Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)
advertisement

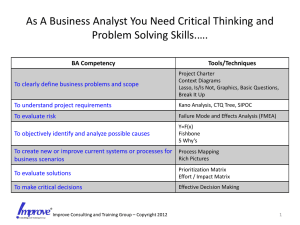
Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (FMEA) Tom Hannan & Kevin Kowalis Eastern Illinois University School of Technology Total Quality Systems INT 5133 What is FMEA? “Is an analytical technique that combines the technology and experience of people in identifying foreseeable failure modes of a product or process and planning for its elimination.” () OR Before-The-Event action that makes it easier to find flaws in the system Reliability Is the probability of the product to perform as expected for a certain period of time, under the given operating conditions, and at a given set of product performance characteristics. Reliability Requirements Based on the definition of the part, assembly, or process under consideration, the reliability of each sub-system and the factors involved in the reliability must be found, and the appropriate relationships for each part, class, or module of the product must be computed. Failure Rate Periods of failure can conveniently be modeled by an exponential distribution, and the probability of survival of the product or process may be viewed as: Rt = e ^(-T *F) = e ^ -(T/o) Rt = the period of operation without failure T = time specified for operation w/o failure F = Failure rate O = the mean time to failure Intent of FMEA An Essential Part of Total Quality Management is FMEA! • Provides Training • Helps communicating similar problems • Tracks the progress of a project • Uncovers oversights, misjudgments, and errors • Calculate the probabilities of failures •Determine if product or process failure effects on other aspects. FMEA Team FMEA methodology is a team effort where the responsible engineer involves who? • Assembly • Service • Manufacturing • Quality • Supplier • Materials • Customer FMEA Documentation • Block Diagram • Design or Process Intent • The Customer Needs and Wants • The FMEA Form Class Assignment !!!!!! Make A Simple Block Diagram Divide up into four groups (N,S,E and W) • Change Tire • Flashlight • Unicycle • Bicycle Stages of FMEA • Specifying Possibilities • Quantifying Risk • Correcting High Risk Causes • Re-evaluation of Risk Specifying Possibilities Functions Possible Failure Modes Root Causes Effects Detection/Prevention Quantifying Risk Probability of Cause Severity of Effect Effectiveness of Control to Prevent Cause Risk Priority Number Correcting High Risk Causes Prioritizing Work Detailing Action Assigning Action Responsibility Check Points on Completion Re-evaluation of Risk Recalculation of Risk Priority Number RPN = (S) * (O) * (D) S = SEVERITY O = OCCURRENCE D = DETECTION RAKING 19 The Design FMEA Document • FMEA Number • Item • Design Responsibility • Prepared By • Model Number/Year • Key Date • Core Team • FMEA Date The Design FMEA Document • Item/Function • Potential Failure Mode • Potential Effect(s) of Failure • Severity (S) • Classification (CLASS) • Potential Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) of Failure • Occurrence (O) The Design FMEA Document (Con. 1) Current Design Controls Detection (D) Risk Priority Number (RPN) Recommended Actions Responsibility and Target Completion Dates Actions Taken The Process FMEA Document (Con. 2) Process Function/Requirements Potential Failure Mode Potential Effect(s) of Failure Severity (S) Classification (CLASS) Potential Cause(s)/Mechanism(s) of Failure Occurrence (O) Current Process Controls Limitations: FMEA document’s do not fix the identified problem Def. of the action to fix the problem Will not replace the basic problemsolving process. ?Questions?