Exam 2 Review
advertisement

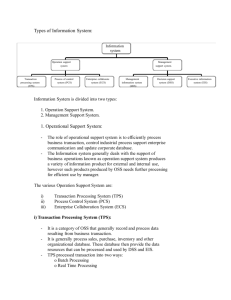
Exam 2 Review Topics Chapter 5 Data Resource Management Database Terminology Types of Relationships Comparison to File Systems Labs Introduction to Databases Wagemart Scheduling (DSS) Supply Chain Mgmt. & RFID Fund Trading Lab (DSS) Student Presentations & Related Reading (see website) DBMS CRM ERP SCM EIS DSS GIS Expert System will be on the final but not this exam First, understand the big picture. Historical Perspective Information Systems were initially designed to meet the needs of traditional functional areas of business Accounting Production or Operations Marketing Finance Human Resources Modern View Enterprise Systems are so valuable and superior, Functional System are rarely developed anymore An Enterprise System can replace several Functional Systems CRM System Production or Operations (PCS) Finance System Accounting System Marketing System HR System Modern IS Systems The big software developers (Oracle for example), now sell Enterprise Systems (cross-functional), not functional systems. i.e., they don’t sell a marketing System, but they do sell a CRM system. Why? Oracle Siebel Essential for Operations Finance System Used by Accounting Used by Marketing HR System In the Real World You might use more than one Enterprise System. Example, if you work in Accounting, you might use 2 different Enterprise Systems and one functional system. ERP System CRM System Production Accounting System Finance Accounting Marketing Human Resources Why this course matters Accountant’s without a back-ground in MIS might not understand the roles these three systems play and why all three are necessary. ERP System CRM System Production Accounting System Finance Accounting Marketing Human Resources Key Principle These system exist because of common goals and the need to share information. Business Processes are not isolated to one area ERP System CRM System Production Accounting System Finance Accounting Marketing Human Resources Traditional Classification (Types of Systems) Information Systems Operations Support Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Process Control Systems (PCS) Management Support Systems Enterprise Collaboration Systems (ECS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) Executive Information Systems (EIS) Modern View But, Cross-Functional Systems are so complex, they do not fit into one Information category. Systems Operations Support Systems Management Support Systems Process Control Systems (PCS) CRM System Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Executive Information Systems (EIS) Enterprise Collaboration Systems (ECS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) WTF? Q: Why did we study the different types if modern systems rarely fit one specific type? A: Some basic systems still fit perfectly into a category Example: Outlook is just an ECS. A: Some enterprise system lack a certain characteristic. Example: A poorly design CRM may not have any DSS characteristics. In the Real World Does this mean an ERP system replaces all these other systems? Information Systems Operations Support Systems ERP System Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Process Control Systems (PCS) Management Support Systems Enterprise Collaboration Systems (ECS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) Executive Information Systems (EIS) In the Real World It means that an ERP system has some of the characteristics of all these types of systems. But, you still might need a basic TPS to handle your point of sale operations and ECS to collaborate. Information Systems Cash Register System (POS) Peoplesoft Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Operations Support Systems Process Control Systems (PCS) Management Support Systems Enterprise Collaboration Systems (ECS) Outlook Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) Executive Information Systems (EIS) Second, make sure you understand databases Almost all information systems have an underlying database Basic Information System Architecture Forms Reports Charts Applications DBMS Algorithms User User Interface Queries Information Systems that transform Data into something more useful… Database: Tables Relationships Metadata Logical vs. Physical Logical Access Layer how to access the DBMS Forms Physical Access Layer how to actually fetch the data from a hard disk or server Reports Charts Applications DBMS Algorithms User User Interface Queries Information Systems Database Why Databases are so great… Database Management System (DBMS) does all the nitty-gritty work. Information Systems just have to deal with Logical (high-level) Access. Logical Access Layer how to access the DBMS Physical Access Layer how to actually fetch the data from a hard disk or server DBMS Before Databases Sales Team Warehouse Manager Marketing Application Inventory Management System (TPS) Customer Data Docs Special Inventory Data File Financial Calculator Tool Financial VP of Finance Spreadsheets These Information Systems are custom built based on the data (documents, files, spreadsheets) Functional Systems built with DBMS Sales Team Warehouse Manager VP of Finance Marketing System Inventory Management System (TPS) Customer Data DBMS Inventory Data Finance System Financial Data These Information Systems are now Database Applications Enterprise Systems built with DBMS Sales Team Warehouse Manager VP of Finance CRM System Inventory Management System (TPS) Customer Data DBMS Inventory Data ERP System Financial Data These Information Systems are now Database Applications Databases But, databases are not just a bunch of tables Orders OID CID PID Quantity 001 508 199 500,000 002 508 201 2 003 510 201 1 Customers Products CID FName LName Address PID Description Cost 508 Eric Breimer ... 