Globalization and Trade PPT
advertisement

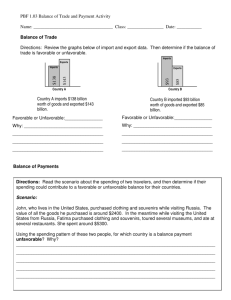
Bellringer • Objective: Analyze how globalization has impacted trade. • Homework: Answer: Do you think that international trade is in general a good thing or a bad thing? Why? • In your groups, find objects in the classroom and locate what country they are made in. – Note: You can use clothing, electronics, toys, notebooks, et cetera—but DO NOT go into anyone else’s stuff! – Using your handout, write the item on the country it derives from. • You have five minutes in your group. The group that comes up with the most items wins! CURRENT EVENTS AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE EQ: How can we explain the impact of current events and globalization on the international economy Objective 9.04: Assess how current events impact decisions made by consumers, producers, and government policy makers. Objective 9.05: Explain the impact on the United States economy of international trade and global products. Objective 9.06: Investigate the ways that domestic and international economies are interdependent. Where do you think these companies are located? Switzerland Japan Great Britain United States Canada United States England The Netherlands Thailand GLOBALIZATION: when countries depend on each other politically and economically Why do countries trade with one another? • International trade helps nations get all the goods they need even though they can only produce a limited amount of goods. • International trade affects our… – Gross Domestic Product (GDP): the goods and services a country produces in a year • The US GDP ONLY includes things produced in the United States! • Determines whether a country is DEVELOPING or DEVELOPED – Consumer Price Index (CPI): measures the average prices of goods and services • How do you think trade affects prices? • How do countries decide which goods to produce? – Comparative advantage: when a country can produce a good or service at a low cost compared to other countries – Things considered in comparative advantage: • Climate • Resources available (land? water?) • What consumers in that country are likely to buy (ex. Can consumers in Ethiopia afford to buy cars? Probably not. So Ethiopia shouldn’t make cars.) What a Developed Country Looks Like… 1.High Energy Consumption 2.More service oriented or industrial jobs 3.Low Infant Mortality Rate What a Less Developed Country Looks Like (LDC)… • Low energy consumption • More agrarian and some industrial • High Infant Mortality Rate Does every country benefit equally from international trade? Import: a good brought in from another country Examples: US Does every country benefit equally from international trade? US Export: a good sent to another country Examples: Does every country benefit equally from international trade? • Trade balance: the relationship between a nation’s imports and its exports • Trade surplus: nation exports more than it imports • Trade deficit: nation imports more than it exports • Favorable balance of trade: a country with a trade surplus • Unfavorable balance of trade: a country with a trade deficit • What sort of balance of trade do you think the US has? • Are all countries with a favorable balance of trade are benefitting from international trade? • Are all countries with an unfavorable balance of trade being hurt by international trade? If a country exports $2.5 billion worth of goods but imports $4.2 billion worth of goods, what sort of balance would this be? • Is this favorable? – Is the country making a profit? • Or is this unfavorable? – Is the country at a loss? Analyze the Chart and Answer Questions • • • • What is this chart comparing? How much does the U.S. export or sell to China? How much does the U.S. import or buy from China? Redefine favorable balance of trade: China-US Interdependence Explained • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T1dDIrOC bUo&feature=related Trade simulation How does the government limit trade? • IMPORT QUOTA: a trade barrier that limits the amount of a good that can be imported • Ex. US has import quotas on sugar to help protect American sugar growers and make sure they’re earning enough $$! How does the government limit trade? • EMBARGO: completely stopping trade with a country – no trade • Ex. US embargo against Cuba—US refuses to trade with Cuba until it develops a democratic government (this is why Cuban cigars are so expensive and rare!) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W50RNAb my3M How does the government limit trade? • TARIFF: a tax on imported good • Ex. Between 2002-2003, US had a tariff on imported steel to help steel-makers in the US earn money! How does the government limit trade? • FREE TRADE: openly trading with other countries • Ex. North American Free Trade Alliance (NAFTA) between Canada, Mexico, and the US—we can trade freely! LEAST LIMITED TRADE MOST LIMITED TRADE Which would you use if you were trying to… • Prohibit trade with another country? • Encourage trade with another country? • Protect American jobs and industries that compete with other countries? Is globalization a positive or negative thing? How has it impacted people around the world? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ruh0O_mj 1v0 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pLwVycO7 Vk&playnext=1&list=PLFA3768BD2A38654D&fe ature=results_main Summarize: Is globalization and interdependence a necessity for our survival? • On the back of your paper, answer the above question in at least 5 sentences. – Be sure to include 3 of the below words: – Interdependence, Quota, China, favorable balance of trade, unfavorable balance of trade, comparative advantage, A look inside the Jean Curtain http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nwMZ2b9hdTY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CCrUZuyZHyk – A look inside the “Denim Curtain”… – Take notes on things that strike you as concerning. – Is globalization a necessary evil?