Chapter 3 Chemical Compounds
advertisement

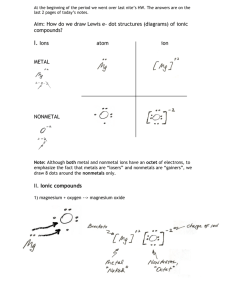
Naming Simple Compounds • I. Binary compounds: are those composed of only two elements. • 1) Binary compounds of metals and nonmetals. • If one element is metal and the other a nonmetal; the binary compound is made up of ions. The simplest are monatomic ions. A monatomic ion is an ion formed from a single atom. • Table 4.1 Common Monatomic Ions of Man-Group Elements IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA Period 2 Li+ Be2+ B C N3- O2- F- Period 3 Na+ Mg2+ Al3+ Si P S2- Cl- Period 4 K+ Ca2+ Ga3+ Ge As Se2- Br- Period 5 Rb+ Sr2+ In3+ Sn2+, Sn4+ Sb Te2- I- Period 6 Cs+ Ba2+ Tl+, Tl3+ Pb2+, Pb2+ Bi3+ Period 1 H+, H(hydride) Binary compounds When use old group number- Roman numeral plus letter A or B, the charge on a cation for main-group element, in most cases, equals the group number ( the Roman numeral). For example, aluminum, which is in group IIIA, has an ion with charge 3+. Some exceptions are noted for elements of high atomic number such as lead, in group IVA, whose common ion is Pb 2+. The charge on an anion euals the group number minus 8. Oxygen, in group VIA, has an anion charge of 2- (6-8). Most transition elements have cations of several different charges (see Table 4.2). For example, iron has the cations Fe2+ and Fe3+. Table 4.2 Some Common Ions of the Transition Elements: only ions Ions Cr3+ Mn2+ Systemic Name Chromium (III) Manganese (II) Common Name Chromic Manganous Fe2+ Fe3+ Co2+ Iron (II) Iron(III) Cobalt(II) ferrous ferric cobaltous Ni2+ Cu2+ Ag+ Zn2+ Nickel(II) Copper(II) Silver Zinc Cupric name a binary compound of a metal and nonmetal • - Write the unmodified name of the metal. • - Then write the name of the nonmetal, modified to end in ide. name unchange Sodium chloride NaCl ide ending - The overall zero charge is provided for by adjusting the ratio of cations and anions. tin(II) fluoride SnF2 calcium chloride CaCl2 silver sulfide Ag2S chromium(III) chloride CrCl3 The main group metals and nonmetals form ions related to their group number. Elements that can form more than one cation • If an element can form more than one cation, the positive charge of the ion is denoted by a Roman numeral in parentheses following the element name. Most of transition metals have cations of several different charges. • Fe2+ iron(II) ion FeS iron(II) sulfide • Fe3+ iron(III) ion Fe2S3 iron(III)sulfide • In an earlier system of nomenclature, such ions are named by adding suffixes ous and ic to a stem name of the element to indicate the ions of lower and higher charge, respectively. The ending ous is used for lower oxidation state of the metal and ic ending for the higher oxidation state. You need to know this system of nomenclature since it is still commonly used. • Cu+ cuprous ion Cu2O cuprous oxide. • Cu2+ cupric ion CuO cupric oxide. Binary Compounds of two Nonmetals or metalloids Write the element with positive charge first • - Then, write the name of the following element, modified to end in ide • E.g. HCl hydrogen chloride • When two elements form more than one compound, we indicate relative number of atoms through the appropriate prefixes: • - • • • • • • • Table 1 Greek Prefixes for Naming Compounds____________ Number Prefixes Number Prefixes 1 mono 6 hexa 2 di 7 hepta 3 tri 8 octa 4 tetra 9 nona 5 penta 10 deca___ • Example: • CO carbon monoxide • BCl3 boron trichloride • N2O dinitrogen monoxide • PCl5 phosphorus pentachloride CO2 carbon dioxide CCl4 carbon tetrachloride B2Br4 diboron tetrabromide SF6 sulfur hexaflouride Polyatomic ions • A polyatomic ions is an ion consisting of two or more atoms chemically bonded together and carrying a net electric charge. • The most familiar polyatomic cations are the following: • NH4+ ammonium ion Hg22+ mercury (I) or mercurous ion • The name mercury(I) is given to Hg22+ because it can be considered to consist of two Hg+ ions. Mercury also occurs as the monoatomic Hg2+ ion, which is known as the mercury(II) or mercuric ion. • Very few polyatomic anions carry the ide ending in their names. • OH¯ hydroxide ion CN¯ cyanide ion O22peroxide ion oxoanions. An element common to many polyatomic ions is oxygen, usually in combination with another nonmetal. Such anions are called oxoanions. Certain nonmetals such as Cl, N, P and S from a series of oxoanions containing different numbers of oxygen atoms. When an element has two oxoanions, the name of the one with higher oxidation state (more oxygens) ends in –ate; the name of the one with lower oxidation state (less oxygen) ends in –ite. • NO2¯ nitrite ion SO32¯ sulfite ion • NO3¯ nitrate ion SO42¯ sulfate ion • When the series of oxoanions of a given element extends to three or four, the prefix hypo indicates less oxygen and the prefix per indicates more oxygen is used along with the suffixes ite and ate. • • • • • increasing oxidation state of nonmetal hypo_ite _ite _ate increasing number of oxygen atoms ClO¯ ClO2¯ ClO3¯ hypochlorite chlorite chlorate per _ate ClO4¯ perchlorate ion • d) Some series of oxoanions also contain varying numbers of H atoms. These ions are named by prefixing the word hydrogen or dihydrogen as appropriate, to the name of hydrogen-free anion. • IUPAC name common name • HCO3¯ hydrogen carbonate ion bicarbonate ion • HSO4¯ hydrogen sulfate ion bisulfate ion • HPO42¯ hydrogen phosphate ion • H2PO4¯ dihydrogen phosphate ion • e) All the common oxoanions of Cl, Br, and I carry a charge of 1-. • f) The prefix thio signifies that a sulfur atom has been substituted for an oxygen atom. • S2O32thiosulfate ion Acids • An acid is a substance that produces one or more hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. • a) Binary Acid • Binary acids are certain compounds of H with other nonmetal atoms yield acidic solution when dissolved in water. • In naming acids we use the prefix hydro followed by the name of the other nonmetal modified with an ic ending. • _binary compound acid solution___________ • HF(g) hydrogen fluoride HF(aq) hydrofluoric acid • H2S(g) hydrogen sulfide H2S(aq) hydrosulfuric acid Oxoacids • An oxoacid is an acid containing hydrogen, oxygen and another element. In water the oxoacid molecule yields one or more hydrogen ions and an oxoanion. • The name of oxoacid and corresponding oxoanion are related. When the name of anion ends in -ite, the name of acid ends in -ous. • Oxoanions whose names end in ate have associated acids whose names end in -ic. Prefixes in the name of the oxoanion are retained in the name of the acid. Some Oxoacids and Their Corresponding Oxoanions Oxoacids Oxoanions H2CO3 HNO2 HNO3 H3PO4 carbonic acid nitrous acid nitric acid phosphoric acid CO32NO2¯ NO3¯ PO43- carbonate ion nitrite ion nitrate ion Phosphate ion H2SO3 H2SO4 HClO sulfurous sulfuric acid hypochlorous acid SO32SO42ClO¯ sulfite sulfate hypochlorite ion HClO2 chlorous acid ClO2¯ chlorite ion HClO3 chloric acid ClO3¯ chlorate ion HClO4 perchloric acid ClO4¯ Perchlorate ion