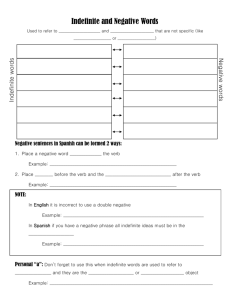
Farm_2 - Івано-Франківський національний медичний
advertisement

Міністерство охорони здоров’я України ДВНЗ «Івано-Франківський національний медичний університет» Кафедра мовознавства База тестових завдань з навчальної дисципліни «Англійська мова» Модуль 2 Фармацевтичний факультет Спеціальність «Фармація» Виберіть англійський еквівалент українського терміну: скарга a) confusion b) self-medication c) complaint d) suffering здуття a) nausea b) bloating c) confusion d) rejection передчуття a) anticipation b) antimicrobal c) fatigue d) suggestability згортання крові a) blood clotting b) bleeding c) blood pressure d) blood circulation сечогінні засоби a) antiemetics b) diuretics c) carminatives d) antihypertensives займатись самолікуванням a) self-medicate b) drug abuse c) self-treat d) drug use живлення a) diet b) indigestion c) nutrition d) back свербіж a) vomiting b) itching c) wheezing d) swelling оцет a) vinegar b) sugar c) fungus d) ether рак a) cancer b) nausea c) bleeding d) cinchona незворотній a) irritable b) vulnerable c) susceptible d) irreversible рідка мазь a) liquid b) lozenge c) liniment d) powder протиалергічні засоби a) antihistamines b) antimicrobal c) antihypertensitive d) anticipation втома a) sleep aids b) fatigue c) confusion d) cough розлад травлення a) dietary supplements b) diuretics c) indigestion d) decongestant зловживання лікарським засобом a) drug addiction b) drug abuse c) drug perception d) drug distribution кора a) bark b) berry c) blossom d) dark розчинність a) solubility b) elasticity c) potency d) efficiency етноботаніка a) etnobotany b) ethnbiology c) ethnopharmacology d) ethnobotanic peчовина a) substance b) portion c) presence d) proportion побічна дія A) intrinsic activity; B) frustration; C) redox reaction; D) adverse reaction. нейтралізувати A) to strain; B) to counteract; C) to release; D) to label. основа A) base; B) potency; C) liberation; D) inhibition. засіб від кашлю A) decongestant; B) carminative; C) antitussive; D) counterirritant. леткий A) volatile; B) dense; C) adequate; D) coincidental. недостатність A) rejection; B) failure; C) confusion; D) defect. свербіж A) suffering; B) tremor; C) swelling; D) itching. фермент A) substance; B) estrogen; C) enzyme; D) fluid. крохмал A) clove; B) starch; C) anise; D) hazelnut. нейтральний A) inert; B) holistic; C) raw; D) viable. окисно-відновна реакція A) redox reaction; B) oxigen reaction; C) oxigen-new reaction; D) renewing reaction. випаровуватися A) to melt; B) to derive; C) to evaporate; D) to boil. щільність A) strength; B) density; C) resistance; D) versatility. обчислювальний A) clinical; B) numeral; C) numerous; D) computational. льодяник A) lollipop; B) ice-pill; C) cold tablet; D) decongestant. хімікат-сирець A) wet chemical; B) raw chemical; C) biochemical; D) indigenous chemical. самолікування A) self-treatment; B) self-management; C) self-control; D) self-medication. мохоподібний A) stem-like; B) angiosperm; C) bryophyte; D) seedless. петрушка A) parsley; B) chamomile; C) peppermint; D) aloe. генетична будова A) genetic building; B) genetic make-up; C) genetic construction; D) genetic composition. відвертач A) abductor; B) adductor; C) flexor; D) extensor. A) regurgitation; B) gnawing; C) vomiting; D) bloating. A) carpus; B) gullet; C) conduit; D) coccyx. B) swelling; C) wound; D) tumour. B) swimming; C) supernatant; D) sticky. B) atrium; C) ventricle; D) apex. B) fatigue; C) plague; D) pallor. B) patella; C) fibula; D) spine. B) pharynx; C) gullet; D) throat. B) lobule; C) lobe; D) part. здуття куприк рана A) injury; плаваючий на поверхні A) biconcave; камера A) chamber; судорога, судома A) cramp; хребець A) vertebra; глотка A) esophagus; долька A) donor; кров A) bile; B) bone; C) urea; D) blood. A) vomiting; B) nausea; C) itching; D) pallor. A) vehicle; B) breach; C) bile; D) amber. C) auricle; D) apex. C) knee; D) thigh. C) sacral; D) lumbar. C) bile; D) peptone. C) vomiting; D) cyanosis. C) hollow; D) viscous. нудота бурштин передсердя A) atrium; B) chamber; щиколотка A) uncle; B) ankle; шийний A) cervical; B) thoracic; жовч A) saliva; B) enzyme; блювота A) bloating; B) nausea; плямистий A) patchy; B) sticky; чутливий a) sensitive b) resisting c) irreversible d) reversible рідина a) lipophilic b) liquid c) liniment d) linolin препарат для пониження кров’яного тиску a) antibacterial b) antiemetics c) antihypertensitive d) anticipation знічення a) sleep aids b) fatigue c) confusion d) insomnia нетрадиційна медицина a) conventional medicine b) аlternative medicine c) modern medicine d) ancient medicine живлення a) enzyme b) supplement c) metabolism d) nutrition діюча речовина a) daughter metabolite b) parent compound c) active ingredient d) organic compound серцевий напад a) heart attack b) heart beating c) heart rate d) heart contractions покращуватися a) to inject b) to interact c) to integrate d) to improve розпад a) disintegration b) dissolving c) dyspepsia d) dysfunction правець A) influenza; B) smallpox; C) whooping cough; D) tetanus. грушоподібний A) pyriform; B) bean-shaped; C) vermiform; D) wedge-shaped. закупорювати розрив A) to coagulate; B) to plug a breach; C) to clot the blood; D) to dress the wound. в’язка рідина A) supernatant liquid; B) serotonin; C) clear water; D) viscous fluid. півмісяцевий клапан A) semilunar valve; B) tricuspid valve; C) mitral valve; D) half month valve. грудна жаба A) angina pectoris; B) thorax frog; C) breast animal; D) frog’s disease. засіб поширення A) amber; B) vehicle; C) phagocytosis; D) viscous fluid. мітральний клапан A) ventricular systole; B) tricuspid valve; C) semilunar valve; D) mitral valve. сприйнятливий a) sensible b) reacting c) susceptible d) irreversible таблетка для смоктання a) ointment b) lozenge c) liniment d) pill протирвотні засоби a) vomiting b) antiemetics c) antihypertensitive d) anticipation безсоння a) sleep aids b) fatigue c) confusion d) insomnia харчові добавки a) dietary supplements b) diuretics c) indigestion d) decongestant звикання до препарата a) drug addiction b) drug disintegration c) drug perception d) drug distribution вихідна сполука a) daughter metabolite b) parent compound c) active compound d) organic compound засіб, що знімає подразнення a) counterirritant b) counterpart c) irritability d) irritation втрата свідомості a) loss of weight b) loss of consciousness c) loss of motion d)l oss of sensitivity самолікування a) self-medication b) self-healing c) self-service d) self-control куприк A) tailbone; B) hip bone; C) breastbone; D) finger bone. жовчний міхур A) jejunum; B) gold bladder; C) cholecystitis; D) gallbladder. двовгнутий A) biconcave; B) minute; C) twice injured; D) two times turned. тристулковий клапан A) mitral valve; B) semilunar valve; C) tricuspid valve; D) cardiac valve. жовчний тракт A) digestive tract; B) biliary tract; C) gastro-intestinal tract; D) gallbladder tract. кашлюк A) smallpox; B) tetanus; C) influenza; D) whooping cough. живлення, пожива A) water depletion; B) waste product; C) nourishment; D) noxious substance. бобоподібний A) ring-shaped; B) bean-shaped; C) wedge-shaped; D) detergent-like. сполука A) substance; B) liquid; C) solid; D) compound. ефір A) amine; B) alcohol; C) tar; D) ether. двоатомний A) monoathomic; B) diatomic; C) a molecule containing a least three atoms; D) a complex unit of various particles. штучно A) artificially; B) readily; C) easily; D) slightly. суглоб A) joint; B) ankle; C) wrist; D) knee. осадок, атмосферний осадок A) transpiration; B) evaporation; C) precipitation; D) transition. випадати в осад A) to precipitate; B) to evaporate; C) to evolve; D) to fall down. фарба, барвник A) lichen; B) dye; C) litmus; D) colour. глитати, ковтати A) to ingest; B) to intend; C) to dispense; D) to supervise. пронос A) cramp; B) hives; C) patch; D) diarrhea. правець A) influenza; B) smallpox; C) whooping cough; D) tetanus. селезінка A) pancreas; B) kidney; C) intestine; D) spleen. медичні банки A) cups; B) glasses; C) mugs; D) sippers. речовина A) equipment; B) substance; C) thing; D) component. вирішувати A) to confirm; B) to promote; C) to realize; D) to decide. тиск крові A) blood pressure; B) blood transfusion; C) blood platelets; D) blood circulation. тіло A) trunk; B) body; C) leg; D) head. психіатрія A) physiology; B) psychiatry; C) psychiatrist; D) psychology. присвячувати A) to devote; B) to discharge; C) to detect; D) to develop. грушоподібний A) pyriform; B) bean-shaped; C) vermiform; D) wedge-shaped. заряд A) grid; B) charge; C) valency; D) decay. нафталінова кулька A) mothball; B) petrolenm ether; C) aromatic solvent; D) paradichlorobenzene. ядро A) neon; B) nitrogen; C) neutron; D) nucleus. крохмаль A) alkali; B) starch; C) cellulose; D) crust. з’єднувати A) to support; B) to combine; C) to reduce; D) to indicate. парá A) vapour; B) pear; C) pair; D) gas. суспензія A) solution; B) solute; C) solvent; D) suspension. лакмус A) lichen; B) dye; C) litmus; D) label. обтяжливий, громіздкий A) cumbersome; B) handsome; C) subtantial; D) unique. рецидив, повторення хвороби A) cramp; B) relapse; C) convalescence; D) resistance. закупорювати розрив A) to coagulate; B) to plug a breach; C) to clot the