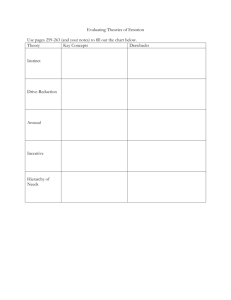
Instinct Theory Certain behaviors are innate and due to evolutionary
advertisement
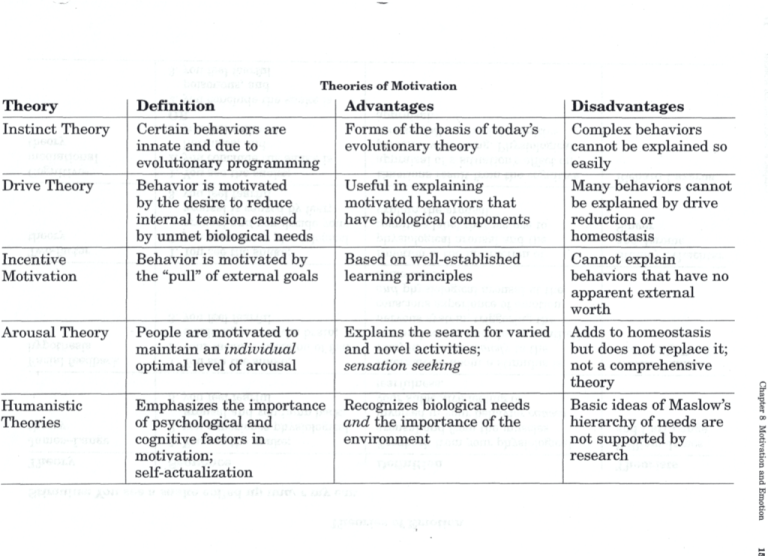
Theories of Motivation Theory Definition Advantages Disadvantages Instinct Theory Certain behaviors are innate and due to evolutionary programming Behavior is motivated by the desire to reduce internal tension caused by unmet biological needs Behavior is motivated by the "pull" of external goals Forms of the basis of today's evolutionary theory Useful in explaining motivated behaviors that have biological components Arousal Theory People are motivated to maintain an individual optimal level of arousal Explains the search for varied and novel activities; sensation seeking Humanistic Theories Emphasizes the importance of psychological and cognitive factors in motivation; self-actualization Recognizes biological needs and the importance of the environment Complex behaviors cannot be explained so easily Many behaviors cannot be explained by drive reduction or homeostasis Cannot explain behaviors that have no apparent external worth Adds to homeostasis but does not replace it; not a comprehensive theory Basic ideas of Maslow's hierarchy of needs are not supported by research Drive Theory Incentive Motivation Based on well-established learning principles