Failure Mode Effects Analysis
advertisement
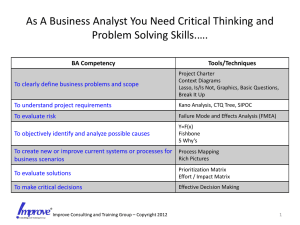
Failure Mode Effects Analysis Powerful Prevention Tool and Knowledge Base Kathleen Stillings – CPM, CQE, CQA, MBB Today’s Goals To understand the role and function of the FMEA To understand the concepts and techniques of the process FMEA and how to apply them. To complete a Process FMEA 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 2 What is it? Aka FMEA Actions Prevention / reduction of failures Tool for risk reduction 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 3 What it is not The FMEA is not a stand-alone tool to be used to solve problems The FMEA presents the opportunities but does not solve the problems 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 4 Where did it come from? Introduced in 1940 by US Armed Forces Implemented further in 1960 by Apollo Space program Commercially implemented in 1970 by Ford Motor Company Used widely in many industries today 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 5 What can FMEA be used for? Competing Prevention of Litigation Identify Weak areas of a process/product A bottom-up approach To evaluate the effectiveness of the current control plan Prioritize tasks 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 6 FMEA Types Concept Design/Product Process Equipment System Service Software 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 7 FMEA Challenges Continuous Brainstorming Lengthy consensus-building Not capturing all possible issues Team Environment only Determining and Implementing the action that drives reduction in risk Ensuring the high risk failure modes are addressed Remember to include interfaces 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 8 FMEA Benefits Improve product/process reliability and quality Increase customer satisfaction Early identification and elimination of potential product/process failure modes Prioritize product/process deficiencies Capture engineering/organization knowledge Emphasizes problem prevention Documents risk and actions taken to reduce risk Identify CTQs 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 9 Function Fill tub Failure mode Effects Liquid High level spills on sensor customer never trips floor 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings S Cause(s) O Current controls level sensor failed Fill timeout based level sensor on time to fill to low 8 disconnected 2 level sensor CRIT (critical S RPN characteri stic 5N Recommended actions Perform cost analysis of adding additional sensor halfway between low and high 80 level sensors Responsi bility and target completio n date Action taken Jane Doe 10-Oct-10 10 FMEA Start-Up Process Define the FMEA Scope Determine the FMEA Boundaries Define the Scope of Responsibility Define the Provisions Assemble the Team Define your ratings 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 11 Bring your Data Nonconformance reports Unscheduled outages Customer complaints Improvement projects Equipment failures Excess shipping charges Excess returned material charges Design changes Process capability studies 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 12 FMEA Procedure Identify the function(s), failure(s), effect(s), cause(s) and control(s) for each item or process to be analyzed. Evaluate the risk associated with the issues identified by the analysis. Prioritize and assign corrective actions. Perform corrective actions and re-evaluate risk. Distribute, review and update the analysis, as appropriate. 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 13 FMEA Cycle Source 1 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 14 Sources http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Failure_mode_and_effects_analysis http://www.npd-solutions.com/fmea.html FMEA Minus the Headache – Gavind Ramu – Quality Progress March 2009 AIAG: The Automotive Industry Action Group provides the ability to purchase the AIAG FMEA Third Edition (FMEA-3) guidelines. http://elsmar.com/FMEA/sld007.htm http://lssacademy.com/wp-content/uploads/2007/06/fmea-template.xls The Quality Toolbox – Nancy R. Tague – ASQ Quality Press Second Edition. www.QualityWBT.com 4/12/10 Kathleen Stillings 15