blood; D) to dress the wound. в’язка рідина A) supernatant liquid; B) serotonin; C) clear water; D) viscous fluid. півмісяцевий клапан A) semilunar valve; B) tricuspid valve; C) mitral valve; D) half month valve. пряме вдихання випарів A) direct inhalation of vapours; B) indirect exhalation of fumes; C) direct inhalation of vapours; D) indirect inhalation of fumes. патентована назва A) brand name; B) trade name; C) proprietary name; D) official name. наліплювати ярлик A) to mark; B) to sign; C) towrite; D) to label. дозрівання плодів і насіння A) aging of fruit and flowers; B) maturing of fruits and seeds; C) ripening of berries and seeds; D) pollination of flowers and seeds. напівчиста суміш A) half-clean mixture; B) semi-clean solution; C) semi-pure mixture; D) half-pure solution. визначити побічну дію A) to identify adverse effects; B) to quantify adverse effects; C) to study deleterious effects; D) to exclude adverse effects. легкий освіжаючий напій A) easy fresh drink; B) light alcohol drink; C) severe refreshment; D) light refreshment. клінічні випробування A) polyclinical analyses; B) clinical trials; C) clinical errors; D) hospital tests. органічний розчинник A) organic solvent; B) organic solution; C) organic mixture; D) organic tincture. схожі властивості A) different properties; B) same features; C) various properties; D) similar properties. грудна жаба A) angina pectoris; B) thorax frog; C) breast animal; D) frog’s disease. засіб поширення A) amber; B) vehicle; C) phagocytosis; D) viscous fluid. мітральний клапан A) ventricular systole; B) tricuspid valve; C) semilunar valve; D) mitral valve. куприк A) tailbone; B) hip bone; C) breastbone; D) finger bone. жовчний міхур A) jejunum; B) gold bladder; C) cholecystitis; D) gallbladder. двовгнутий A) biconcave; B) minute; C) twice injured; D) two times turned. тристулковий клапан A) mitral valve; B) semilunar valve; C) tricuspid valve; D) cardiac valve. жовчний тракт A) digestive tract; B) biliary tract; C) gastro-intestinal tract; D) gallbladder tract. жування A) articulation; B) obstruction; C) percussion; D) mastication. ворітна вена A) hepatic vein; B) superior vena cava; C) portal vein; D) pulmonary vein. шия A) trunk; B) skull; C) neck; D) vertebra. етикетка A) ethics; B) label; C) indication; D) paper. захист A) definition; B) dependence; C) determination; D) defense. переплутати A) to confirm; B) to confuse; C) to control; D) to conclude. кабінет лікаря A) nurses’ room; B) doctor’s consulting room; C) dressing room; D) physiotherapeutic room. верхній A) upper; B) lower; C) middle; D) inner. терапія A) pediatrics; B) therapy; C) dentistry; D) surgery. майбутній A) present; B) future; C) past; D) previous. кровотворення A) hemopoiesis; B) hemostasis; C) coagulation; D) hemorrhage. артеріосклероз A) arteriosclerosis; B) sclerosis diseases; C) angiosclerosis; D) atherosclerosis. реанімація A) rhesus incompatibility; B) exposure; C) treatment; D) resuscitation. зупинка кровотечі A) coagulation; B) hemostasis; C) hemopoiesis; D) hemorrhage. синець, гематома A) bruise; B) burn; C) gangrene; D) hypothermia. луг A) lanthanide; B) layout; C) actinide; D) alkali. розчинність A) solubility; B) refraction; C) polarity; D) piezoelectricity. крихітний A) minute; B) great; C) large; D) second. тверде тіло A) solid; B) liquid; C) vapour; D) gas. прозорий A) tasteless; B) colourless; C) transparent; D) odourless. споживати A) to solve; B) to resolve; C) to consume; D) to contain. випаровуватися A) to evaporate; B) to precipitate; C) to evolve; D) to acidify. хлористий водень A) hydrochloric acid; B) hydrogen chloride; C) potassium hydroxide; D) aqueous medium. патентовані ліки A) proprietary drugs; B) prescription drugs; C) nonprescription drugs; D) potent remedy. зловживання A) relapse; B) misuse; C) overuse; D) poor use. віспа A) whooping cough; B) smallpox; C) measles; D) tetanus. штучний A) sharp; B) artificial; C) natural; D) tremendous. втома A) fatigue; B) drowsiness; C) paleness; D) wakefulness. давати рецидив A) to recur; B) to regurgitate; C) to lodge; D) to recurperate. кашлюк A) hacking cough; B) whooping cough; C) smallpox; D) tetanus. витривалість A) tolerance; B) intolerance; C) expiration; D) inspiration. грудина A) tailbone; B) breastbone; C) hip bone; D) finger bone. акушерство A) gynaecology; B) acute disease treatment; C) acupuncture; D) obstetrics. кіркова кістка A) sesamoid bone; B) cancellous bone; C) cortical bone; D) fractured bone. ворсинки A) vehicles; B) papillae; C) villi; D) appendices. несумісність A) irresistance; B) inability; C) insufficiency; D) incompatibility. дзвоноподібний A) funnel-shaped; B) bean-shaped; C) wedge-shaped; D) ring-shaped. сосочок язика A) tongue papilla; B) vermiform appedix; C) small intestine; D) hydrochloric acid. жовчний міхур A) jejunum; B) bile; C) gallbladder; D) sigmoid colon. скорочення A) obstruction; B) clotting; C) constipation; D) contraction. несумісний A) incompatible; B) inarticulate; C) instable; D) incompetente. переливання крові A) blood group; B) blood platelet; C) blood transfusion; D) blood component. ускладнення A) content; B) cooperation; C) coexistence; D) complication. спостерігати A) to investigate; B) to observe; C) to associate; D) to contribute. кров’яний тиск A) blood supply; B) blood pressure; C) blood corpuscle; D) blood circulation. травлення A) disruption; B) dysfunction; C) digestion; D) disturbance. сонливість A) fatigue; B) drowsiness; C) sleepless; D) resilience. біопсія кісткового мозку: A) functional biopsy; B) bone marrow biopsy; C) biochemical biopsy; D) frozen section biopsy. халькоген A) halogen; B) gallium; C) germanium; D) chalcogen. запах A) odour; B) solubility; C) sublime; D) smell. речовина A) matter; B) particle; C) arrangement; D) argon. густина A) combustion; B) stability; C) density; D) ability. підтримувати A) to support; B) to combine; C) to reduce; D) to indicate. невидимий A) transparent; B) invisible; C) aquatic; D) tasteless. оцет A) vinegar; B) cura; C) lactose; D) acid. гідрооксид натрію A) ammonium hydroxide; B) calcium hydroxide; C) potassium hydroxide; D) sodium hydroxide. розшифровувати A) to decipher; B) to record; C) to intend; D) to consider. пліснява A) fungus; B) mold; C) protozoa; D) bacteria. серцебиття A) heart stroke; B) heart circumference; C) heart flow; D) heart beat. бобоподібний A) bean-shaped; B) button-shaped; C) pear-shaped; D) ring-shaped. легеня A) vein; B) blood; C) heart; D) lung. нудота A) fatigue; B) bleeding; C) nausea; D) weakness. лікування хвороби A) prescription of treatment; B) therapeutic treatment; C) treatment of disease; D) diagnosing of disease. для внутрішнього вживання A) for external use; B) for somebody’s use; C) for internal use; D) for the patient’s use. трави A) powder; B) ointment; C) herbs; D) cups. палата A) palate; B) bedroom; C) ward; D) palace. міряти температуру A) to have a temperature; B) to run a temperature; C) to take a temperature; D) patient’s temperature. передпліччя A) forehead; B) shoulder; C) arm; D) forearm. стравохід A) pharynx; B) esophagus; C) intestines; D) rectum. серце A) heart; B) head; C) hand; D) brain. жувати A) to moisten; B) to pull; C) to chew; D) to cripple. в’язка рідина A) venous liquid; B) viscous fluid; C) whole fluid; D) toxic liquid. залоза A) gland; B) nerve; C) lobe; D) part. переплутати ліки A) to check drugs; B) to confuse remedies; C) to sell medicines; D) to use remedies. живлення A) nutrition; B) function; C) regeneration; D) material. наука A) branch; B) field; C) science; D) study. головний біль A) backache; B) headache; C) stomachache; D) toothache. лікоть A) index; B) elbow; C) ankle; D) thigh. хвороби органів черевної порожнини A) severe diseases; B) abdominal diseases; C) common diseases; D) surgical diseases. спалах A) break out; B) outbreak; C) breakdown; D) break through. полегшувати біль A) to produce pain; B) to relieve pain; C) to control pain; D) to prevent pain. призначення ліків A) taking drugs; B) drug manufacturing; C) administration of drugs; D) dosage of drugs. хірург A) physician; B) practitioner; C) surgeon; D) stomatologist. порожнина A) valve; B) cavity; C) canal; D) duct. кір A) measles; B) malaria; C) mastitis; D) mumps. дослідник A) lecture; B) scientist; C) professor; D) researcher. всмоктування A) dispertion; B) absorption; C) distribution; D) dissemination. живлення A) nutrition; B) excretion; C) liberation; D) distribution. випаровуватись A) to steep; B) to evaporate; C) to brew; D) to strain. азотна кислота A) hydrochloric acid; B) acetic acid; C) sulfuric acid; D) nitric acid. скарга A) complaint; B) complete; C) complex; D) cumbersome. застуда A) cold; B) flu; C) chickenpox; D) malaise. жирова тканина A) hard tissue; B) muscle tissue; C) fat tissue; D) soft tissue. важка форма A) grave form; B) light form; C) easy form; D) good form form. печінкова недостатність A) lung failure; B) kidney failure; C) heart failure; D) liver failure. щока A) neck; B) cheek; C) gum; D) head. атомна вага A) atomic number; B) tabular display; C) atomic weight; D) artificial atom. твердий A) solid; B) liquid; C) diverse; D) tar. частинка A) particle; B) matter; C) proton; D) neon. запах