Organizing Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphism: the process that creates metamorphic rocks.
advertisement
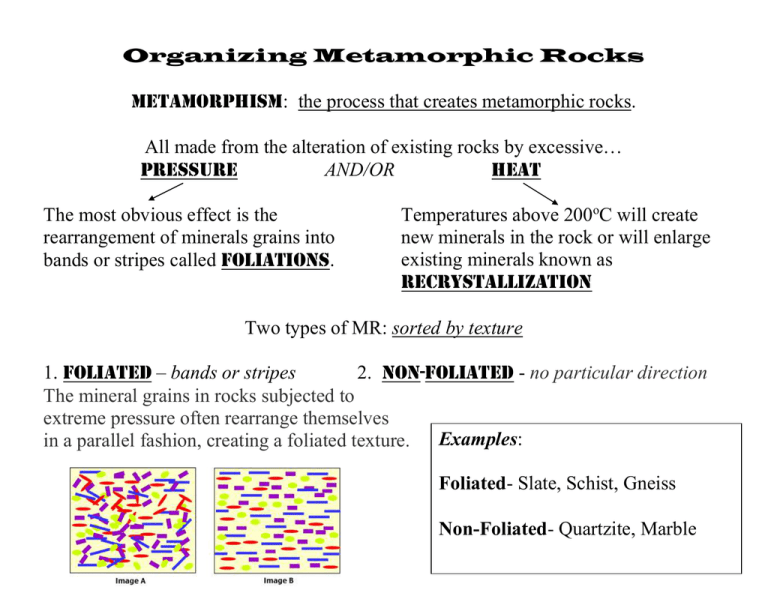
Organizing Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphism: the process that creates metamorphic rocks. All made from the alteration of existing rocks by excessive… pRESSURE AND/OR hEAT The most obvious effect is the rearrangement of minerals grains into bands or stripes called foliations. Temperatures above 200oC will create new minerals in the rock or will enlarge existing minerals known as recrystallization Two types of MR: sorted by texture 1. Foliated – bands or stripes 2. Non-Foliated - no particular direction The mineral grains in rocks subjected to extreme pressure often rearrange themselves in a parallel fashion, creating a foliated texture. Examples: Foliated- Slate, Schist, Gneiss Non-Foliated- Quartzite, Marble How does metamorphism happen? What force has the power to squish & heat rocks until the crystals change? Regional Metamorphism Occurs over large areas (as big as states or countries!) Existing rock will change by the heat and pressure created during mountain building. (A) continents collide (B) ocean crust subducts Contact metamorphism Occurs over small areas. Existing rock is heated when it comes in contact with magma or lava. The lava flow (in gray) seen in this road cut has baked the mud beneath it into brick. (c) 2005 Andrew Alden, licensed to Geology.About.com http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/10g.html The tan rock is the igneous intrusion Diabase. The original host rocks are red siltstones. Contact metamorphism created the gray hornfels. Metamorphic Rocks Come From “Other Rocks” Rock Type Parent Rock Metamorphic Rock SR MR MR MR SR SR IR IR Shale Slate Phyllite Schist Sandstone Limestone Basalt Granite Slate Phyllite Schist Gneiss Quartzite Marble Schist Gneiss