Advanced Organizational Management Chapter 2
advertisement

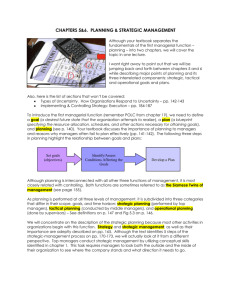
Strategic Planning – Mission and Values Overview Planning is the most important and basic management function Involves setting objectives and then establishing policies, procedures and action plans Strategic planning establishes the direction the organization will take over a long term Involves developing goals for the future that reflect current threats and opportunities Match the strength and weakness of the organization Quality planning identifies the needed resources, both current and future, including space, materials, equipment and human A. Organizational Planning Planning is one of the primary management functions or an organization Planning entails establishing objectives and then setting policies, procedures, and action plans to achieve objectives Types of Planning – four main types: Strategic planning – long term; Tactical planning – short term; Operational planning – day-to-day; Contingency planning – coping with unforeseen A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Strategic planning establishes long-term goals agreed upon by the entire organization Establishes clear parameters for recognizing and achieving success Directs a process of continuous adaptation Formal process of planning to fit the mission and values of the organization Done by upper level management – does not work well without support from the top managers A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Tactical planning – involves setting short-term goals that show how to achieve the broad objectives specified in the strategic plans Operational planning – involves first-line managers conducting day-to-day activities necessary to achieve longer term tactical and strategic goals Contingency planning – involves developing action plans to help organizations cope with any unforeseen events that may arise A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Strategic Planning Process: First steps – first goal is to clarify a vision and a mission of the organization Mission – most broadly stated objective of an organization is called its mission; basic purpose for the organization’s existence! Senior management determines its mission; all managers are responsible for understanding, communicating and implementing the mission Strategy – describes the plan the general or team manager or planner has for using the organization’s resources to achieve a specific objective A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Three levels of strategy: Corporate-level – involves the entire corporate organization (General Motors, for example) Business-level – involves the independent business unit of a larger company (Cadillac, a division of GM) Functional – departments within a business unit can also have goals, objectives, and mission statements (GM engineering group) A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Data Collection and Analyses Crucial to the process of strategic planning Universal approach to analysis is called SWOT analysis SWOT = stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for the organization System used to scan the environment and understand the factors that will affect the strategy designed SWOT analysis is a long-standing technique used by co’s for planning Every aspect of the business is included in the analysis: 1) business activity, 2) goals, 3) resources, 4)weaknesses A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Conducting SWOT Task force engages in a session that looks like brainstorming or a focus group Posting lists of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats Participants vote Leader guides group through discussion of outcome Tabulating the SWOT Internal and external audits – another method used for analyzing a corporation’s strengths and weaknesses Internal audit reviews the mission statement and the degree of success the business mission has had External audit addresses five categories: economic forces, social forces, political forces, technological forces and competitive forces A. Organizational Planning (cont’d) Gap Analysis measures the gap between perception and reality within the organization Other analyses – collected from external and internal sources: government data; business association data; research trends Current trends influencing strategic planning Globalization of the marketplace Technology innovation Security – post 9/11 employment B. Managing the Strategic Plan Formulation of a strategic plan involves the preparation of a mission statement and the formulation of a set of goals that connect the mission to the activity of the organization Objectives = goals: refers to the end results an organization seeks to attain to fulfill the organization’s mission Objectives are the primary management tool for achieving any plan Objectives are measurable and observable Multiple objectives Short-term, intermediate and long-term objectives B. Managing the Strategic Plan (cont’d) Necessary objectives Peter Drucker, noted management theorist, identified eight key areas in which any organization should have specific objectives on which to focus: Market standing Innovation Profitability Productivity Physical and financial resource Managerial performance and development Worker performance and attitude Public responsibility B. Managing the Strategic Plan (cont’d) Action Guidelines Objectives establish WHAT is to be done Action guidelines guide the organization’s employees in how the work is to be performed Policies, procedures and rules Policies are general statements developed by org. mgmt and communicated to managers and supervisors Policies define limits, govern and direct Procedures are sets, or sequences of steps to be followed in performing specific tasks or actions Procedures specify behavior for managers to follow in making decisions B. Managing the Strategic Plan (cont’d) Policy focuses on a wide range of actions or decisions that may be made by organization members at any level of the organization Policy governs = describes the way actions are completed or decisions are made Policy directs = policy statement represents management’s preference or commitments on a subject; subordinates are expected to follow the policy guideline as they exercise authority, make decisions or take actions Procedure = set of steps to be followed in performing a specific task or action B. Managing the Strategic Plan (cont’d) Rule = states exactly what is to be done; most commonly established in matters of health, safety and other areas of importance Duration of plans Strategic – long range Tactical – shorter duration, more specific and objective Operational – responsibility of first-line managers; specific and objective; just a few hours to a few days Contingency – designed to assist the organization in dealing with dynamic environments B. Managing the Strategic Plan (cont’d) Types of plans Standing-use plans – guide regular activity of an organization Procedure guidelines, calendars, report cycles, documents Strategic, tactical, operational, contingency could be considered standing-use plans Single-use plans – cover an activity such as a technology transition, physical move to a temporary location, installation of complex machinery or systemwide software Evaluation of plans – determining success and making adjustments C. Communicating Mission and Values Mission and values of an organization must be communicated throughout the organization Communicating is the process of sharing ideas in such a way that others will understand and be able to use the transmitted information Upper management levels create policy statements Policy statements specify how management and employees will work together in the organizational structure Employees are expected to follow policies; in order to implement policies effectively, procedures must be carefully developed and articulated C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Policies need to be stated and communicated explicitly Formal policies must be written and wording of a written policy cannot be changed by word of mouth Written policy helps new supervisors become more familiar with the company and its established policies quickly Development of companywide policies and procedures manuals help standardize many practices that formerly were hearsay Public and employee relations Public relations policies must be established so that products and services are provided that meet public demand Customers and clients are provided with expected service Marketing practices adhere to requirements of legislation C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Employee relations policies Hiring new employees Training Promoting employees EAPs – special services provide help for employees who are having difficulty with stress, drug abuse, alcoholism, finances or other personal problems Retiring and discharging employees Employee benefits Support of formal authority system – policies and procedures in effect within an organization communicate the expectations of the formal authority system C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Management by Objectives (MBO) – systematic approach to planning and controlling activities whereby superiors and those who report to them (subordinates) collaborate on setting objectives One of the more popular management approaches that begin as a planning process Peter Drucker is generally credited with originating this approach Mutual setting of objectives – employee and supervisor together initiate a set of specific goals for areas of responsibility C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Setting of measurable objectives Regular monitoring and performance evaluation Effectiveness of MBO Some problems or limitations with the use of MBO: Time consuming Top management must support MBO and be involved in it Emphasis on short-term objectives Some individuals are not positively motivated! Managers are reluctant to share the goal-setting process C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Ethics = standards of right and wrong behavior that guide people Common ethical principles generally include: Honesty Fairness Respect for others Nonviolence Helpfulness Code of ethics = actual statement made by corporations stating its ethical views in its mission statements C. Communicating Mission and Values (cont’d) Physicians subscribe to the Hippocratic Oath Stockbrokers have codes against using information that was gained from “insiders” Businesses publish “codes of conduct” Corporate social responsibility Enron scandal – 2001 led to public scrutiny, cynicism and skepticism Public has heightened skepticism about the social responsibility of businesses and corporations Corporations have an ethical responsibility to all of its stakeholders – all persons whom the organization is dedicated to serve