A) lack; B) luck; C) odour; D) taste. отруйний A) insulating; B) poisonous; C) transparent; D) tasteless. співіснувати A) to precipitate; B) to co-exist; C) to cooperate; D) to co-create. однорідний A) appreciable; B) occasional; C) homogeneous; D) varied. соляна кислота A) acetic acid; B) nitric acid; C) sulphuric acid; D) hydrochloric acid. ветеринар A) dog’s doctor; B) cat’s physician; C) venereal disease; D) veterinarian. грибок A) fungus; B) protozoa; C) mold; D) microorganism. Виберіть український еквівалент англійського терміну drowsiness a) нудота b) сонливість с) закреп d) втомлюваність bark a) крохмаль b) стебло c) корінь d) кора potency a) сила b) патент с) опірність d) полярність adverse a) пpoтилежний b) загрозливий для життя с) забарвлений d) агресивний droplets a) свічки b) капсули с) пігулки d) краплі enzyme a) кореневище b) фермент c) виразка d) слиз to contract a) скорочуватися b) затримувати с) руйнувати d) протидіяти bleeding a) звуження b) кровотеча с) блювання d) подразнення liniment a) відвар b) рідка мазь с) настій d) крем volatile a) леткий b) вільний с) подібний d) алергенний solubility A) твердість; B) вологість; C) розчинність; D) щільність. lichen A) лишайник; B) лакмус; C) барвник; D) літій. target A) висновок; B) ціль; C) виділення; D) початок. fungi A) різновиди; B) суміші; C) мікроби; D) грибки. to mature A) доходити зрілості; B) населяти; C) замовляти; D) вирощувати. infusion A) відвар; B) аромат; C) настій; D) лікувальний чай. sleep aid A) снодійний засіб; B) обезболюючий засіб; C) проносний засіб; D) протиалергічний засіб. complaint A) обстеження; B) скарга; C) аналіз; D) опитування. hives A) охриплість; B) застуда; C) вітряна віспа; D) кропив’янка. rash A) тремтіння; B) висип; C) настрій; D) вада. ulcer A) артрит; B) виразка; C) відрижка; D) ензим. fatigue A) нудота; B) набряк; C) нездужання; D) втомлюваність. insomnia A) безсоння; B) сонливість; C) чутливість; D) накопичення. syringe A) посуд; B) пробірка; C) шприц; D) таблетка для смоктання. habitat A) звичка; B) місце поширення; C) мешканець; D) різновид. compatible A) інший; B) величезний; C) суперечливий; D) сумісний. nutrition A) живлення; B) співробітництво; C) необхідність; D) зниження. data A) дата; B) день тижня; C) дані; D) мета. solid A) кислий; B) твердий; C) солений; D) сильний. conductor A) каталізатор; B) резонанс; C) катіон; D) провідник. conduit A) канал; B) двигун; C) сифон; D) обгін. A) ШОЕ; B) ДНК; C) СНІД; D) ВІЛ. A) лінійка; B) оболонка; C) ерозія; D) виразка. B) горло; C) кишечник; D) фермент. B) супінатор; C) згинач; D) розгинач. B) ангел; C) двигун; D) шпигун. B) білок; C) крохмаль; D) жир. B) віспа; C) сказ; D) кашлюк. B) крохмаль; C) білок; D) жир. AIDS lining throat A) стравохід; internal rotator A) пронатор; engine A) ангіна; carbohydrate A) вуглевод; tetanus A) правець; protein A) вуглевод; obstruction A) обертання; B) конструкція; C) закупорка; D) судорога. A) інфекція; B) імплантація; C) імунізація; D) грип. A) печінка; B) гепатолог; influenza hepatitis sinus C) гепатит; D) цироз печінки; A) син; B) синдром; C) судина; D) пазуха. A) доля; B) воля; C) лоб; D) жовч. A) сечовина; B) сеча; C) слина; D) сировина. A) двигун; B) канал; C) пазуха; D) судина. A) опірність; B) огрядність; C) огрубілість; D) кволість. A) твердість; B) пружність; C) близькість; D) опірність. A) судорога; B) емболія; C) закупорка; D) бляшка. A) грудина; B) хребет; C) таз; D) ключиця. A) глотка; B) горло; C) стравохід; D) язик. A) дихання; B) дихати; C) видихати; D) дути. A) нудота; B) накопичення; C) ніс; D) нерв. A) слина; B) сироватка; C) мокрота; D) сік. A) артерія; B) передсердя; C) артеріола; D) аорта. A) суміш; B) поверхня; C) матеріал; D) волокно. A) викачувати; B) з’єднувати; C) всмоктувати; D) виділяти. A) клапан; B) шлуночок; C) вена; D) печінка. A) зв’язка; B) кістка; C) хрящ; D) залоза. A) виділяти; B) включати; C) збільшувати; D) містити. A) судина; B) клітина; C) тканина; D) артерія. A) білки; B) жири; C) вуглеводи; D) солі. lobe urea conduit obesity resilience cramp breastbone gullet breathing nausea saliva arteriole mixture to absorb valve cartilage to contain vessel proteins dental handpiece a) наконечник для бормашини b) щипці для видалення зуба c) підпора для рота d) двигун для бормашини tungsten carbide a) карбід вольфрама b) фтор c) хлорофіл d) мідь measles a) краснуха b) кандидоз c) лейкемія d) кір petroleum jelly a) лізин b) вазелін c) ксилітол d) преднізон blister a) пухир b) набряк c) рана d) опік to plug a) морщитися b) з’являтися c) закупорювати d) видобувати glossitis a) лейкоплакія b) неприємний запах з рота c) сухість в роті d) запалення язика vestibule a) переддвер’я b) вихід c) вуздечка d) язичок hose a) стоматологічний інструмент у формі коня b) світильник c) двигун бормашини d) шланг lead a) свинець b) фтор c) хлорофіл d) мідь prodrome a) ознака, що передує початку b) надокучання c) тривога d) страх flare up a) пухирець b) пухир c) спалах d) опік efficacy a) прискорення b) припинення с) дієвість d) сумісність basicity a) лужність b) розчинність c) кислотність d) чистота resistance a) вибірковість b) токсичність с) опірність d) термостійкість remedy a) вивільнення b) ревматизм с) ліки d) пошкодження bleeding a) кровотеча b) кров с) кровообіг d) кров’яний тиск to heal a)зцілитися b)покращитися c)трапитися d)поранитися hives a)кір b)вітряна віспа с)кропив’янка d)краснуха irritation a)звуження b)закреп с)відторгнення d)подразнення tincture a)настій b)аромат с)екстракт d)краплі dosage a)звикання до препарата b)дозування препарата с)пропорція d)реакція на препарат duct a) протока b) слизова оболонка c) сосочок d) виступ to sip a) піддавати небезпеці b) врізатися c) закупорювати d) пити маленькими ковтками halitosis a) лімфома b) неприємний запах з рота c) надмірна слинотеча d) запалення язика lump a) гуля b) щільність c) ямка d) плямка pubis A) пряма кишка; B) сіднична кістка; C) ободова кишка; D) лобкова кістка. percussion A) вистукування; B) вислуховування; C) виздоровлення; D) виправлення. esophagus A) глотка; B) горло; C) язик; D) стравохід. external rotator A) пронатор; B) супінатор; C) привертач; D) відвертач. ischium A) клубова кістка; B) сіднична кістка; C) променева кістка; D) лобкова кістка. auscultation A) вислуховування; B) вистукування; C) виглядання; D) випинання. exertion A) вправляння; B) напруження; C) виконання; D) кругообіг. ulcer A) пухлина; B) пошкодження; C) виразка; D) припухлість. enzyme A) фермент; B) шлунковий сік; C) соляна кислота; D) жовч. to release a)прискорити b)припинити с)удобрювати d)вивільняти acidity a)випаровування b)розчинність c)кислотність d)чистота to melt a)вибирати b)плавитися с)випаровувати d)діяти adverse a)пpoтилежний b)загрозливий для життя с)забарвлений d)агресивний seedless a)безнасінний b)насінина с)голонасінний d)покритонасінний nausea a)інсульт b)нудота c)сонливість d)запаморчення to counteract a)взаємодіяти b)нейтралізувати с)руйнувати d)кип'ятити constipation a)звуження b)закреп с)відторгнення d)подразнення decoction a) відвар b) аромат с) смак d) всмоктування blood pressure a) кровотеча b) згортання крові с) кровообіг d) кров’яний тиск to pull A) стискати; B) розтягувати; C) перев’язувати; D) спотворювати. ilium A) клубова кістка; B) сіднична кістка; C) лобкова кістка; D) ліктьова кістка. stroke A) стан; B) страйк; C) припадок; D) сонливість. hydrochloric acid A) соляна кислота; B) сірчана кислота; C) луг або основа; D) сірчиста кислота. sacrum A) сідниці; B) грудина; C) крижі; D) сухожилля. bruit A) брутальність; B) шум серця і легень; C) блідість шкіри; D) прискорена пульсація. to contract A) контактувати; B) циркулювати; C) скорочувати; D) виштовхувати. small intestine A) замалий кишечник; B) товстий кишечник; C) тонкий кишечник; D) дванадцятипала кишка. large intestine A) великий кишечник; B) сліпа кишка; C) тонкий кишечник; D) товстий кишечник. cancellous bone A) сітчаста кістка; B) сезамоїдна кістка; C) кіркова кістка; D) ракова кістка. duodenum A) порожня тонка кишка; B) клубова кишка; C) дванадцятипала кишка; D) ободова кишка сигмоподібна. dye a) шприц b) зонд c) щит d) фарба to strike a) затинати b) з’являтися c) затьмарити d) проникати abfraction a) розкришення b) кiста c) стирання d) зношування stain a) виїмка b) пляма c) руйнування d) зрощення burn a) неприємний запах b) обмороження c) опік d) обвітрення liver a) печінка b) стравохід c) легеня d) шлунок blister a) ранка b) пухир c) бляшка d) пошкодження telltale a) слабкий b) зігнутий c) сигнальний d) уразливий radius A) променева кістка; B) ліктьова кістка; C) малогомілкова кістка; D) плечова кістка. medullary cavity A) черевна порожнина; B) кістковий мозок; C) порожнина тіла кіркової кістки; D) мозкова порожнина. to percuss A) вистукувати; B) пульсувати; C) турбувати; D) сифонити. auricle A) шлуночок серця; B) тристулковий клапан; C) вушко передсердя; D) серцевий м’яз. pancreas A) панкреатит; B) підшлункова залоза; C) панкреаталгія; D) панкреатектомія. sesamoid bone A) сітчаста кістка; B) кіркова кістка; C) мозкова порожнина; D) сезамоїдна кістка. to tap A) вистукувати; B) турбувати; C) сифонити; D) виконувати. vascular A) венозний; B) артеріальний; C) судинний; D) капілярний. coagulation A) фагоцитоз; B) кровотворення; C) зупинка кровотечі; D) зсідання. jejunum