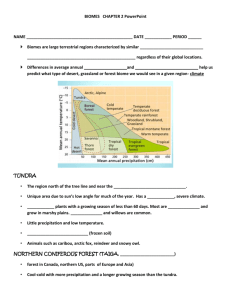
ecosystem - Teacher Notes
advertisement

How Can We Develop & Maintain a Sustainable Future? Management Techniques Conservation: Protecting of resources that might otherwise be expended with less responsible pattern of use: • • Includes education of consumer Incentives to decrease consumption Preservation Provides ample reserve of resources for the future use Different from conservation which simply reduces use of resources 1964 Wilderness Act Restoration Bringing a damaged ecosystem back to its unspoiled, natural condition. Remediation vs Reclamation Remediation: Using chemical, biological, physical methods to remove chemically active (either hazardous or toxic) pollutants Superfund Reclamation: Returning devastated land to a condition that is environmentally useful and socially/politically acceptable. What is the difference between, restoration, remediation, reclamation? Mitigation Refers to finding a solution to a problem Establishing another ecosystem elsewhere in place of damage done as a result of development What Services Do The Following Major Systems Provide? Forests Grasslands/Savannas Croplands Wetlands Desert/Tundra Coastal Oceans Coral Reefs Open Oceans How Do We Determine Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY)? The highest possible rate of use that the system can match with its own rate of replacement or maintenance. Important consideration is carrying capacity Optimal population is half the carrying capacity What’s the problem with determining MSY? What’s Happening to Our Ocean Ecosystems? Pollution Overfishing Destruction of habitat International Whaling Whales were heavily exploited and depleted until 1980s Only limited whaling allowed by Japan, Norway, Canada, Alaska and Greenland Endangered and vulnerable species include: N. Atlantic Right Whale, Blue Whale, N. Pacific right Whale, Fin, Sei, Bowhead, Humpback, Gray, & Sperm Will Aquaculture Be Able to Fill the Gap? Coastal Aquaculture Open Ocean Carp, Tilapia, milkfish and mollusks make up 80% of production Fishing Methods Protecting Our National Forests! Although we have cut all but 5% of the forests since the colonists first arrived, deforestation is no longer a problem in the US There are more trees today than in 1920 Forests as Obstacles Worldwide, only about 10% of forests are protected Because of El Nino, droughts have led to increased forest fire (1998 known as “the year the Earth caught fire”) Difficult to exploit forest for food, therefore conversion to agriculture is #1 leading cause of deforestation Between 1960-1990 loss of 20% of tropical forests (up to1.1 billion acres) the size of 2/3 of US Types of Forest Management Silviculture: Objective of producing a specific crop Clear cutting: removing an entire stand Selective cutting: some mature trees are removed leaving behind a diversity of biota Shelter-wood cutting: cutting mature trees in groups over a period of 10-20 years. Ecosystem Management Clinton administration’s Forest Service Chief (Mike Dombeck) declares no building new logging roads Bush administration announced “Healthy Forests Initiative”, by reducing “fuel load” (shrubs & trees) to prevent forest fires Rainforests of the World Crucial in maintaining Earth’s climate Greater economic development & rapid population growth Indonesia plans to convert 20% of its forests (1 million hectares) What incentives and assistance could the US offer Brazil or African countries to keep tropical rain forests from further harm due to conversion? Sustainable Forest Management Plantation of trees for wood or other products Extractive Reserves: Latex, nuts, fibers fruits Preserving Forests: Use as tourist attractions Place forest under the control of indigenous villagers World Bank: Will finance only logging companies with sustainable practices, and improve livelihoods of the millions of poor who live and depend on the forests Remote Sensing: Using radar and satellite imagery, Brazil monitors its forests. Forest Resources Assessment 2000 (FRA) measured world forests in this manner Wetlands To Development It would cost more than $100,000 a year to duplicate the water purification and fish propagation of a single acre of natural tidal wetlands