Are We Creating a Performance System or Hodgepodge of
advertisement

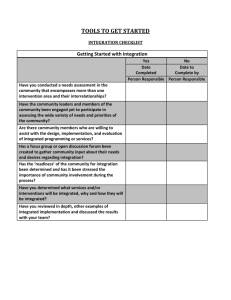
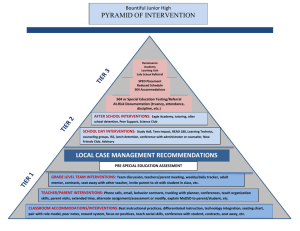
Are We Creating a Performance System or Hodgepodge of Interventions? Training Session Created by Ryan Watkins and John Wedman Published in the 2011 Pfieffer Annuals Objectives • Identify what it takes to accomplish something. • View accomplishments from a systems perspective. • Connect accomplishments to performance improvement. • Analyze a situation using a performance improvement model. • Critically view performance improvement from a systems perspective. Hell, there are no rules here - we're trying to accomplish something. ~Thomas Edison Short of following Edison’s mantra, how are significant results accomplished? Significant Accomplishment Good Idea • We choose to go to the moon Resources • Money (lots of money), bright scientist, committed politicians, etc. Support System • • • • Scientific knowledge/skills Rewards for innovation and risk taking Communication and coordination Desire to succeed Alignment Significant Accomplishment Support System Resources Good Idea Systems Dynamics The support system consumes resources while enabling the idea to become reality. If the support system consumes more resources than produced by the accomplishment, a ‘death spiral’ results. Accomplishments generate new resources and set the stage for new ideas. If the new ideas are not better than the status quo, obsolescence is unavoidable. Performance Improvement View Significant Accomplishment Continual Monitoring Performance Capability Knowledge & Skills Expectations & Feedback Motivation & Self-Concept Environment, Tools, & Processes Incentives, Rewards, & Recognition Organizational Culture Resources Continual Monitoring Vision, Mission, & Objectives Wedman’s Performance Pyramid Pyramid Questions Are they mentally, socially, & physically able to perform? Do they have the knowledge and skills needed to perform? Performance Capability Knowledge & Skills Expectations & Feedback Do they know what to do and why? Do they know how well they are doing? Motivation & Self-Concept Environment, Tools, & Processes Are they want to perform? Do they think they are competent? Incentives, Rewards, & Recognition Is the environment OK? Do they have the tools to do the job? Do processes work? Do incentives drive change? Is good performance rewarded? Performance Interventions Sample Interventions: Sample Interventions: Performance Capability Skills & Knowledge • New Employee Recruitment • Employee Selection & Retention • Resource Allocations • Workforce Forecasting • Outsourcing • Succession Planning • Job Rotations • Cross-training • Interview Standards • Competency Models • • • • • • • • Traditional Training Job Aids Knowledge Management On The Job Training E-learning Brown-Bag Lunches Train-the-trainer On-boarding & Orientation Performance Interventions Cont’ • • • • • • • Sample Interventions: Sample Interventions: Motivation & Self-Concept Expectations & Feedback Career Coaching Motivation Workshops Team Building Self-esteem Job Rotations Counseling Confidence Building • • • • • • • Performance Reviews Balanced Scorecards Retreats and Roundtables Town Hall Meetings Reference Manuals On-boarding & Orientation 360 Degree Evaluations Performance Interventions Cont’ Sample Interventions: Sample Interventions: Tools, Environment, & Processes Incentives, Rewards, & Recognition •New technology •Workplace Redesign •Process Redesign •Ergonomics •Electronic Performance Support •Labeling •Color Coding • • • • • • • • Awards Programs Employee of the Month Recognition Messages Peer Recognition Job Sharing Flex Hours Telecommuting Financial incentives Systemic Analysis • Goal: Examine each subsystem to determine its relation with the performance gap (i.e., difference between current and desired results). • Example: Expectations & Feedback – Do staff know what results they are expected to achieve? – Do staff receive timely feedback on their performance in relation to the achievement of desired results? – Do managers meet routinely with staff to describe expectations and provide performance feedback? • Example: Organizational Culture – How does the organization’s culture support the achievement of desired results? – What elements of the organization’s culture oppose desired performance? Performance System Design • Goal: Create holistic performance systems that accomplish desired results. • Example: Incentives, Rewards, and Recognition – What incentives can be used to encourage staff to accomplish desired results? – How can we reward the achievement of desired results? – How can we recognize those employees who achieve desired results? Significant Accomplishment Continual Monitoring Performance Capability Knowledge & Skills Expectations & Feedback Motivation & Self-Concept Environment, Tools, & Processes Incentives, Rewards, & Recognition Organizational Culture Resources Continual Monitoring Vision, Mission, & Objectives .…is it a system? OK…but… General Systems Theory • Ludwig von Bertalanffy • Béla H. Bánáthy • Used in many scientific disciplines and “real world” applications – Biology, physics, psychology, economics, etc. – Management, software, family therapy, etc. Principles of Systems Theory Principle Pyramid Examples Interrelatedness New tools require new skills. Rewards are based on meeting expectations. Capability shapes self-concept. Interdependence Clarifying performance expectations without providing adequate resources and supportive environment will not accomplish sustainable results. Connectivity Learning requires inputs from participants, clients, managers, suppliers, and others. Synergy Alone, changes in incentives or rewards will not achieve desired and sustainable improvements. Equifinality There is no single set of interventions or activities that will accomplish results, there are many options to considered and compared. Theory Application • Models, Frameworks, Rubrics, Algorithms • Examples of “Systems Models” – Kaufman’s Organizational Elements Model – Mager’s Performance Analysis Flow Chart – Rummler’s Nine Performance Variables – Wedman’s Performance Pyramid • Examples of “Systems Thinking” in the literature – Peter Senge, Margaret Wheatley, Richard Swanson *More information on each of these models is available in: Wilmoth, F., Prigmore, C., and Bray, M. (Reprint). HPT Models: An Overview of the Major Models in the Field. In Watkins, R. and Leigh, D. (2010). Handbook for Improving Performance in the Workplace – Vol. 2: Selecting and Implementing Performance Interventions. San Francisco:Wiley/Pfieffer. Summary • With a few notable exceptions, accomplishments result from aligning a good idea with resources, and performance support. • Performance improvement requires a combination of several interrelated interventions. • Wedman’s Performance Pyramid is one example of a performance improvement system. • Lacking a systemic framework, performance improvement is a hodgepodge of interventions.