A) порожня тонка кишка; B) клубова кишка; C) сліпа кишка; D) ободова кишка сигмоподібна. shaft A) тіло довгої кістки; B) діафіз; C) епіфіз; D) мозкова порожнина. femur A) колінна чашечка; B) стегно; C) передплесно; D) плесно. bone marrow a) кістковий мозок b) головний мозок c) слизова оболонка d) перелом кістки herpes labialis a) вірус простого герпеса b) пухирець c) герпес на губах d) вторинний герпес dull a) тупий b) гострий c) нестерпний d) сильний to grind a) заслуговувати b) товкти c) успадковувати d) нахиляти cursory a) поверховий b) букальний c) променевий d) пом’якшувальний dissection a) заміна b) видалення c) зондування d) розтин stiffness of movements a) плавність рухів b) нееластичність рухів c) рухомість зубів d) нерухомість зубів to merit a) проривати b) зневоднювати c) заслуговувати d) видаляти erythroblastosis A) еритроцит; B) червона кров’яна клітина; C) збільшена кількість еритроцитів; D) відсутність еритроцитів. ileum A) сліпа кишка; B) клубова кишка; C) дванадцятипала кишка; D) пряма кишка. bone marrow A) кісткова порожнина; B) кістковий мозок; C) кіркова кістка; D) перелом кістки. physique A) фізик; B) фізіотерапевт; C) фізична культура; D) фізичні дані, статура. superior A) верхній; B) нижній; C) внутрішній; D) зовнішній. atrium A) артерія; B) аорта; C) артеріола; D) передсердя. to siphon A) текти; B) сипати; C) спиняти; D) симулювати. influenza A) запалення; B) застуда; C) грип; D) безсоння. wheezing A) свистяче дихання; B) свербіж; C) набряк; D) кропив’янка. skin rash A) шкірна хвороба; B) тургор шкіри; C) свербіння шкіри; D) висип на шкірі. mucus A) шлунковий сік; B) слиз; C) виразка; D) фермент. healing A) зцілення; B) захворювання; C) заварювання; D) приймання. to respond A) переносити; B) передавати; C) реагувати; D) досліджувати. life-threatening A) життєвий; B) життєвоважливий; C) що захищає життя; D) що загрожує життю. vomiting A) зловживання; B) блювання; C) нудота; D) отруєння. numbness A) оніміння; B) почервоніння; C) чутливість; D) набряк. raw chemical A) хімічна сполука; B) хімічний елемент; C) хімікат-сирець; D) хімічна добавка. coagulation A) закупорка; B) зсідання; C) переливання; D) координація. pyloric sphincter A) кардіальний сфінктер; B) воротарний м’яз-замикач; C) круговий м’яз; D) універсальний м’яз-замикач. duodenum A) тонка кишка; B) товста кишка; C) сигмовидна кишка; D) дванадцятипала кишка. burn A) відмороження; B) опік; C) гіпотермія; D) гематома. to cripple A) критикувати; B) калічити; C) розтягувати; D) скорочувати. upper extremity A) верхня частина; B) верхня щелепа; C) верхня кінцівка; D) верхня порожниста вена. coagulation A) зв’язування; B) живлення; C) поєднання; D) згортання. palpitation A) сонливість; B) блідість; C) синюшність; D) сильне серцебиття. dental engine a) штучна коронка b) водопровідний кран c) шланг d) двигун бормашини copper a) карбід вольфрама b) фтор c) хлорофіл d) мідь lichen planus a) плоский лишай b) дріжджовий грибок c) плоскоклітинна карцинома d) вірус простого герпеса vesicle a) пухирець b) опух c) рана d) опік thrush a) висипка b) подразнення c) пліснявка d) грибок to swab a) брати мазок b) врізатися c) закупорювати d) припиняти dissection a) розтин b) дизінфекція c) проба d) знеболення laterally a) вбік b) вниз c) вперед d) вгору cranial bones A) кістки тазу; B) кістки нижньої кінцівки; C) кістки черепа; D) кістки грудної клітки. frostbite A) синець; B) укус; C) відморожене місце; D) подряпина. impairment A) збільшення; B) покращення; C) запалення; D) розлад. coagulation A) закупорка; B) переливання; C) зсідання; D) зупинка. throat A) глотка; B) горло; C) стравохід; D) грудна клітка. carotid artery A) сонна артерія; B) порожниста вена; C) артеріола; D) мала артерія. benign tumour A) ревматичний поліартрит; B) плазматична мембрана; C) відморожене місце; D) доброякісна пухлина. swollen A) кровоточивий; B) набряклий; C) уражений; D) пошкоджений. vessel A) судина; B) клітина; C) білок; D) переливання. pulmonary vein A) легенева вена; B) ворітна вена; C) яремна вена; D) порожниста вена. vertebral column A) плечовий пояс; B) хребетний стовп; C) грудна клітка; D) лицева кістка. mitral A) тристулковий; B) мітральний; C) мінімальний; D) моментальний. oxygen A) вуглекислий газ; B) кисень; C) речовина; D) повітря. bile A) кров; B) сироватка; C) жовч; D) лімфа. heredity A) спадковість; B) хронічність; C) сповільнена консолідація; D) гіпотермія. tolerance A) толерантність; B) витривалість; C) тривалість; D) тривога. benign tumour A) злоякісна пухлина; B) доброякісна пухлина; C) незначна набряклість; D) значна припухлість. stem cell A) стовбурова клітина; B) червона кров’яна клітина; C) біла кров’яна клітина; D) кров’яна клітина. septum A) верхівка; B) шлуночок; C) клапан; D) перегородка. irritability A) дратівливість; B) сонливість; C) мінливість; D) підступність. diastole A) систола; B) серцевий цикл; C) серцевий м’яз; D) діастола. palpitation A) пальпація; B) потовиділення; C) прискорена пульсація; D) перкусія. heredity A) хворобливість; B) спадковість; C) випадковість; D) тривалість. delayed union A) незрощення; B) неправильне зрощення; C) сповільнена консолідація; D) надмірно швидка консолідація. to label A) відносити до категорії; B) приклеювати; C) пришивати; D) збільшувати кількість еритроцитів. menopause A) менструальний період; B) клімактеричний період; C) чоловіча пауза; D) перша менструальна пауза. detergent-like effect A) очищуюча дія; B) ефект схожий на попередній; C) ефект згортання; D) згортаючи дія. mal-union A) незрощення; B) неправильне зрощення; C) сповільнена консолідація; D) погана реанімація. vena cava A) істина в вині; B) Віденська кава; C) пружна судина; D) порожниста вена. embolism A) емпіричне сприйняття; B) надмірна повнота; C) клімактеричний період; D) закупорка судини. to split A) спльовувати; B) розпадатися; C) вичерпувати; D) звільнятися. gnawing A) постійний ниючий біль; B) переривчастий гострий біль; C) гниття м’яких частин тіла; D) відригування неперетравленої їжі. swelling a) опух b) чутливiсть c) загострення d) дiатез to elicit a) набрякати b) протистояти c) виявляти d) морщитися hereditary a) харчовий b) невiдкладний c) спадковий d) промiжний comprehensive a) всебiчний b) хiрургiчний c) допомiжний d) ручний blemish a) контур b) пляма c) набрякання d) рана to poke a) опухати b) з’являтися c) проникати d) совати ulceration a) виразковiсть b) неправильний прикус c) укус d) обрис burst a) знiмок b) фарба c) спалах d) барвник non-union A) погане зрощення; B) незрощення; C) неправильне зрощення; D) сповільнена консолідація. origin A) місце прикріплення м’яза; B) м’яз-згинач; C) м’яз-розгинач; D) м’яз-відвертач. occlusion A) закриття, закупорка; B) розкриття, роз’єднання; C) судорога, судома; D) огрядність. transfusion A) транслітерація; B) трансляція; C) трансплантація; D) переливання крові. bloating A) блювота; B) здуття; C) нудота; D) синюшність. ulna A) ліктьова кістка; B) променева кістка; C) плечова кістка; D) п’ясток. fertilization a)прискорення b)припинення с)удобрювання d)сумісність purity a)випаровування b)розчинність c)кислотність d)чистота selectivity a)вибірковість b)токсичність с)опірність d)дієвість dye a)помирати b)смерть с)барвник d)лакмус gymnosperm a)безнасінний b)запилений с)голонасінний d)поширений stroke a)інсульт b)настрій c)сонливість d)запаморчення chickenpox a)кір b)вітряна віспа с)алергічний висип d)краснуха constriction a)звуження b)закреп с)відторгнення d)подразнення scent a)настій b)аромат с)смак d)всмоктування blood clotting a)кровотеча b)згортання крові с) кровообіг d)препарат крові expulsion A) вислуховування; B) вистукування; C) виштовхування; D) виздоровлення. stem cell A) стебло; B) стовбурова клітина; C) біла кров’яна клітина; D) осередок. regurgitation A) відригування; B) перфорація; C) рецидив; D) ерозія. starchy A) крохмалистий; B) жирний; C) білковий; D) вуглеводневий. sigmoid colon A) пряма кишка; B) клубова кістка; C) сіднична кістка; D) сигмоїдна кишка. dye A) лакмус; B) фарба; C) помирати; D) пляма. solubility A) м’якість; B) твердість; C) полярність; D) розчинність. inflorescence A) суцвіття; B) квітка; C) листок; D) пелюстка. ether A) спирт; B) ефір; C) амін; D) етил. fungus A) вірус; B) грибок; C) осад; D) дно. lollipop A) цукерка; B) таблетка; C) льодяник; D) свічка. rhizome A) стебло; B) кора; C) кореневище; D) корінь. melting point A) точка плавлення; B) випаровування; C) точка кипіння; D) замерзання. bark A) корінь; B) кора; C) стебло; D) кореневище. scent A) запах; B) цент; C) наука; D) ладан. Виключіть зайве слово з логічного ряду A) muscles; B) triangles; C) ligaments; D) tendons. A) fracture; B) tumour; C) deformity; D) spleen. A) intestinal crypt; C) enzyme; A) cholesterol; B) hydrochloric acid; D) gastric juice. B) bile acid; C) marrow; D) bilirubin. A) progressive disease; C) disease treatment; B) acute disease; D) chronic disease. a) hose c) spit-sink b) worklight d) denture a) fear c) peace b) anxiety d) panic a) pseudomania c) hydrophobia b) tocophobia d) monophobia a) disease c) remedy b) illness d) sickness a) bridge c) denture b) crown d) biopsy a) scratch c) inflammation b) lesion d) patch A) marginal ulcer; C) stress ulcer; B) esophageal ulcer; D) ulcer