. 13 V: 0 Complete the Topographic Map card sort with your shoulder partner. Homework & Agenda Homework Grade Level: Earth’s Atmosphere Pre-AP: Earth’s Atmosphere Today’s Agenda Due Friday, Jan. 17 -Trade & Grade Homework -Before & After -Exit Ticket V: 0 TEKS V: 0 8.9 (C) Interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weather. Vocabulary contour line contour interval altitude successive topographic map V: 0 satellite view land feature erosional feature weathering erosion EQs & Objectives V: 0 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does Earth’s surface change? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -Interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering. Trade & Grade Homework V: 1 Trade your homework with someone at your table. Before & After V: 1 Look at the before and after pictures from a natural disaster. Make 3 observations and a prediction about what happened to the land. Satellite Images What land feature is shown below? V: 1 Satellite Images V: 1 What land feature is shown below? Mississippi River (delta, flood plain) Satellite Images What land feature is shown below? V: 1 Satellite Images V: 1 What land feature is shown below? Mount St. Helens (volcano) Satellite Images What land feature is shown below? V: 1 Satellite Images V: 1 What land feature is shown below? Rio Grande (river) Satellite Images What land feature is shown below? V: 1 Satellite Images V: 1 What land feature is shown below? Grand Canyon Satellite Images V: 1 Exit Ticket V: 1 Complete the Landforms and Maps Card Sort with your shoulder partner. DO NOW Tuesday What is the difference in elevation in meters Jan. 14 between Point X and Point Y? V: 0 Homework & Agenda Homework Grade Level: Earth’s Atmosphere Pre-AP: Earth’s Atmosphere Today’s Agenda Due Friday, Jan. 17 -Topographic Map and Satellite Views Quiz -Cover Page for Weather V: 0 TEKS V: 0 8.9 (C) Interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weather. Vocabulary contour line contour interval altitude successive topographic map V: 0 satellite view land feature erosional feature weathering erosion EQs & Objectives V: 0 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does Earth’s surface change? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -Interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering. QUIZ Read and re-read the passage. Underline the question Bubble important words Identify the key idea, write it in margin. Eliminate the wrong answers Select the correct answer ✓ V: 0 Cover Page - Weather V: 0 Create a Weather cover page that includes the word “Weather” and 3 pictures that you think of when you hear the word “weather”. DO NOW Wed/Thrs Describe what the arrows represent Jan. 15-16 and what is happening in the image to the right. V: 0 Homework & Agenda Homework Grade Level: Earth’s Atmosphere Pre-AP: Earth’s Atmosphere Today’s Agenda Due Friday, Jan. 17 -Moving Circles lab -Convection Current Reading -BrainPop: Ocean Currents -Ocean Current Map -Wrap Up Questions V: 0 TEKS V: 0 8.10 (A) Recognize that the sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents. Vocabulary weather weather map atmosphere ocean currents wind cold front warm front meteorologist barometer V: 0 air pressure air mass high pressure air mass low pressure air mass convection thermal energy Coriolis effect atmospheric movement EQs & Objectives V: 0 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does Earth’s surface change? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -make observations about how convection currents relate to ocean currents and air currents. Moving Circles Lab V: 2 1. Put on your safety goggles. 2. Fill the plastic container ¾ full of water 3. Balance the container on the 4 cups and let the water settle. Moving Circles Lab V: 2 4. Slowly squeeze red food coloring onto the bottom of the container toward one side. 5. Remove ice from cup and place in the container on the opposite side. Moving Circles Lab V: 2 6. Using safety gloves, pick up beaker of hot water and place it under the container beneath the red food coloring. 7. In your INB, draw a picture and record your observations. CONVECTION IN LIQUIDS! Convection Current Reading V: 0 In your INB, set up a page with the following: What is a convection How do convection current? currents affect winds? What is the source of energy that drives convection currents? Student Choice…. Write a question and answer it using text evidence from the reading. Convection Current Reading V: 0 Read about convection currents and then answer the questions. • Turn to your partner and answer the question: “What is wind?” “What causes the wind to blow?” • Together, select the explanation you both think is the most accurate. • Share with the class! What is wind? Wind is air in motion. It is produced by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun. Since the earth’s surface is made of various land and water formations, it absorbs the sun’s radiation unevenly. What causes the wind to blow? As the sun warms the Earth's surface, the atmosphere warms too. Some parts of the Earth receive direct rays from the sun all year and are always warm. Other places receive indirect rays, so the climate is colder. Warm air, which weighs less than cold air, rises. Then cool air moves in and replaces the rising warm air. This movement of air is what makes the wind blow. What is wind? (Brainpop) http://www.brainpop.com/science/weather/wind/ CONVECTION transfer of heat by the movement of warmed matter; hot air/water rises, cool air/water sinks Hot Air is Less Dense! (so it rises) What Can Convection Do? CONVECTION Moves air in the atmosphere! CONVECTION Wind over the shore changes direction because of EARTH’S UNEVEN WARMING & COOLING! What Causes Wind? Bill Nye’s Explains Wind in 2 minutes! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uBqohRu2RRk&feature=related Bill didn’t use the word “convection”… but he described it! How did he demonstrate convection? BrainPop Video Ocean Currents V: 0 Ocean Currents Map Label currents on the ocean map. Cold Currents – BLUE Warm Currents – RED Glue the ocean current map into your INB. V: 1 Ocean Currents Map V: 1 CONVECTION causes deep ocean currents! Ocean Currents and Coastal Temperatures Inland vs. Coastal Cities Wrap Up Questions V: 1 1. Explain how the blue water and red water moved in the container in the Moving Circles lab. 2. Why do you think they moved that way? 3. If the water in the containers represented the ocean, how does the water in the ocean move? 4. Recall that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler areas. How is this concept illustrated in this model? DO NOW Friday Jan. 17 V: 0 Meteorologists predict the weather patterns everyday. What tools do you think they need in to do their job? Homework & Agenda Homework Grade Level: Earth’s Atmosphere Pre-AP: Earth’s Atmosphere Today’s Agenda Due Today -Weather Tool Stations -Weather Tool Card Sort V: 0 TEKS V: 0 8.10 (A) Recognize that the sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents. Vocabulary Barometer Thermometer Weather vane Psychrometer Anemometer V: 0 EQs & Objectives V: 0 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: - How does Earth’s surface change? DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -identify lab equipment used to observe weather and describe what it is used for. Weather Tool Stations V: 2 With your table group, visit each of the stations. At each station, record the following: - Name of the equipment - Description of the tool - Describe a situation when the tool would be most useful Weather Tool Card Sort V: 2 Complete the card sort with your shoulder partner.