A roller coaster ride is a thrilling experience which involves a wealth
advertisement

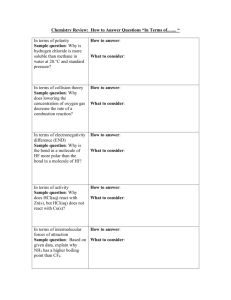
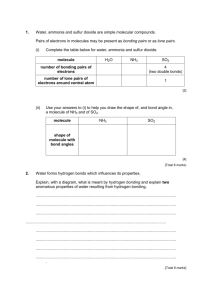
Do Now Name ……………………………………………. Team ………………………. Title: Atomic Chemistry Date ……………………… Draw Lewis dot structures for each of the following **C **Al **Si S **NH3 CO2 *CH4 CaCl2 Rapid Knowledge Name ……………………………………………. Title: Formula Team ……………………… Date ……………………… What is the correct chemical formula for : **Al with Cl **Mg with O **H with O *Mg with SO4- *Ca with SO4 *Li with SO4 H with PO4 Al with CO3- Describe the trends in the Electronegativity found in the periodic table Notes Information Sheet More explaining Diagrams Definitions quotes and smart phrases Equations Key points CFU for lecture 1 A covalent bond contains A covalent triple bond contains A molecule of nitrogen contains Lecture 1 summary Lecture Notes More explaining Diagrams Definitions quotes and smart phrases Key points Equations Practice Name ……………………………………… Title: VSEPR Team ………………………. Date ……………………… Paired work *Write a summary of the key points about VSEPR theory? *Arrange the following in decreasing order of repulsion for bonding pairs and lone pairs: Bp-lp, bp-bp, lp-lp Draw out the structure and write out the standard bond angle CH4 Independent work Draw out the structure and write out the standard bond angle for each of the following shape of molecules ** BF3 PF3 ** H2O ** SF6 * PCl5 * NH3 Exit Ticket 1) ** ** ** Name …………………………………………… Team ………………………. Title:Shapes of molecules Date ……………………… For each of the following compounds, draw lewis structures and then determine the bond angles, and molecular shapes. a) carbon tetrachloride b) BH3 c) silicon disulfide d) C2H2 e) PF3 SiS2 HWK ** Name ………………………………………… Team ………………………. Title:Q numbers and definitions Date ……………………… II. Draw Lewis Structures for the following molecules predict the shapes and the bond angles. PCl3 ** CH4 ** CH3Br * F2O * IBr NH2Cl Deduce the shape of the molecule whose dot and cross diagram is shown above: For the first 5 questions I will provide lewis dot structure and students will have to decide on the shape and the bond angle 3 final questions will require students to draw lewis bond structures and decide on shape and angles The energy of each Bohr orbit is quantized. Molecules of Methane, CH4, ammonia, NH3, water, H2O and hydrogen fluoride, HF The directional nature of covalent bonds is shown in the diagrams of molecules above. The shape of the methane molecule is tetrahedral because the four bonding pairs of electrons repel each other equally, and the equilibrium position of all four bonding electron pairs is tetrahedral. How to work out the Shape of a Molecule It is possible to work out the shape of a small molecule that has a formula XYn by applying a few simple rules. We will use ammonia as an example to illustrate the idea. The Shape of Ammonia, NH3 Rule 1. First find the number of bonding pairs of electrons in the molecule. The number of bonding pairs of electrons in the molecule NH3 can be seen in the formula. There must be three bonding pairs of electrons holding the three hydrogens onto the nitrogen. Rule 2. Find the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer energy level) on an atom of the central atom (The one of which there is only one.) Nitrogen is in group V, so the The Shape of Ammonia nitrogen has five electrons in the outer energy level. Rule 3. Find the number of lone pairs on the central atom by subtracting the number of bonding pairs (3) from the valence electrons (5) to find the number of electrons (2) that will make up lone pairs of electrons. Divide this number by 2 to find the number of lone pairs, 2/2 = 1. Rule 4. Distribute all the electron pairs around the central atom and learn the angles they will make from molecules with no lone pairs. Rule 5. Learn that the repulsion between lone pairs of electrons is greater than the repulsion between bonding pairs, and subtract 2o from the bond angles for every lone pair. Rule 6. Learn the names of the shapes. The shapes are named form the position of the atoms and not the position of the orbitals. Table of Shapes There is one more rule to learn, and it concerns the shape of polyatomic ions. The Shape of Ammonia, NH3 Rule 2a. If the molecule is an ion, e.g. ammonium (NH4+), subtract 1 from the number of valence electrons for every + charge on the ion and add 1 to the valence number for every - charge, then proceed as before. Some more Examples Molecular Shapes & VSEPR (Only consider molecules of 3 atoms or more) Molecular geometry derived from following basic shapes: Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) is able to predict shapes! 1, 2, or 3 pairs of electrons between 2 atoms called electron domain. There are 2 types of domains: 1. BONDING DOMAIN All electrons within a given single, double, or triple bond are in the same domain 2. NONBONDING DOMAIN Pair of electrons associated with a single atom (lone pair) VSEPR Electron Domains Total 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 Bonding Non-bonding 2 3 2 4 3 2 5 4 3 2 6 5 4 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 Molecular Geometry linear triangular-planar bent tetrahedral trigonal pyramidal bent trigonal bipyramidal seesaw T-shaped linear octahedral square-pyramidal square-planar Examples CO2 BeF2 BF3 NO3-1 CCl2 NO2-1 CH4 NH4+1 NH3 CH3-1 H2O NH2-1 PCl5 SF5+1 SF4 IF4+1 ClF3 SF3-1 XeF2 SF2-2 SF6 PCl6-1 BrF5 SF5-1 XeF4 SF4-2