therapy. A) eosinophiles; C) neutrophiles; B) basophiles; D) thrombocytes. A) paleness; B) pallor; C) rosiness; D) whiteness. A) cranium; B) skull; C) eye; D) head. A) strained ligaments; C) complete healing; B) dislocated joints; D) fractures. A) duodenum; B) jejunum; C) ileum; D) villi. A) sugar; B) glycogen; C) saliva; D) glucose. A) advanced liver cirrhosis; C) liver transplantation; B) progressive liver cirrhosis; D) mild liver cirrhosis. a) premolar b) molar c) incisor d) tooth a) injury b) wound c) damage d) mucus a) tongue b) eye c) cheeks d) teeth a) forward b) downward c) laterally d) immediately a) newborn b) child c) baby d) adult a) severe b) sharp c) blunt d) acute A) peptic ulcer; C) stress ulcer; B) esophageal ulcer; D) ulcer therapy. A) thrombocytes; C) agranulocytes; B) basophiles; D) polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A) vomiting; B) sickness; C) nausea; D) joint pain. A) mandible; B) maxilla; C) jaw; D) ear. A) pulled muscles; C) strained ligaments; B) complete healing; D) broken bones. A) duodenum; C) small intestine; D) villi. B) jejunum; A) sphincter of Oddie; C) smooth muscle; B) ring-shaped muscle; D) pyloric sphincter. A) to cure; C) to treat; B) to heal; D) to be sick. A) to recur; C) to persist; B) to happen again; D) to cease. A) eosinophiles; C) polymorphonuclear leukocytes; B) thrombocytes; D) monocytes. a) dens invaginatus с) carabelli cusp b) periodontitis d) taurodontism a) enamel b) pulp с) dentin d) palate a) gastritis b) glossitis с) pulpitis d) gingivitis a) groove b) stain с) plaque d) spot a) tablet b) lozenge с) pill d) liquid a) root b) crown с) neck d) skin A) desire; B) pain; C) ache; D) hurt. A) eyebrow; C) rib; B) clavicle; D) breastbone. A) Microsoft Windows; C) computed tomography scan; B) X-ray examination; D) magnetic resonance imaging. A) duodenum; B) jejunum; C) large intestine; D) villi. A) fats; B) vitamins; C) minerals; A) to be sick; C) to treat; A) to cease; D) kidneys. B) to cure; D) to restore to health. B) to recur; C) to persist; D) to return. A) agranulocytes; C) thrombocytes; B) lymphocytes; D) monocytes. A) arteries; C) veins; B) kidneys; D) capillaries. a) amphetamine с) xerostomia b) antigistamine d) methamphetamine a) xeromycteria b) xerophyte с) xerosis d) xylitol a) bruxism b) thrush с) moniliasis d) candidiasis a) talon cusp с) carabelli cusp b) dens evaginatus d) supernumemrary roots a) dental caries с) cariology b) tooth decay d) dental cavity a) cancer с) sailography b) malignant tumour d) carcinoma A) ilium; B) ischium; C) pubis; D) humerus. A) flexors; B) extensors; C) adductors; D) legs. A) jejunum; C) villi; A) dermatitis; B) ileum; D) large intestine. B) biliary colic; C) cholecystitis; a) case record c) dental history b) diagnosis d) family history a) forceps c) probes b) mouth prop d) debris D) jaundice. a) stomatitis b) swelling c) sores d) growths a) dental caries b) stomatitis c) measles d) halitosis a) dental examination c) dental handpiece b) dental syringe d) dental engine a) folate c) bur b) lead A) to heal; C) to make well; B) to be sick; D) to alleviate. A) to recur; C) to return; B) to cease; D) to come back. A) to stick; B) to attach; A) myocardium; C) barium; A) humerus; A) abductors; C) to join; d) mercury D) to cut. B) pericardium; D) endocardium. B) femur; C) ulna; D) radius. B) internal rotators; C) arms; D) external rotators. A) large intestine; B) digestion; C) caecum; A) nausea; C) distaste; B) vomiting; D) prevention. A) to make well; C) to be sick; B) to restore to health; D) to alleviate. A) to recur; C) to cease; B) to reappear; D) to come again. A) to cut; D) rectum. B) to stick; C) to join; D) to fuse. A) upper and lower chamber; C) ventricle; B) atrium; D) ear. a) tongue b) palate с) gums d) glands a) hose b) bur с) decay d) faucet a) fear b) pleasure с) phobia d) anxiety a) anodontia b) mitochondria с) oligodontia d) hypodontia a) bite-wing X-rays с) occlusal X-rays b) periapical X-rays d) panoramic X-rays a) toothpaste с) breath freshener b) mouthwash d) bad breath A) carpi; B) metacarpi; C) patella; D) phalanges. A) flexors; rotators. B) kidneys; C) adductors; D) A) large intestine; B) digestion; C) caecum; D) colon. A) urine; C) stool; B) hair; D) excrements. A) to treat; C) to restore to health; B) to make well; D) to be sick. internal A) endoscopy; C) gastric analysis; B) barium contrast X-rays; D) gastric inflammation. A) to connect; B) to cut; C) to join; D) to fuse. A) leg; B) mitral valve; C) septum; D) ventricle. A) tibia; B) humerus; C) radius; D) metacarpi. A) extensors; C) abductors; A) digestion; B) lungs; D) external rotators. B) caecum; C) sigmoid colon; D) rectum. a) dental syringe с) dental handpiece b) dental mirror d) dental pulp a) measles b) tongue с) oral cancer d) leukemia a) mercury b) roof с) bismuth d) folate a) tip b) intestine с) esophagus d) stomach a) surgeon b) physician с) remedy d) nurse a) incision b) punch с) excision d) forward A) abscess; C) diagnosis; A) illness; B) gangrene; D) perforation. B) cure; A) to analyze; C) to get rid of; A) recipient; C) healing; D) therapy. B) to eliminate; D) to eradicate. B) receiver; C) beneficiary; D) donor. A) tricuspid valve; B) arm; C) atrium; D) auricle. A) tarsals; C) phalanges of the toes; B) metatarsi; D) metacarpi. A) esophagus; B) spleen; C) stomach; D) intestine. A) child; B) adult; C) infant; D) baby. A) treatment of the disease; C) salivary gland enlargement; B) breast enlargement in men; D) hair loss. a) adenocarcioma с) melanoma b) lymphoma d) erythema a) oligospermia с) osseous b) oliguria d) oligodactylism a) hose b) faucet с) debris d) bur a) tongue b) tooth с) liver d) palate a) macrodontia с) oligodontia a) stomatitis b) hypodontia d) hyperdontia b) glossitis с) appendicitis A) duodenal ulcer; C) marginal ulcer; B) ulcer therapy; D) stress ulcer. A) leucocytes; C) granulocytes; B) thrombocytes; D) eosinophiles. A) weakness; C) energy; B) fatigue; D) drowsiness. d) pulpitis A) ventricles; B) arterioles; C) venules; D) vessels. A) ulnae; B) carpi; C) fibula; D) phalanges. A) eyes; C) abductors; B) flexors; D) external rotators. A) large intestine; B) digestion; C) sigmoid colon; D) rectum. A) to meet; C) to drink; B) to eat; A) therapy; C) treatment; A) decrease; D) to feed. B) illness; D) rehabilitation. B) reduce; C) diminish; D) increase. A) newborn; B) baby; C) infant; D) adult. a) to treat b) to remove c) to cure d) to heal a) solid b) hard c) firm d) soluable a) seedless c) gymnosperm a) sedative b) angiosperm d) ethnobotanic b) diuretic c) anesthetic a) distribution c) disorientation b) dispersion d) dissemination a) essential oil c) herbal tea b) tincture d) leaf d) allergic A) anterior; B) frontal; C) posterior; D) forward. A) humerus; B) ulna; C) metacarpus; D) tarsals. A) cold injury; B) hypothermia; C) frostbite; D) rupture. A) fundus; B) body; C) antrum; D) brain. A) cholecystitis; C) cirrhosis; B) hepatitis; D) appendicitis. A) healing; B) therapy; C) illness; D) treatment. A) increase; B) decrease; C) lessen; D) decline. A) adult; B) baby; C) infant; D) child. A) semilunar valve; C) mitral valve; B) enlarged vulva; D) tricuspid valve. A) radii; C) metatarsi; B) carpi; D) phalanges. A) papillae; C) fats; B) proteins; D) carbohydrates. A) cardiac sphincter; C) smooth muscle; B) ring-shaped muscle; D) pyloric sphincter. A) surgical intervention; C) kidney failure; B) obstructed bile flow; D) liver encephalopathy. A) bark; B) root; C) stem; D) genus. A) infusion; B) tea; C) decoction; D) pill. A) antitussive; C) drug; B) carminative; D) diuretic. A) brand name; C) chemical name; B) plant name; D) official name. A) herb; C) superconductor; B) catalyst; D) cation. A) hydrochloric acid; C) sulfuric acid; B) nitric acid; D) baking soda. A) remedy; B) medicine; C) medication; D) illness. A) reduce; B) increase; C) diminish; D) decline. A) to invade; B) to maturate; C) to attack; D) to infect. A) atrial systole; C) peristalsis; B) ventricular systole; D) diastole. A) femur; B) patella; C) tibia; A) proteins; B) papillae; C) carbohydrates; D) nutrients. A) folds; B) enzymes; C) wrinkles; D) rugae. A) elderly; B) infant; C) baby; D) newborn. A) illness; C) medication; B) remedy; D) preparation. A) plasma; C) leukocytes; B) erythrocytes; D) thrombocytes. A) liver; B) spleen; C) head; A) atrial systole; B) cardiac cycle; C) diastole; D) humerus. D) kidney. D) peristalsis. A) ulna; B) patella; C) tibia; A) fats; B) carbohydrates; C) papillae; D) fibula. D) nutrients. A) infection; C) hydrochloric acid; B) mucus; D) precursor of pepsin. A) arthritis; C) pneumonia; B) gastritis; D) chickenpox. A) diluting; B) treating; C) healing; D) curing. A) pill; B) placebo; C) tablet; D) droplet. A) penicillin; B) warfarin; C) barbiturate; D) ibuprofen. A) diuretics; B) antiemetics; C) antibiotics; D) vitamin. A) flavour; B) scent; C) odour; D) ether. A) redness of palms; C) curling up of fingers; B) treatment of the disease; D) spiderlike veins in the skin. A) medicine; C) medication; A) potassium; B) water; B) illness; D) preparation. C) calcium; D) iron. A) subtle; B) slight; C) faint; D) obvious. A) arteries; C) arterioles; B) areas; D) capillaries. A) tibia; B) radius; C) fibula; D) tarsals. A) teeth; B) gums; C) palates; D) food. A) gastrin; C) histamine; B) hormone; D) esophagus. A) curling