Human Systems Engineering Concentration

Human Systems
Engineering
Concentration
Amy Bayes
15 October 2014
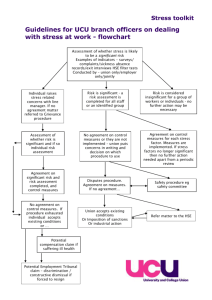
HSE vs HSI
Human Systems Integration (HSI), a DoD-centric term, divides the HSE discipline into 7 distinct domains
A recognized discipline and specifically called out in DoD acquisition guidance and Systems Engineering (SE) standards
Initiated early in the acquisition process and continues throughout the program life cycle (cradle-to-grave)
INCOSE HSI Working Group’s charter is to promote the benefit of placing the proper focus on the role of people in the development and operation of systems
Human Systems Engineers perform HSI
HSI Domains
Human
Factors
Engineering
Manpower Personnel Training
Environmental,
Safety, and
Health
Survivability Habitability
Physical & Mental
Capabilities &
Limitations
Anthropometrics
& Biomedical
Criteria
Human-Machine
Interface
Mission,
Function, &
Human
Requirements
Analysis
Knowledge,
Skills, and
Abilities
Performance
Assessments
Wartime
Requirements
Deployment
Considerations
Force Structure
Operating
Strength
Manning
Concepts
Personnel
Classification &
Selection
Demographics
Accession
Rates
Attrition Rates
Promotion
Rates
Promotion Flow
Retention Rates
Training Flow
Training
Concepts &
Strategy
Based on Task
Analysis
Media/
Equipment
Simulation
OP Tempo
Training System
Evaluation
Training
Development
Plan
System
Safety/Health
Hazards Plan
Human Error
Analysis
System
Reliability
Analysis
Environmental
Considerations
Protective
Equipment
Damage
Control
Systems
Protection
System
Integrity &
Egress
Physical
Environment
Living
Conditions
Physical
Conditioning
Requirements
These domains define human interaction with the system and impact operational effectiveness
HSI in the SE Spiral
User Identification
& Profile
Needs Analysis
Data Collection
Mission Performance
Analysis
Threat Assessment
Operational Needs
Operational Data Collection
Training
Maintenance
User Performance Assessment
Improvement Identification
Lessons Learned
Engineering Measurement Programs
Test & Evaluation
Product Development
& Production
Iterate
Function Analysis/Allocation
Decision Analysis
Cognitive Task Analysis
Benchmarking
Human Performance Model
HMI Requirements
Enabling Science & Technology
Hypothesis, Concept
Development Trade-offs &
Critical Experiments
Modeling and Simulations
Conduct Usability Test
Run Performance Models
Create User Guide
Support Software Development
Build-Test-Build
Process
Prototype Development
Laboratory Demonstration
At-Sea Experiments
HMI Specification
Low Fidelity Prototype
Technology Knowledge Transfer
Key Screen(s) High Fidelity Prototype
Style Guide
Training Development
Team Considerations
Whiting School of Engineering
Systems Engineering Concentration Areas
Project Management
Biomedical Systems Engineering
Information Assurance Systems Engineering
Modeling and Simulation Systems Engineering
Software Systems Engineering
Human Systems Engineering (HSE) http://ep.jhu.edu/graduate-programs/systems-engineering
Purpose
The objective is not to create human factors engineers
The objective is to create systems engineers with a strong understanding of how the human fits into the system and keen judgment to know how to incorporate human systems engineering into the project
The driving force is the desire for a comprehensive Systems Engineering program to produce graduates well versed in the human component of a system
HSE Concentration Core Courses
Foundations of Human Systems Engineering
Provides a broad foundation in the Human Systems Engineering discipline teaching a domain-specific vocabulary
Instructors: Maggie Beecher and Jen McKneeley
Integrating Humans and Technology
Builds on the foundation created in the Core 1 course by teaching the application of Human Systems Engineering concepts/methods to the
Systems Engineering process
Instructors: Bill Fitzpatrick and Kath Straub, PhD
HSE Electives
Social and Organizational Factors in Human-Systems
Engineering
Provides students with the knowledge of organizational structure, social interaction, and group behavior needed to reflect the full context of use in the practice of systems engineering
Instructors: Nathan Bos, PhD and John Gersh
Methods in Human-System Performance Measurement and Analysis
Focuses on human-systems performance measurement (HsPM) methods used to determine whether human-system requirements are met and if the systems’ design provides effective and efficient humansystem performance
Instructors: Maggie Beecher and Carlos Compertore, PhD
Course Offerings
Classroom and online
Spring 2015
Integrating Humans and Technology
Methods in Human-System Performance Measurement and Analysis
Fall 2015
Foundations of Human Systems Engineering
Methods in Human-System Performance Measurement and Analysis