199 Viagra $45.99 509 Andrew Zych ... 200 Tooth Paste $2.58 510 Greg Smith ... 201 Hair Gel $5.99 A database also includes relationships between the different tables Types of Relationships One to One ThingA ThingB Relationship Man Woman Married Types of Relationships One to Many Student Faculty Student Student Advises Get Advisement Types of Relationships Many to Many student takes course Student Course Student Course Student Student course has a student Supply Chain Management Systems Remember Lindsey and Deanna’s presentation. Process of SCM: SCM systems assist with flow of Raw materials Producing products Providing service Delivering the product to the end consumer. Goals of an SCM system: Speed Efficiency Reduce Cost Improve Supply chain cycle times (to get a company’s products from concept to market) Five Basic Components: 1. Plan 2. Source 3. Make 4. Deliver 5. Return Third, review student presentations See the website… Also, the website tells you the corresponding reading. Know the supply chain… This wasn’t adequately covered in any of the presentations. What if you don’t have enough bike parts? What if there aren’t enough bikes in Finished Inventory? SCM Example Supply Chain Systems are so complicated that its sometimes hard to see simple solutions. Simple Solution: The guy who orders parts queries the Finished Inventory Database and the Orders Database. In the older system, he only looked at the Parts database to see if they should re-order parts. SCM Fundamentals Implementing and then using an SCM can reengineer a company. However, notice that an SCM system if very Operational This could improve the company’s operations significantly Leads to Strategic Advantage Its used everyday to support the core business process. ERP systems are very different… ERP Systems So how are they different than SCM Systems? The key is the word “Planning” Planning is a forward thinking process Supply Chain management Planning for next year… Planning for your next order Implementing and using an ERP can re-engineer a company in even more strategic ways. SCM system are more focused on ….? ERP Example Remember the presentation by… Shalagh, Tara, and Kristen One ERP System: Peoplesoft Peoplesoft by ORACLE Helps Companies with: Customer Relationship Management Financial Management Supply Chain Management Project Management Asset Lifecyle Management Sales and Other Application ERP ADVANTAGES Complete orders faster Fewer errors Security features to protect against outside crime Better customer service Improved efficiency and productivity Easier to share data across departments Complete revenue cycle faster Do you get it? What’s more likely… An ERP system has a CRM and SCM built into it. A SCM system has an ERP and CRM built into it. Here is another distinction SCM system help deliver products to customers faster… CRM systems can also help with this… But, CRM system are more focused on things like Customer Service Improving Sales Marketing Support Remember Ken & Nicole’s presentation… Sales - Marketing Marketing & Customer Service Customer service could be an operational devision. Training - HR CRM and Human Resources Professional Development Performance Management Human Resource Development & Compensation Players Within a CRM Customer Advocates & Experience Designers Performance Managers & Marketing Analysts Customer & Employee Surveyors & Analysts Input Database with: Customer’s interactions with the organization Support information Requests Complaints Interviews Survey responses DSS Julie, Lizzy, and Mike’s presentation is a must see… Why Use a DSS? Linear Programming Regression Analysis Decision Trees Forecasting Analytical Modeling Type of Modeling Example What-if analysis If we raised our advertising budget by 15% of our employees, what would happen to sales? Sensitivity analysis Continuously raise our advertising budget by 1% to monitor its relationship to sales Goal-seeking analysis Increase our advertising budget until sales reach $10 million Optimization analysis What number of advertisements maximizes our overall profit? In the real world… Most Management Information Systems are now so interactive that…. Every MIS is really a DSS. Interactivity and Data Modeling are the key ingredients that distinguish a DSS from an MIS. Where do GIS’s fit in? There are a new kind of DSS that integrates geographic data with regular table-based data. Maps + Spatial Data + Tables See the presentation by Jill, Will, and Stacey… Things to look at: Raster vs. Vector EIS: The top of the pyramid A picture is worth a thousand words: An Executive EIS SCM CRM MIS PCS External Data DSS MIS MIS TPS EIS see Larissa &Ciara’s slides for more details…