Criteria/Job Analysis Slides
advertisement
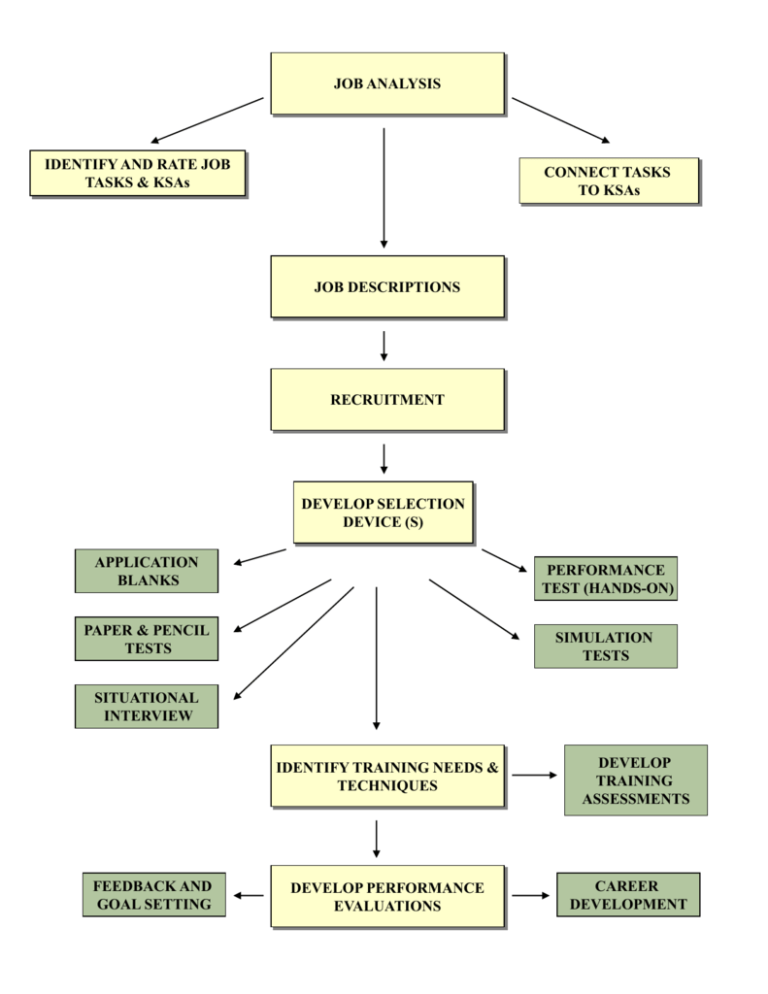
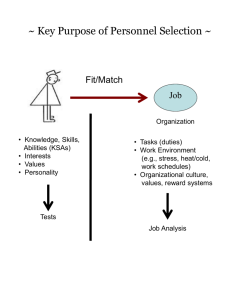
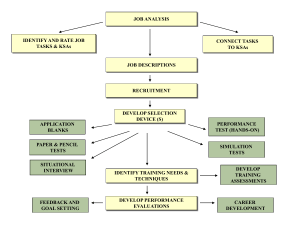
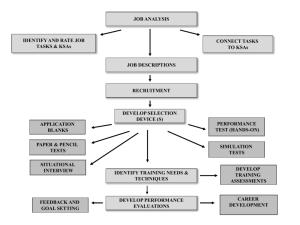
JOB ANALYSIS IDENTIFY AND RATE JOB TASKS & KSAs CONNECT TASKS TO KSAs JOB DESCRIPTIONS RECRUITMENT DEVELOP SELECTION DEVICE (S) APPLICATION BLANKS PERFORMANCE TEST (HANDS-ON) PAPER & PENCIL TESTS SIMULATION TESTS SITUATIONAL INTERVIEW IDENTIFY TRAINING NEEDS & TECHNIQUES FEEDBACK AND GOAL SETTING DEVELOP PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS DEVELOP TRAINING ASSESSMENTS CAREER DEVELOPMENT Job Analysis Example: JOB Task 1 Task 4 Task 2 Task 3 KSAs KSAs KSAs KSAs Key Issues Regarding Conducting a Job Analysis: • Clearly state the purpose of a job analysis • Emphasize the benefits of performing a job analysis • Describe the process to be used (and time commitment) Basic Methods to Collect Job Analysis Information A) Interviews (individual or group) with employees and/or supervisors • Make purpose of the job analysis clear • Interviewers need to be trained • Use a structured format Note: Employees may distort the responsibilities of their job. Supervisor may lack detailed information as to how the job is actually done. B) On-Site Observation • Best used for structured jobs • Need to get a representative sample • Need to be unobtrusive Note: Many suggest that it’s best to observe before conducting interviews. In some cases, observations may not be possible (e.g., safety concerns, union objections). C) Questionnaires (e.g., Position Analysis Questionnaire; PAQ) Note: Cannot clarify questions or follow up on respondents answers (often administered anonymously) Other sources of job analysis information: O*NET, Occupational Outlook Handbook “Typical” Job Analysis Process Develop Task Statements Develop KSA Statements Rate Task & KSA Statements Connect Tasks & KSAs Basic Task Statement Components 1) What is the action being performed? (using an action verb 2) To whom/what is the action directed? (the object, or receiver, of the action verb) 3) How is the action performed? (e.g., use of certain procedures, equipment, tools). 4) Why is the action being performed? (the purpose of the action). Sample Task Statement What? To What/Whom? Inspects (visually or manually) parts, equipment, and systems such as valves, thermostats, filters, motors, pumps, space heating equipment, boilers, generators, incinerators, burner systems, air handling units, and How? piping systems by using calibration equipment hand tools, multi-meters, and temperature and pressure gauges following oral and written instructions (e.g., supervisor Why? directives, operator manuals) in order to comply with maintenance requirements and determine the cause of malfunctions. Sample Task Statements 1) Performs mathematical, algebraic, and geometric computations, such as fractions to decimals, metric units to English, computing ratios and percentages, and calculation of area and volume by using rules, charts, formulas, calculators, and tables in order to maintain a variety of mechanical equipment. 2) Performs a variety of measurements such as motion, forces, temperature, and fluid properties using temperature thermostats, barometers, motion detectors, and pressure gauges in order to obtain a reading. 3) Lifts materials of varying weights and sizes such as pumps, blowers, piping, valves, and rotating and reciprocating equipment by the proper and safe use of hoists, pulleys and rigging accessories in order to set and maintain equipment and avoid personal injury and property damage. 