up of fingers; C) treatment of the disease; B) spiderlike veins in the skin; D) breast enlargement in men. A) remedy; C) illness; B) medicine; D) cure. A) red blood cell; C) hemoglobin; B) erythrocyte; D) phagocytosis. A) energy; B) weakness; C) fatigue; D) tiredness. A) venules; B) veins; C) ventricles; D) vessels. A) fibula; B) tarsals; C) carpi; D) metatarsi. A) gums; C) food; A) sweat; B) palates; D) salivary glands. B) collagen; C) protein; D) meat. A) cholecystitis; C) hepatitis; B) cirrhosis; D) myocarditis. A) ulcer therapy; C) gastric ulcer; B) duodenal ulcer; D) marginal ulcer. A) thrombocytes; C) leucocytes; B) white blood cells; D) granulocytes. a) feeling b) suggestion c) sense d) perception a) damage b) harm c) benefit d) injury a) to react b) to respond c) to act d) to reduce a) sedative b) antianxiety c) relaxing d)toxic a) medicine b)remedy c)surgery d)drug a)dangerous b) insecure c)risky d)desired A) weakness; B) energy; C) exhaustion; D) tiredness. A) arteries; B) capillaries; C) veins; D) intestines. A) arteriole; B) vein; C) capillary; D) acid. A) leukocyte; B) erythrocyte; C) thrombocyte; D) bone. A) thoracic; B) rectal; C) lumbar; D) sacral. A) liver; B) spleen; C) failure; D) pancreas. A) pill; B) syrup; C) droplets; D) mucus. A) arnica; C) chamomila; A) facet; B) bark; D) belladonna. B) tisane; C) decoction; D) infusion. A) chickenpox; C) influenza; B) pneumonia; D) toxicity. A) rhizome; C) stem; B) flavour; D) inflorescence. A) vitamins; C) dietary supplements; B) minerals; D) bleeding. A) flexor; B) adductor; C) artery; D) abductor. A) valve; B) trauma; C) burn; D) frostbite. A) spinal column; C) thoracic vertebrae; B) immediate resuscitation; D) pelvic bones. A) tendon; C) cartilage; B) ligament; D) saliva. A) skin surface; C) rhesus-factor; B) blood type; D) blood transfusion. A) stomach; C) esophagus; B) wound; D) small intestine. A) frostbite; B) flexor; C) burn; D) bruise. A) bile; B) biliary tract; C) gallbladder; D) elbow. A) shaft; B) rib; C) diaphysis; D) epiphysis. A) hepatitis; B) jaundice; C) auscultation; D) cirrhosis. A) ilium; B) ischium; A) aortic sound; C) bird sound; A) lack; C) pubis; D) spleen. B) pulmonic sound; D) heart sound. B) deficiency; C) pathology; D) shortage. A) enzyme; C) mucus; B) digestive juices; D) finger. A) carbon dioxide; C) inhalation; B) oxygen; D) liver. A) toxic; C) poisonous; B) life-threatering; D) restorative. A) tiny; B) intolerable; C) small; D) minute. A) bloating; C) confusion; B) nausea; D) constipation. A) mucus; C) stomach acid; B) insulin; D) chickenpox. A) bleeding; C) breathing; B) prevention; D) blood clotting. A) reflux; C) cortisol; B) estrogen; D) thyroid hormone. A) fundus; B) saliva; C) antrum; A) bone marrow; B) sesamoid bone; C) flat bone; D) body. D) long bone. A) leukocyte; C) eyesight; B) thrombocyte; D) erythrocyte. A) lumber vertebrae; C) cervical vertebrae; B) tailbone; D) mandible. A) arteriole; B) energy; C) vein; D) vessel. A) engine; B) mixture; C) suspension; D) solution. A) conduit; C) auscultation; B) electrocardiography; D) percussion. A) respiration; C) hemorrhage; B) bleeding; D) blood leakage. A) juice; B) acid; C) throat; D) pepsin. A) whooping cough; C) tetanus; B) smallpox; D) agglutinin. A) resuscitation; B) frostbite; C) burn; D) bruise. A) skull; B) sternum; C) kidney; D) pelvis. A) delicate; B) tiny; C) microscopic; D) large. A) adductor; C) flexor; A) grind; B) hemostasis; D) internal rotator. B) to masticate; C) to construct; D) to chew. A) myocardial infarction; C) cardiosclerosis; B) jaundice; D) angina pectoris. A) proteins; C) carbohydrates; D) infection. B) fats; A) resuscitation; B) frostbite; C) burn; D) bruise. A) intestine; B) mucus; C) jejunum; D) ileum. A) spleen; B) bladder; C) bone; D) liver. A) atrial systole; C) angina pectoris; B) diastole; D) ventricular systole. A) vomiting; C) itching; A) hemostasis; C) thrombocyte; B) lining; B) leukocyte; D) erythrocyte. D) shivering. A) disease; B) illness; C) disorder; D) treatment. a)seed b)infant c)embryo d)gamete a)tincture b)decoction c)lozenges d)syrup a)family b)class c)kingdom d)relative a)oxygen b)hydrogen c)carbon d)ion a)disintegrate b)break down c)interact d)dissolve a)smell b)flavor c)odour d)sensitivity A) duodenum; B) sigmoid colon; C) rectum; D) pharynx. A) marginal ulcer; C) duodenal ulcer; B) chronic ulcer; D) gastric ulcer. A) cirrhosis C) stomatitis; B) hepatitis; D) Botkin’s disease. A) diaphysis; B) shaft; C) rectum; D) epiphysis. A) humerus; B) ulna; C) radius; D) vertebra. A) lungs; B) stomach; C) duodenum; D) intestine. A) hepatitis; C) cirrhosis; B) ulcer; D) Botkin’s disease. a) antihypertensive c) anticipation b) antihyperglycemic d) antibiotic a) pharmacognosy c) pharmacology b) pharmaceutical chemistry d) pharmacophore a) classification c) distribution b) absorption d) excretion a) ethnobotany c) phytochemistry b) pharmacokinetics d) zoopharmacognosy a) species b) genus c) rhizome d) kingdom a) seedless b) gymnosperm c) angiosperm d) species A) intestine; B) jejunum; C) ileum; D) mucus. A) jaundice; C) anemia; B) leukemia; D) hemorrhage. A) heart; B) atrium; C) stomach; D) ventricle. A) artery; B) infarction; C) capillary; D) vein. A) triangles; B) tendons; C) ligaments; D) cartilages. A) complete healing; C) strained ligaments; B) pulled muscles; D) dislocated joints. A) intestinal crypt; C) enzyme; B) bile; D) gastric juice. A) estrogen; C) testosterone; B) lymph node; D) adrenal hormone. A) hair loss; C) shrinking of testes; B) treatment of the disease; D) abnormal nerve function. A) gastric ulcer; C) ulcer therapy; B) marginal ulcer; D) esophageal ulcer. A) granulocytes; C) thrombocytes; B) eosinophiles; D) basophiles. A) bleeding; B) blood loss; C) hemorrhage; D) blood test. Виберіть правильний варіант пояснення терміну homeopathy a) is a system of chemistry that works on the principle that “like cures like” b) is a system of medicine that works on the principle that “like cures like” c) is a system of medicine that works on the principle that “dislike cures dislike” d) is a system of medicine that works on the principle that “like kills like” drug dose a) a specified quantity of a therapeutic agent prescribed to be taken at one time or at stated intervals b) temporal and spatial distribution patterns of a substance in a bodily system c) the ability of the drug to produce the desired therapeutic effect d) the process of drug producing over the counter drugs a) medicines authorized by pharmacopeias and recognized formularies b) medicines that are patented or controlled by a private organization or manufacturer c) medicines that may be sold directly to a consumer without any prescription form d) medicines that may be sold directly to a consumer with a prescription form antihistamine drugs a) are used to treat allergy b) are used to lower the level of sugar in the blood c) are used to combat infections d) are effective against vomiting and nausea epidemiology a) the science of drugs, including their composition, uses, and effects b) the science of statics applied to the analysis of biological and medical data c) the branch of medicine that deals with the study of causes, distribution and control of disease in population d) science dealing with collection, preparation, and standardization of drugs phytotherapy a) the use of living cells and cell materials to research and produce pharmaceutical products that help treat and prevent human diseases b) the science which studies how plants are used for medicinal properties in various cultures c) the branch of chemistry concerned with plants, their chemical composition and processes d) the use of plants or plant extracts for medicinal purpose molecule a) a substance that contains atoms of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds b) the simplest unit of a chemical compound that can exist, consisting of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds c) a chemical compound that combines with an acid to form a salt and water d) an electrically charged atom or group of atoms sulfate a) a salt of sulfuric acid b) a salt of carbonic acid c) a salt of nitric acid d) baking soda long bones A) very strong, broad at the ends bones found in the thigh, lower leg, and upper and lower arm; B) small, rounded bones resembling a grain of sesame in shape found near joint; the knee cap is the largest example of this type of bone; C) bones found covering soft body parts; these are the shoulder bone, ribs, and pelvic bones; D) bones which have small, irregular shapes found in the wrist and ankle. ossiculoplasty A) a tumour composed of bony tissue; B) pertaining to ribs and vertebrae; C) plastic surgery of auditory bones; D) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition. omoclavicular A) pertaining to the pelvis and clavicle; B) pertaining to the clavicle, neck and skull; C) pertaining to the shoulder girdle and clavicle; D) pertaining to shoulder and hyoid bone. tongue A) the roof of the mouth; B) the organ for containing food and its digestion; C) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; D) any of numerous hairlike vascular processes