Bellwork - Mrs. Van Es
advertisement

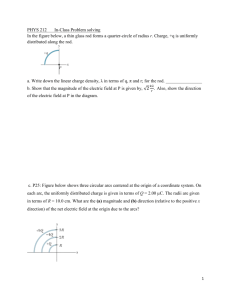
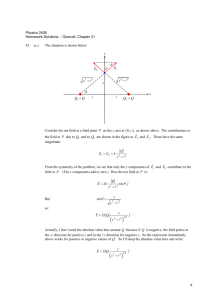
Bellwork Thursday, January 15, 2015 Refer to the electrostatic series, Table 1, p. 275 1. You rub an acetate rod with cotton. a. What charge is on the acetate rod? b. What happens when the charged acetate rod touches a neutral pith ball? Include a diagram of the rod touching the ball in your answer. c. What happens when you ground the acetate rod? Draw a picture of the rod being grounded. 2. Are the following statements true for INSULATORS or for CONDUCTORS? a. Electrons can move freely between atoms. b. Electrons can’t move freely between atoms. c. Examples are glass, paper, rubber, wood, and fur. d. Examples are metals like silver, aluminum, and nickel. e. If you charge one spot, the charge stays put. f. If you charge one spot, the charge spreads out evenly throughout the material. 3. Plastic is an insulator. Draw the negative charges in the plastic strip below before and after the shaded end has been rubbed with silk. (Refer to electrostatic series) + + + + + + + Before rubbing (neutral) + + + + + + + After rubbing shaded spot 4. Repeat question 3 using a copper strip. Copper is a conductor. Bellwork Thursday, January 15, 2015 Refer to the electrostatic series, Table 1, p. 275 1. You rub an acetate rod with cotton. a. What charge is on the acetate rod? Positive b. What happens when the charged acetate rod touches a neutral pith ball? Include a diagram of the rod touching the ball in your answer. The positive rod attracts electrons from the pith ball. The electrons move into the rod. + + + + + + + Touching + + + + + + + After contact Rod is still positive (but less positive than before). Pith ball is also positive. 2. Are the following statements true for INSULATORS or for CONDUCTORS? a. Electrons can move freely between atoms. Conductor b. Electrons can’t move freely between atoms. Insulator c. Examples are glass, paper, rubber, wood, and fur. Insulator d. Examples are metals like silver, aluminum, and nickel. Conductor e. If you charge one spot, the charge stays put. Insulator f. If you charge one spot, the charge spreads out evenly throughout the material. Conductor 3. Plastic is an insulator. Draw the negative charges in the plastic strip below before and after the shaded end has been rubbed with silk. + + + + + + + + Before rubbing (neutral) + + + + + + After rubbing 4. Repeat question 3 using a copper strip. Copper is a conductor. + + + + + + + Before rubbing + + + + + + + After rubbing