4) Measures objects, shafts, and distances using non-precision and precision instruments such as rulers, inside and outside calipers, micrometers, and dial indicators in order to check for clearances, tolerances, and discrepancies. Sample KSA Statements A) Ability to perform mathematical operations, using a calculator, to compute conversions, ratios, and percentages. B) Ability to select and use a variety of precision and nonprecision measuring instruments. C) Ability to troubleshoot equipment by using an analytical, step-by-step process, standard procedures, and troubleshooting guides. D) Knowledge of mechanical principles, terminology, and equipment E) Ability to read, comprehend, and follow complex written instructions and procedures. F) Ability to transport equipment and supplies weighing up to 100 pounds either manually or with the use of equipment (e.g., hoists, hand trucks) for a distance of 30 feet. . Task Rating Form A Frequency of use 5 = almost all of the time 4 = frequently 3 = occasionally 2 = seldom 1 = not performed at all 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 B C D E Importance of performing successfully 5 = extremely important 4 = very important 3 = moderately important 2 = slightly important 1 = of no importance Importance for new hire Distinguishes between superior & ad performance Damage if error occurs 5 = extremely important 4 = very important 3 = moderately important 2 = slightly important 1 = of no importance 5 = a great deal 4 = considerably 3 = moderately 2 = slightly 1 = not at all 5 = extreme damage 4 = considerable damage 3 = moderate damage 2 = very little damage 1 = virtually no damage KSA Rating Form Importance for acceptable job performance 5 = extremely important 4 = very important 3 = moderately important 2 = slightly important 1 = of no importance A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R Importance for new hire 5 = extremely important 4 = very important 3 = moderately important 2 = slightly important 1 = of no importance Distinguishes between superior & adequate performance 5 = a great deal 4 = considerably 3 = moderately 2 = slightly 1 = not at all TASK -- KSA MATRIX To what extent is each KSA needed when performing each job task? 5 = Extremely necessary, the job task cannot be performed without the KSA 4 = Very necessary, the KSA is very helpful when performing the job task 3 = Moderately necessary, the KSA is moderately helpful when performing the job task 2 = Slightly necessary, the KSA is slightly helpful when performing the job task 1 = Not necessary, the KSA is not used when performing the job task KSA Job Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R Sample Job Evaluation Process Selection of Job Tasks/Duties (Criteria) often via a job analysis Selection of Compensable Factors (e.g., Effort, Skill, Responsibility, Work Conditions) Ratings of Job Criteria on Compensable Factors Job Score (e.g., points) Compensation Job Evaluation Example Job Tasks Compensable Ratings Total Ranking Factors (e.g., 1-5 scale) Score $ Task 1 Effort Task 2 Skill Task 3 Responsibility Task 4 Work Conditions Task 5 110 1 100 2 98 3 88 4 76 5 75 6 67 7 65 8 56 9 43 10 Objective Data Production data --- Key importance to an organization • Individual control and variability • Seasonality • Usefulness for managerial positions Sales --• Comparability (e.g., sales region) • Type of goods being