Energy sources in Indonesia
advertisement

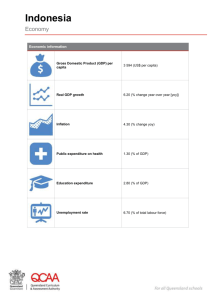
14/15 Academic Year Energy (TKK-2129) Instructor: Rama Oktavian Email: rama.oktavian86@gmail.com Office Hr.: M - F.13-15, oktavianrama.lecture.ub.ac.id Outlines 1. Energy situation 2. Energy source 3. Energy and society 4. Energy conversion and efficiency Energy situation Energy vocabulary and information literacy Energy has its own vocabulary. “Energy” and “Power” are often used interchangeably, but they mean slightly different things. What’s the difference between “Energy” and “Power”? Energy: quantity Ability to do work Power: rate Work over time Energy situation Energy units Energy has many units. Energy situation Power Power is a Rate of Energy Power: work performed over a period of time ‣Or energy produced over a period of time ‣Or energy consumed over a period of time ‣It’s a “rate” not a quantity Energy situation Power Power is a Rate of Energy Units: ‣Watt (W, kW, MW, GW,…) ‣Horsepower •Power density: W/m2 ‣Heat flux density, irradiance,… Energy situation Energy = Power × Time •A light bulb consumes energy at a rate of 100 W •Its instantaneous power consumption is 100 W •After 1 hour, it has consumed 100 Wh or 0.1 kWh •After 10 hours, it has consumed 1 kWh Energy situation Energy = Power × Time •Example: A nuclear plant has a power capacity of 1 GW ‣After 1 hour, generates 1 GWh of electricity ‣After 1 year, generates 8,760 GWh of electricity ‣NOTE: 8,760 hours per year •Converting from GWh to kWh ‣1 GWh = 1 million kWh ‣Total U.S. electricity in 2011: 4,000 billion kWh Energy situation Energy notation Energy situation Energy notation •MW = megaWatts = 1 million watts •MMBTU = million BTU = thousand, thousand BTU •MMBD = million barrels per day = thousand, thousand barrels per day ‣also sometimes noted “mbd” ‣BOE = “barrel of energy” or “barrel of oil equivalent” ‣MMBDOE = million barrels per day of oil equivalent (an amount of energy) Energy situation Energy notation for natural gas •The energy content of 1,000 SCF of natural gas is approximately 1 million BTU ‣SCF = standard cubic foot ‣MCF = thousand cubic feet (also “mcf” or “Mcf” or “mil”) ‣1,028 BTU per cubic foot ‣1,000 SCF = 1 MCF = 1.028 MMBTU •Price is often given in MCF or MMBTU Energy situation Energy conversion: Tons •A ton is about a tonne •English system: ‣Ton = dry ton = short ton = 2000 lbs •Metric/SI system: ‣Tonne = metric ton = metric tonne = MT = 1,000 kg •1 kg = 2.2 lbs •1 metric ton = 1000 kg = 2200 lbs = 1.1 tons •1 metric ton = 1 tonne = 1.1 tons ‣Only wrong by 10% Energy situation Primary energy demand, 2035 (Mtoe) World Energy Outlook, EIA 2013 Energy situation 2012 Worldwide Per Capita Energy Use Source: International Energy Agency • Graphic: Michael E. Webber, The University of Texas at Austin Energy situation Energy situation Energy use in Indonesia ESDM, Indonesia Energy Outlook 2010 Energy consumption in industry sector Energy situation Energy use in Indonesia ESDM, Indonesia Energy Outlook 2010 Energy consumption in household and commercial sector Energy situation Energy use in Indonesia ESDM, Indonesia Energy Outlook 2010 Energy consumption in household and commercial sector Energy source Primary and secondary energy Energy source Non-renewable energy sources ž Hydrocarbon Supplies: —Coal —Oil —Natural Gas Renewable energy sources ž Renewable Sources —Biomass (Wood, Corn Ethanol, etc.) —Hydro (Dams) —Wind —Geothermal —Solar Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia ž Oil Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia ž Oil Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Natural gas Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Natural gas Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Coal Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Coal Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Renewable energy sources in Indonesia Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Renewable energy sources in Indonesia-Geothermal Energy source Energy sources in Indonesia Renewable energy sources in Indonesia-Geothermal Energy and society Energy flow in society Energy and society Energy flow in society Energy conversion and efficiency Energy conversion First law of thermodynamics •Energy is conserved: the best you can do is break even ‣Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ‣The total energy of an isolated system remains the same. •Energy exists in many forms •Energy forms can be converted from one to another Energy conversion and efficiency Energy exists in many forms •Mechanical (m) ‣Gravitational potential ‣Kinetic •Thermal (t) •Electrical (e) •Radiant (r) •Chemical (c) •Atomic (a) Energy conversion and efficiency Example Energy conversion and efficiency Energy efficiency 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Entropy No system gives you as much back as you put in ‣Losses ALWAYS occur Energy conversion and efficiency Energy efficiency •Efficiency for a process is always <1 •For a system, the overall efficiency is the product of the individual efficiencies within the system ‣NOT the sum of efficiencies ‣NOT the average of efficiencies •Minimizing the number of steps is beneficial Energy conversion and efficiency Energy efficiency