in the small intestine. cholestasis A) abnormally high blood pressure in the portal vein, the large vein that brings blood from the intestine to the liver; B) a reduction or stoppage of bile flow; C) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells; D) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream. erythrocyanosis A) an apparatus for measuring and counting of red blood cells; B) abnormal bluish pink colour of the skin of shin and thigh; C) a virus that affects red blood cells; D) cyanosis (blue colour) of the red blood cells (the scientific explanation of the expression "blue blood"). ventricle A) lower chamber of the heart; B) upper chamber of the heart; C) the vessel of the human body that carries oxygenated blood; D) the vessel of the human body that carries deoxygenated blood. phlebosclerosis A) hardening and loss of elasticity of the veins; B) origin and development of atheromatous platelets in the inner lining of the arterial wall; C) a fatty deposit on or within the inner lining of the an artery, often causing an obstruction of blood flow; D) a degenerative disease of the arteries characterized by patchy thickening of the inner lining of the arterial walls, caused by deposits of fatty material. short bones A) very strong, broad at the ends bones found in the thigh, lower leg, and upper and lower arm; B) bones which have small, irregular shapes found in the wrist and ankle; C) bones found covering soft body parts; these are the shoulder bone, ribs, and pelvic bones; D) small, rounded bones resembling a grain of sesame in shape found near joint; the knee cap is the largest example of this type of bone. ossification A) a tumour composed of bony tissue; B) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition; C) bony substance formation; D) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones. omohyoid A) a doctor trained to treat shoulder, clavicle and hyoid bone diseases; B) pathologic softening of the shoulder girdle and hyoid bone; C) pertaining to the shoulder girdle and clavicle; D) pertaining to shoulder and hyoid bone. villus A) the roof of the mouth; B) the organ for containing food and its digestion; C) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; D) any of numerous hairlike vascular processes in the small intestine. portal hypertension A) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream; B) the inflammation of the gallbladder; C) the destruction of normal liver tissue that leaves nonfunctioning scar tissue surrounding areas of functioning liver tissue; D) abnormally high blood pressure in the portal vein, the large vein that brings blood from the intestine to the liver. hemodynamics A) blood corpuscle; B) study of the movements of the blood; C) scientific study of red and white blood cells; D) diagnosis by examination of the blood. tricuspid valve A) one-way valve that separates the two chambers of the heart; B) a valve located at the point of origin of the aorta in the left ventricle; C) a valve located at the point of origin of the pulmonary artery in the right ventricle; D) a valve located at the entrance and exit of each ventricle. atherosclerosis A) a degenerative disease of the arteries characterized by patchy thickening of the inner lining of the arterial walls, caused by deposits of fatty material; B) origin and development of atheromatous platelets in the inner lining of the arterial wall; C) a fatty deposit on or within the inner lining of the artery, often causing an obstruction of blood flow; D) hardening and loss of elasticity of the veins. flat bones A) bones which have small, irregular shapes found in the wrist and ankle; B) small, rounded bones resembling a grain of sesame in shape found near joint; the knee cap is the largest example of this type of bone; C) bones found covering soft body parts; these are the shoulder bone, ribs, and pelvic bones; D) very strong, broad at the ends bones found in the thigh, lower leg, and upper and lower arm. cleidocostal A) pertaining to clavicles and ribs; B) pertaining to clavicles and head; C) resection of a baby's clavicle during delivery; D) pertaining to ribs and vertebrae. pyelitis A) plastic surgery on the pelvis; B) inflammation of the pelvis of a kidney; C) inflammation of the kidney and pelvis because of bacterial infection; D) any pelvis disease. kleptomania a) is an irresistible urge to steal items of trivial value b) intense desire to be in open spaces c) compulsion for grinding teeth d) abnormal craving for alcohol introvert a) a person with weight problems b) a person with urgent desire to lie c) a person wholly or predominantly concerned with and interested in one's own mental life d) a person concerned primarily with the physical and social environment intercostals a) situated between the ribs b) situated beneath the ribs c) situated or occurring between cells d) situated or occurring inside a cell or cells hypodontia a) having a small lower jaw b) congenital absence of some of the teeth c) under the tongue d) an abnormally low sensitivity to pain odontalgia a) the arrangement of the teeth in the mouth b) the study of the teeth c) toothache d) congenital absence of some of the teeth gingivitis a) teeth grinding b) inflammation of the mucous lining in the mouth c) inflammation of gums d) dry mouth duodenum A) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; B) the first section of the small intestine between the stomach and jejunem; C) a large, elongated gland: cells islets of Langerhans in the gland produce hormone insulin; D) the largest glandular organ which secretes bile. cholecystitis A) damage to the liver that results from excessive drinking of alcohol; B) the so-called epidemic or infectious hepatitis, an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts; C) the inflammation of the gallbladder; D) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream. hemodiagnosis A) blood corpuscle; B) making a correct diagnosis without taking a blood sample; C) study of the movements of the blood; D) diagnosis by examination of the blood. diastole A) the first phase of short contraction of both atria; B) the second phase of a more prolonged contraction of both ventricles; C) the third phase of alternative contractions of atria and ventricles; D) the period of rest of the cardiac muscle. atheroma A) a fatty deposit on or within the inner lining of the an artery, often causing an obstruction of blood flow; B) origin and development of atheromatous platelets in the inner lining of the arterial wall; C) a degenerative disease of the arteries characterized by patchy thickening of the inner lining of the arterial walls, caused by deposits of fatty material; D) hardening and loss of elasticity of the veins. pseudomania a) craze for starting fires b) mania for money c) irrational fondness of lying d) abnormal craving for alcohol teratoma a) any of various usually malignant tumours that arise in the lymph nodes or in other lymphoid tissue b) tumour consisting of different types of tissue, as of skin, hair, and muscle, caused by the development of independent germ cells c) a dark-pigmented, usually malignant tumour arising from a melanocyte and occurring most commonly in the skin. d) a small benign epithelial tumour, such as a wart, consisting of an overgrowth of cells on a core of smooth connective tissue hoarseness a) a term referring to abnormal voice changes b) the act of expelling air from the lungs suddenly and noisily, often to keep the respiratory passages free of irritating material c) inflammation of the mucous lining in the mouth d) a symptom consisting of the involuntary expulsion of air from the nose glossoplasty a) inflammation of the tongue b) plastic surgery of the tongue c) surgical removal of the tongue d) relating to the tongue and pharynx antiemetic a) a drug that prevents or alleviates nausea and vomiting b) an agent that prevents the clotting of blood c) drugs used in treating high blood pressure d) drugs used to control diabetes mellitus laryngitis a) inflammation of the pulp of a tooth b) inflammation of the tongue c) inflammation of the larynx d) inflammation of the bone due to infection sesamoid bones A) bones found covering soft body parts; these are the shoulder bone, ribs, and pelvic bones; B) small, rounded bones resembling a grain of sesame in shape found near joint; the knee cap is the largest example of this type of bone; C) very strong, broad at the ends bones found in the thigh, lower leg, and upper and lower arm; D) bones which have small, irregular shapes found in the wrist and ankle. cleidocranial A) pertaining to ribs and vertebrae; B) resection of a baby's clavicle during delivery; C) pertaining to clavicles and head; D) pertaining to clavicles and ribs. pyelonephritis A) plastic surgery on the pelvis; B) inflammation of the pelvis of a kidney; C) inflammation of the kidney and pelvis because of bacterial infection; D) any pelvis disease. pancreas A) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; B) the first section of the small intestine between the stomach and jejunem; C) a large, elongated gland: cells islets of Langerhans in the gland produce hormone insulin; D) the largest glandular organ which