Word
advertisement

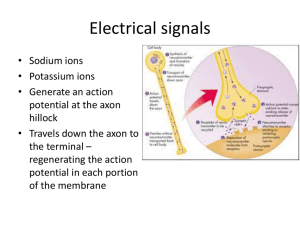
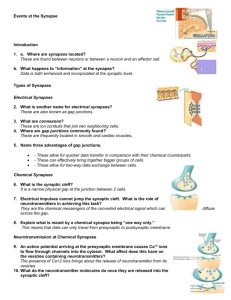
Events at the Synapse Directions: a. Insert your Regulations CD. b. Click the “Contents” button. c. Open the Nervous System File. d. Click Animations. e. Click Events at the Synapse. Introduction 1. a. Where are synapses located? b. What happens to “information” at the synapse? Types of Synapses Electrical Synapses 2. What is another name for electrical synapses? 3. What are connexons? 4. Where are gap junctions commonly found? 5. Name three advantages of gap junctions. - - - Chemical Synapses 6. What is the synaptic cleft? 7. Electrical impulses cannot jump the synaptic cleft. What is the role of neurotransmitters in achieving this task? 8. Explain what is meant by a chemical synapse being “one way only.” Neurotransmission at Chemical Synapses 9. An action potential arriving at the presynaptic membrane causes Ca +2 ions to flow through channels into the cytosol. What affect does this have on the vesicles containing neurotransmitters? 10. What do the neurotransmitter molecules do once they are released into the synaptic cleft? 11. Neurotransmitters cause postsynaptic ion channels to open. Explain how this can lead to either a graded potential or a hyperpolarization. 12. What causes an action potential to be generated? Excitatory and Inhibitory Potentials 13. Opening postsynaptic sodium ion channels cause graded potentials in that membrane. Explain why these are referred to as Excitatory Postsynaptic Membrane Potentials (EPSPs). 14. Opening Cl- or K+ channels on the postsynaptic membrane will generate hyperpolarizations. Explain why these are referred to as Inhibitory Postsynaptic Membrane Potentials (IPSPs). 15. What influence do EPSPs and IPSPs have on whether or not an action potential will be generated at a neuron’s trigger zone? Summation 16. Postsynaptic membrane potentials are summed (combined) and integrated at a neuron’s trigger zone. These membrane potentials come from thousands of synapses from the neuron’s dendrites. a. Define spatial summation. b. Define temporal summation. 17. IPSPs and EPSPs can combine to produce three possible outcomes. Describe what happens with each of the following. a. Hyperpolarization b. Sub-threshold graded potential c. Threshold graded potential