Motivation – Unit 8
advertisement
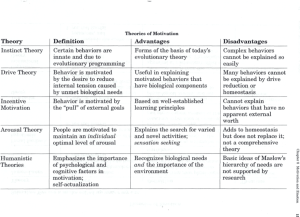
Motivation – Unit 8 Video Hamster Instinct/Evolutionary Theory Influenced by Charles Darwin Lists of behaviors that are instincts Weakness is that it just lists and does not explain motivation for these behaviors Drive Reduction Theory Human motivation is influenced by the combination of needs and drives - biological Homeostasis Body seeks to maintain a stable internal state Body creates a drive if any of its needs are unmet Does not explain some behaviors as curiosity or risk taking Does not account for external incentives Incentive Theory Recognizes that humans are not only pushed into action by an internal drive, but also motivated by the pull of an incentive Push of a drive (hunger) + pull of an incentive (smell of the cookie) = eat the cookie Explains non-biological motivations such as achievement, adventure, and affiliation Not all behavior can be explained by incentives altruistic Arousal Theory Individual is motivated by the desire to remain at a personally determined optimal level of arousal Optimal level of arousal level of excitement preferred by the person Differs from person to person Increased arousal levels result in improved performance Yerkes-Dodson Law Explains relationship between the level of arousal and performance On simple tasks – performance is better if arousal levels are somewhat higher On difficult tasks – performance is better if arousal levels are slightly lower Yerkes-Dodson Law Yerkes-Dodson Law Hierarchy of Needs Abraham Maslow 5 needs Physiological/biological Safety Belonging and love Esteem Self-actulaization Hierarchy of Needs Effectively demonstrates how basic biological and safety needs often have to be met before individuals are motivated towards high level needs Questions Not all proceed sequentially through the levels Self-actualization has been proven difficult to measure Sky diving vs safety