Propaganda Techniques
advertisement

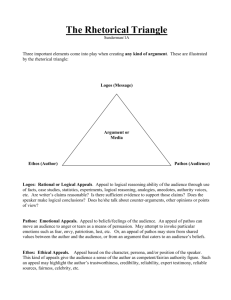
Propaganda/Persuasion Techniques How the media influences us What is propaganda? • A way to persuade people by using images and words to achieve a desired affect or outcome. Propaganda/Persuasive Techniques • Advertisements and other methods of persuasion (political) may contain rhetorical fallacies • Rhetorical Fallacies – An argument that is not sound but may still be convincing (if you really think about it, is it true?) Ad Hominem • “ad hominem” means against the man or against the person (Latin) • Attack the character or circumstance of “the other side” in order to distract from the argument. • Devalues the argument because of the person who is making the claim, regardless of the evidence provided Ad Hominem Examples • “We shouldn't be surprised that Senator Smith supports this new tax - considering how long he has been working in politics, it would be a shock if he didn't support it!” • “John has been proven to be a liar numerous times, therefore you should reject his testimony and acquit my client.” • What are some ad hominem arguments you have heard or used? Exaggeration • An overstatement or excessive representation of more than is true – Everyone gets to go to the party except me. Exaggeration BIC Razors Stereotyping • Generalization that allows everyone who is given a specific label to also have attributed to them a set of characteristics • Can be used to cast a group of people as “good” or “bad” Stereotyping Categorical Claims • A claim is based on the faulty logic of relating two things solely because they are in the same category • Example: Chihuahuas are good inside dogs. Rottweilers are dogs; therefore, Rottweilers would be good inside dogs, too Categorical Claims Testimonial • Famous people, or someone respected or liked, claims that something is good or advertises or promotes a product or idea, even though they may or may not be experts – and may even be getting paid to recommend a product or endorse an idea. Testimonial Logical Appeals • Relies on faulty logic, a mistake in reasoning • For example: Because everything in Texas is bigger, you can expect a bigger salary in Texas • Also referred to as logos Logical Appeals Logical Appeals Emotional Appeals • Appeal to the audience’s emotions • This is usually an unfair appeal because it is using the reader’s fear, anger, or joy to push an idea • Also referred to as pathos Emotional Appeals Ethical Appeals • The author unfairly or unreasonably gives himself authority • Relies on celebrities or authorities • Also referred to as ethos Ethical Appeals Example Appeal to Authority • A writer may mention an important event or person to lend importance or credibility to his/her argument. • Appeals to authority have important and powerful people supporting the product or idea. Appeal to Authority Example Scare Tactics • Informs people that personal danger is imminent if they do or do not take a specific action. Scare Tactics False Need • People are persuaded to do something by letting them know that others are doing it as well. This technique is contrived peer pressure – no one wants to be left out or behind, so they decide they “need” whatever everyone else has. False Need One Final Advertisement… Things to Remember: Be sure to consider • Who is the audience for this image? • Does this image ask the audience to take action of some sort or just believe a certain idea? • What do you think is the author’s/designer’s purpose for creating this? • What is the argument this image makes?