High Pressure & Low Pressure Weather
advertisement

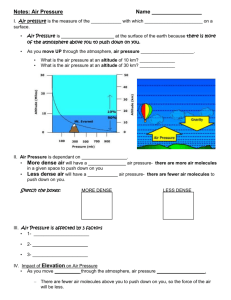
High Pressure & Low Pressure Weather Air pressure - The weight of the atmosphere covering a certain area. • Air pressure increases closer to the surface of the Earth. • Other factors can affect air pressure as well. Cold air is more dense (higher pressure) than warm air Dry air is more dense (higher pressure) than moist air • H2O atomic weight = 10 • N2 atomic weight = 14 • O2 atomic weight = 16 • Water molecules take up space in the air, but don’t add as much mass in the same amount of volume. What is denser? • Warm air or cold air? • Cold air • Moist air or dry air? • Dry air • Which air masses are most dense? • cP- cold and dry • Which air masses are least dense? • mT- warm and moist • These air masses of different densities move around • Remember: air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. • Is this a land breeze or a sea breeze? Observe 1. Fill a small beaker with water and set it on a white piece of paper. 2. Get a dropper full of colored sugar water. 3. Drop it slowly into the center of the still water, record your observations. 4. What happened? Why? 5. Clean out your small beaker and set it to dry on the sink. What happened? • The colored sugar water is more dense than the tap water so it sinks. • Dense air also sinks, now the surface of the Earth has a lot of densely packed air molecules. • This is called a high pressure area. As the air sinks down in a high pressure area, it flows away from the high pressure spot and turns right due to the Coriolis effect. Clouds don’t form when air sinks, so high pressure areas are associated with good, clear weather. High pressure = dense air sinking & good weather •Air that is not very dense (warm and/or moist air) will rise, like a hot air balloon. •These air molecules are not very tightly packed. •This is called a low pressure area. As these air molecules rise, they turn to the right due to the Coriolis effect, causing a counter clockwise wind. • Hurricanes in the Northern Hemisphere all show a counter clockwise swirl around a low pressure center. As the low density air molecules rise (warm and moist), they cool and condense, forming clouds. Low pressure = air rising & stormy weather High and Low Pressure Areas • High pressure causes air to sink • Usually results in several days of clear sunny skies http://www.youtub e.com/watch?v=aiY yCurh_SU • Air rises in low pressure areas and condenses forming water droplets • Usually results in rain and storms Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What is denser, warm or cold air? What is denser, moist air or dry air? Which air will form a High Pressure system, denser or less dense air? Which air will form a Low Pressure system, denser or less dense air? The Coriolis Effect in the northern hemisphere causes wind to be deflected to the right or the left? Why do few clouds form in a High Pressure system? Why are clouds expected to form in a Low Pressure system? What kind of weather is expected in a high pressure system? What kind of weather is expected in a low pressure system?