Unit 6 Study Guide KEY - Madison County Schools
advertisement

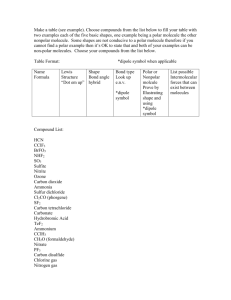
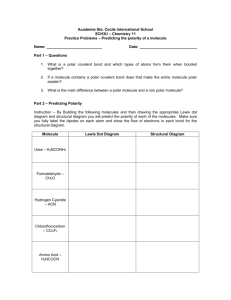
Name: Answer Key Covalent Bonding Study Guide Use the book and notes to answer these questions. You will need to check your answers on Edmodo before you turn this in. 1. How many valence electrons are in the following: Carbon 4 Silicon 4 Chlorine 7 Nitrogen 5 2. What is the name given to the pairs of valence electrons that do not participate in bonding? Lone or unpaired 3. What is the name given to the pairs of valence electrons that do participate in bonding? Shared pair 4. In a covalent bond, electrons are shared between atoms. 5. Which of the following is a covalent molecule (circle one)? LiCl BaO NO2 MgBr2 Writing Formulas for Covalent Compounds 6. Write the formula for the following covalent compounds: Sulfur tribromide SBr3 Dinitrogen tetrachloride N2Cl4 Dihydrogen monoxide H2 O Phosphorus Trihydride PH3 Tetracarbon octahydride C4H8 Nomenclature for Covalent Compounds 7. Name the following covalent compounds: N4O6 tetranitrogen hexoxide SO3 sulfur trioxide SeF4 selenium tetrafluoride PCl5 phosphorous pentachloride XeI4 xenon tetraiodide 8. How many electrons are shared in a single bond? Double bond? Triple bond? Single bond: 2 Double bond: 4 Triple bond: 6 9. Give 2 examples of a diatomic molecule. 10. List 3 properties of covalent molecules. Hydrogen, oxygen, fluorine, Low melting point nitrogen, chlorine, iodine, bromine 2 nonmetals Isn’t soluble 11. In a nonpolar covalent bond, electrons are shared equally. 12. In a polar covalent bond, electrons are shared unequally. 13. Label the partial positive and partial negative charge on the molecule below. 14. Define electronegativity (use the textbook). Ability of an atom to attract electrons 15. Electronegativity determines the type of bond. 16. Draw an example of a polar molecule. 17. Draw an example of a nonpolar molecule. 18. What is an intramolecular force? Provide 2 examples. The forces within a molecule are called intramolecular forces. This includes ionic and covalent bonds. 19. What is an intermolecular force? The forces between 2 molecules are called intermolecular forces. These forces are much weaker than intramolecular forces. 20. Label the intermolecular and intramolecular forces on the figure below: 21. Which force is the strongest, intermolecular or intramolecular? Intramolecular 22. Why are polar molecules “sticky”? Because the partial charges are attracted to one another making them hard to separate. 23. Fill in the chart below: Molecule: F2 Name: fluorine Polar or nonpolar bonds: nonpolar Lewis Structure: Molecule: HCl Name: hydrogen monochloride Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: CCl4 Name: carbon tetrachloride Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: SiO2 Name: silicon dioxide Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: HI Name: hydrogen monoiodide Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: N2H4 Name: dinitrogen tetrahydride Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: CO Name: carbon monoxide Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: CCl4 Name: carbon tetrachloride Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: H2O Name: dihydrogen monoxide Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: Molecule: CO2 Name: carbon dioxide Polar or nonpolar bonds: polar Lewis structure: