The Great Depression Notes Sheet
advertisement

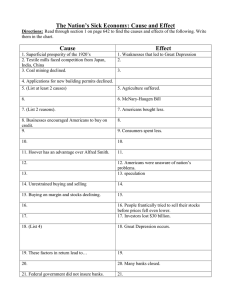
American History 3 The Great Depression Notes Sheet Industries in Trouble: Key Industries such as __________, ___________, and __________ barely made a profit. Coal __________ was especially hit-hard because of new competition for new types of energy emerging. Industries in Trouble Continued: By the 1930's only _________ sources supplied more than half of the energy that used to come from coal. Industries booms of automobiles, construction, and consumer goods started to weaken as well. Construction of new houses steadily declined between 1925-1929. Building permits declined by ____ percent Since the building of houses declined, the need for construction of houses declined so people lost jobs. Farmers Need a Lift: _____________ suffered the worst more than any other part of the economy during the 1920's. Crops such as _________ and _________ (that were in high demand during the war) declined by 50% or more at the conclusion of the war. The McNary-Haugen bill: The government would buy surplus crops, such as wheat, corn, cotton, and tobacco, at guaranteed prices that were higher than the market rate. The government would then sell these crops on the world market for the lower prevailing prices To make up for losses caused by buying high and selling low, the government would place a tax on domestic food sales, thus passing the cost of the farm program along to consumers. Consumers Have Less Money to Spend: Since incomes fell, consumers and families had less money to spend on ________ and __________. Living on Credit: No, many Americans were purchasing goods on a buy now and pay later arrangement that was called __________. These people on credit were on payment plans (that were usually monthly) that also included __________ charges. Uneven Distribution of Income: During the 1920's, nearly half of the nations families earned less than $_________ per year (which was considered amount for a decent standard of living). Families earning _________this much could not afford many of the household products that manufactures produced. Uneven Distribution Continued: Between 1920-1929, the income of the wealthiest 1 percent of the population rose by ____ percent, compared to the ____ percent national average. New President: Hoover wins the election because he was able to point to years of ____________under the Republican Party since 1920. Smith's ___________________________, his religion (Roman Catholicism), and his heavy Brooklyn accent helped lose him the election. Dreams and Riches of the Stock Market: Because of this, Americans rushed to buy stocks and bonds, in this “________ ___________”- A period of rising stock prices. By 1929, about ___ __________ Americans (or ____ percent of the nation’s population) owned stock. Many investors or engaging in, _______________- they bought stocks and bonds on the chance that they might make a quick or large profit, ignoring the risk. Black Tuesday: ____________ ____, _______, known as ___________ ___________, the bottom fell out of the stock market. By min-November, investors had lost ____ __________, an amount equal to American spending in World War I. Causes of the Great Depression _________ ______________- the period from 1929 to 1941, in which the economy was in severe decline and millions of people were out of work. Main Causes of the Great Depression: • An old and decaying industrial base, outmoded equipment made some industries less competitive. • A crisis in the farm sector, farmers produced more than they were able to sell, especially after the end of World War I and the disappearance of markets that the war had opened to them. • The availability of easy credit, many people went into debt by buying goods on the installment plan. • An unequal distribution of income, there was too little money in the hands of working people, who were the vast majority of consumers. Financial Collapse: After the crash, panicked Americans withdrew their money from banks, forcing some banks to close; they could not cover all the withdraws since they had invested in the stock market as well. In 1929, _____ banks shut down. By 1933, nearly ________ banks (or _____-_________ of the nation’s total) had failed. Also, _________ businesses went bankrupt. (Ex: Automobile companies that prospered in the 1920’s.) Unemployment went from ___ _________ (or 1.6 million workers) to ___ _________ (or 13 million workers). One in every four workers did not have a job.