sold; value/worth of goods Turnover (job tenure) --- • Issue of “voluntariness” (e.g., why the person left) • Fired • Better job offer • Quit due to dissatisfaction • Issue of “functionality” (e.g., how well the employee who left was performing. • Evidence that poor employees may voluntarily quit more often than good ones!!! Objective Data (cont.) Absenteeism, Lost time --• Excused versus unexcused; extent of absenteeism (e.g., within allowable limits) • Number of times tardy • Factors impacting absenteeism rates (e.g., incentives, values) Accidents --• Cause of accidents • Definition of accidents • Incentives for safe behaviors (e.g., $$$) Theft --• Percent caught stealing Quality measures --• Number of errors • Number of complaints • Number of returns • Amount of scrap Major Influences on Employee Attendance 3. Personal characteristics Education Tenure Age Sex Family size 7. Ability to Attend: Illness and Accidents Family responsibilities Transportation problems 2. Employee values and job expectations 1. Job Situation: Job scope Job level Role stress Work group size Leader style Co-worker relations Opportunity for advancement 4. Satisfaction with job situation 6. Attendance motivation 8. Employee attendance 5. Pressure to attend: Economic/market conditions Incentive/reward system Work group norms Personal work ethic Organizational commitment R. M. Steers and S.R. Rhodes, “Major Influences on Employee Attendance: A Process Model,” Journal of Applied Psychology, 63 (1978), p. 391-407. Accident Flowchart Supervisor’s Behavior Regarding Safety Physical Condition of Employee Mental Condition of Employee Unsafe Acts by Employee Unsafe Work Conditions Production delays Equipment damage Minor injuries Accidents Disabling injuries Dynamic Criteria Productivity (Sales) by Year 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 • Individual variation is often great across time • More consistency is achieved by using an incentive system and when output is measured over a significant number of occurrences (and over a wide variety of measures) Dynamic Criteria (cont.) Years on job 1 2 Best predictor of performance 3 4 5 6 7 Best predictor of performance • Verbal Ability • Specific work methods • Aptitude Test scores • Co-worker relations Criterion Contamination 1) Knowledge of predictor (test) scores 2) Bias due to group membership (e.g., demographics, reputation of school attended) 3) Bias in ratings (rating scale errors) Expectations, Labeling Supervisor Characteristics (e.g., age, gender, attractiveness, values) Affective Reactions (e.g., liking) Labels Employee Characteristics (e.g., age, gender, attractiveness, values) Supervisor expectations Behavior toward employee Evaluation of performance (memory, process/combine info., attributions) Observation of Performance (selective attention, timing, frequency Employee performance Employee motivation Composite Versus Multiple Criteria Separate Sales Versus Absenteeism Overall Score Tardiness Returns Grades Grades A B A B C B C B Overall GPA • Composites are best for personnel decisions (easy to use and rank) but the separate criteria must be assessing similar things (a common core must exist) • Multiple criteria are best for feedback and training purposes Subjective Performance Criteria (most common type of criteria used) Supervisor judgment regarding employee job performance • Employee ratings using scales (1-5; 1-7 point scales) • Rankings Overlap Between Objective & Subjective Criteria Objective data Subjective data