Cellular Respiration
advertisement

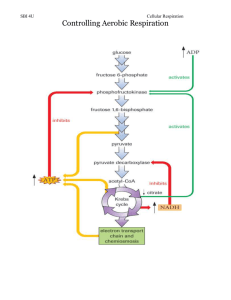
DO NOW •Please go to your testing seats •Pen or Pencil is fine •Good Luck! CELLULAR RESPIRATION OBJECTIVES • SWBAT define Riboflavin and Niacin. • SWBAT identify the inputs and outputs of glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, and ETC CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Aerobic Respiration= NEEDS OXYGEN!! • Occurs in the Mitochondria! • Creates large amounts of energy!! • Process where cells break down glucose to give energy to their cells WHAT YOU NEED…. • 1. Glucose from plants • 2. Oxygen- from breathing!! WHAT YOU GET…. • 1. Carbon Dioxide • 2. Water • ATP CHEMICAL EQUATION!! NADH AND FADH2 (ELECTRON CARRIERS) • FADH2 (Riboflavin) • FADH2 FAD + 2 H+ + 2e- • B2 Vitamin • NADH (Niacin) • NADH NAD+ + H+ + 2e- • B3 Vitamin THE BASIC STEPS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION Step 1: Glycolysis (anerobic) Step 2: Krebs Cycle (aerobic) Step 3: Electron Transport Chain (aerobic) CELLULAR RESPIRATION • 1. Glycolysis: • Occurs in the cytoplasm • We break glucose in half (2 pyruvates) • We make a small amount of ATP (2) • (we made 4 total, but had to use two ATP to break down glucose) • Make NADH (used to make ATP later on) Inputs Outputs 2 ADP 2 ATP 2 NAD+ 2 NADH 1 glucose 2 Pyruvates CELLULAR RESPIRATION • 2. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) • Occurs in mitochondrial matrix • We take the broken glucose (pyruvates) and make more ATP, NADH, and another molecule called FADH2. • The cycle needs to run twice! Why? • We also release CO2 Inputs Outputs 2 Pyruvates 6 CO2 2 ADP 2 ATP NAD+ NADH FAD FADH2 CELLULAR RESPIRATION • 3. Electron Transport Chain • Occurs in the mitochondrial membrane • Takes NADH and FADH2 and makes a lot of ATP (32)!! • Uses Oxygen as a final electron acceptor to make Water Input Output 6 O2 6 H2O 32 ADP 32 ATP NADH NAD+ FADH2 FAD VIDEO! • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fcu_8URp4Ac DO NOW • Label the following structure! C D • Also, Why do we need oxygen? • (Yes, I know to breath but really why? • Grab the worksheet off my desk as well. A B DO NOW • What are the three phases of respiration? • Where does each phase occur? • What happens during each phase? • What is the equation for respiration? DO NOW • Where do we get most of our energy from? • What do we need to get there? • What happens when our bodies we when exercise? • What do you think is causing that to happen? OBJECTIVES • SWBAT compare and contrast alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. • SWBAT design an experiment to try to maximize the amount CO2 produced from fermentation. STAND UP! • Move your arm up and down for three minutes! • Do not stop until the time is up!? • What is happening in your arm? BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES REQUIRE… ENERGY • Moving your arms, like other biological processes, requires energy. • The energy needed is provided by the breakdown of sugars in food to form ATP (cellular respiration) • CR requires Oxygen, but after some time cells are unable to provide the needed amount of oxygen, and lactic acid fermentation occurs. • When lactic acid builds up, the muscles feel sore and fatigued. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? Anaerobic - Does not require Oxygen Aerobic - Does require Oxygen CELLULAR RESPIRATION OCCURS IN TWO MAIN PARTS. Glycolysis Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION • Creates CO2 and Lactic Acid and little energy • Lactic acid is associated with the “burn” associated with heavy exercise • If too much lactic acid builds up, your muscles give out • Occurs in muscles cells, yogurt, and cheese LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Physical conditioning allows your body to adapt to increased activity – The body can increase its ability to deliver oxygen to muscles Long-distance runners wait until the final sprint to exceed their aerobic capacity LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION Inputs Outputs 2 Pyruvates 2 Lactic Acid 2 NADH 2 NAD+ • Ex: • Bacteria that help in making yogurt. • Human muscle cells when out of oxygen. ALCOHOL FERMENTATION • Creates CO2, and ethanol alcohol and little energy. • Occurs in Yeast, Bacteria, Fungus • Used to make beer, wine, and bread • http://www.microbiologybytes.com/video/Scerevisiae.html ALCOHOL FERMENTATION Inputs Outputs 2 Pyruvates 2 Ethonal 2NADH 2 NAD+ 2 CO2 • Ex: • Yeast in wine and beer production. WHY DON’T YOU GET DRUNK OFF BREAD? Take a minute and pair up with the person sitting NEXT to you and discuss this question. DO NOW • Please hand in your labs into the bin. Staple the graph to the back of it. • Then grab the worksheet off my desk, and begin working on it. • Try not to use your notes, (its a last resort!) OBJECTIVES • SWBAT: • Explain the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration • Describe the significance of both processes and how they relate to one another. • Predict what would happen if part of either cycle was compromised. LAB!! DO NOW – LABEL THE AREA THIS HAPPENS • 1. Photosynthesis 5. Chloroplast • 2. Cellular respiration 6. Mitochondria • 3. Glucose 7. Carbon dioxide • 4. Oxygen TRUE OR FALSE 1. The anaerobic pathway that follows glycolysis in the absence of oxygen is fermentation. 2. The hydrogen necessary in the electron transport chain comes from the splitting of carbon dioxide molecules. 3. Cellular respiration in eukaryotes is slightly more efficient than in prokaryotes. 4. The Krebs cycle is sometimes called the TCA cycle or the citric acid cycle. 5. Fermentation occurs in the mitochondria. 6. Skeletal muscle produces lactic acid when the body cannot supply enough oxygen. 7. Alcohol fermentation is found in some bacteria and in humans. 8. The two pyruvate molecules formed during glycolysis result in two Krebs cycles. 9. Electron transport is the first step in the breakdown of glucose.