secretes bile. hypodontia a) permanent tooth development b) absence of tooth development c) excessive tooth development d) lack of some tooth development ectopic enamel a) enamel found in an unusual location b) lack of enamel c) excessive enamel development d) absence of enamel taurodontism a) a condition where the body of the tooth and pulp chamber is enlarged b) a condition where the body of the tooth and pulp chamber is too small c) a condition where the body of the tooth and pulp chamber doesn’t develop d) a condition where the body of the tooth and pulp chamber develops too slowly hypercementosis a) excessive formation of cementum b) absence of cementum c) normal state and quality of cementum d) lack of dental cementum abrasion a) loss of tooth structure due to mechanical forces b) loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution c) gain of tooth structure due to special toothpaste and mouthwash d) inflammation of the tongue and gums xerostomia a) benign tumour in the oral cavity b) inflammation of the pulp c) dry mouth due to lack of saliva d) occasional teeth grinding fatty liver A) damage to the liver that results from excessive drinking of alcohol; B) abnormally high blood pressure in the portal vein, the large vein that brings blood from the intestine to the liver; C) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream; D) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells. hemocyte A) diagnosis by examination of the blood; B) blood corpuscle; C) red blood cell; D) another word for thrombocyte. atrium A) the vessel of the human body that carries oxygenated blood; B) the vessel of the human body that carries deoxygenated blood; C) lower chamber of the heart; D) upper chamber of the heart. atherogenesis A) origin and development of atheromatous platelets in the inner lining of the arterial wall; B) a fatty deposit on or within the inner lining of the an artery, often causing an obstruction of blood flow; C) a degenerative disease of the arteries characterized by patchy thickening of the inner lining of the arterial walls, caused by deposits of fatty material; D) hardening and loss of elasticity of the veins. diaphysis A) each end of a long bone; B) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; C) an area of cartilage tissue in the bone; D) the shaft, or long middle region of a long bone. cleidotomy A) pertaining to clavicles and ribs; B) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones; C) pertaining to clavicles and head; D) resection of a baby's clavicle during delivery. pyelopathy A) plastic surgery on the pelvis; B) inflammation of the pelvis of a kidney; C) inflammation of the kidney and pelvis because of bacterial infection; D) any pelvis disease. liver A) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; B) the first section of the small intestine between the stomach and jejunem; C) a large, elongated gland: cells islets of Langerhans in the gland produce hormone insulin; D) the largest glandular organ which secretes bile. alcoholic liver disease A) the so-called epidemic or infectious hepatitis, an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts; B) abnormally high blood pressure in the portal vein, the large vein that brings blood from the intestine to the liver; C) damage to the liver that results from excessive drinking of alcohol; D) the destruction of normal liver tissue that leaves nonfunctioning scar tissue surrounding areas of functioning liver tissue. cholecystotomy A) the surgical cutting (incision) of the gallbladder; B) the scientific study about gallbladder and liver diseases; C) surgical removal of the gallbladder; D) gallbladder. behavioural treatment a) treatment including different sedative drugs b) treatment including general anesthesia c) treatment that includes teaching individuals relaxation techniques d) treatment that includes teaching patients adequate oral hygiene panoramic x-rays a) examination that shows the entire mouth area on a single x-ray b) examination that shows the entire side of the head c) examination that shows the whole tooth d) examination that shows details of the upper and lower teeth hypalgesia a) an abnormal high sensitivity to pain b) an abnormal high sensitivity to tickling c) an abnormal low sensitivity to tickling d) an abnormal low sensitivity to pain microdontia a) condition where teeth are bigger that the usual size b) condition when a developing tooth incompletely splits into the formation of two teeth c) condition where teeth are smaller than the usual size d) condition in which enamel doesn’t form properly or at all pulpitis a) mortification of the pulp b) inflammation of the pulp c) removal of the pulp d) desensitization of the pulp carcinogen a) any substance producing pain b) any substance producing infection c) any substance producing tumour d) any substance producing anxiety ventricular systole A) the first phase of a very short contraction of one ventricle; B) the first phase of short contraction of both atria; C) the second phase of a more prolonged contraction of both ventricles; D) the period of rest of the cardiac muscle. phlebosis A) pathologic changes in lymphatic vessels; B) pathologic changes in blood vessels of the human body; C) pathologic changes in the veins of non-inflammatory character; D) an apparatus for venous pulse inscription. epiphysis A) each end of a long bone; B) the shaft, or long middle region, of a long bone; C) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; D) an area of cartilage tissue in the bone. cervical vertebrae A) the first seven bones of the spinal column, forming the neck bone; B) the second set of 12 vertebrae; C) the third set of five vertebral bones; D) a fused bone, having been formed from four small bones. pyeloplasty A) plastic surgery on the pelvis; B) inflammation of the pelvis of a kidney; C) inflammation of the kidney and pelvis because of bacterial infection; D) any pelvis disease. gastroenterologist A) a scientific study dealing with the diseases of the stomach and intestine; B) removal of the stomach and intestine; C) a doctor trained to treat the diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; D) inflammation of the stomach and intestine. proctoplasty A) surgical removal of the rectum; B) a special surgical instrument used during proctotomy; C) plastic surgery of the rectum; D) intestinal bleeding. cholecystopathy A) the scientific study about gallbladder and liver diseases; B) the surgical cutting (incision) of the gallbladder; C) any disease of the gallbladder; D) a malignant tumour of the gallbladder and liver in newborns or children. xeroderma a) lip dryness b) skin dryness c) dryness of the mucous membrane of the nose d) dry mouth biopsy a) the removal of vocal cord for diagnostic purposes b) the removal of a sample of tissue for purposes of diagnosis c) surgical removal of the lump d) surgical removal of the lymph nodes mucocele a) containing mucous and pus b) mucous cyst c) of the nature or resembling mucin d) inflammation of the mucous membrane glossoplasty a) plastic surgery of the tongue b) surgical removal of the tongue c) relating to the tongue and pharynx d) paralysis of the tongue bruxomania a) is an irresistible urge to steal items of trivial value b) intense desire to be in open spaces c) compulsion for grinding teeth d) abnormal craving for alcohol lymphoma a) any of various usually malignant tumours that arise in the lymph nodes or in other lymphoid tissue b) tumour consisting of different types of tissue, as of skin, hair, and muscle, caused by the development of independent germ cells c) a dark-pigmented, usually malignant tumour arising from a melanocyte and occurring most commonly in the skin. d) a small benign epithelial tumour, such as a wart, consisting of an overgrowth of cells on a core of smooth connective tissue myocardium A) cardiac contraction; B) endocardium and pericardium; C) cardiac muscle; D) muscle ache. phlebograph A) pathologic changes in the veins of non-inflammatory character; B) an apparatus for heart rate inscription; C) an apparatus for venous pulse inscription; D) an instrument used for measuring the size of the blood vessels. epiphysial plate A) each end of a long bone; B) an area of cartilage tissue in the bone; C) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; D) the shaft, or long middle region of a long bone. thoracic vertebrae A) the first seven bones of the spinal column, forming the neck bone; B) the second set of 12 vertebrae; C) the third set of five vertebral bones; D) a fused bone, having been formed from four small bones. anodontia a) complete lack of tooth development b) permanent tooth development c) excessive tooth development d) partial absence of tooth development macrodontia a) excessive formation of cementum b) excessive formation enamel c) condition where teeth are larger than usual size d) condition where teeth are smaller than usual size xenophobia a) a morbid fear of public places and open spaces b) abnormal fear or dread of water c) a strong feeling of dislike or fear of people from other countries d) an excessive mental preoccupation with one idea fusion a) destruction of two adjacent teeth b) union of two adjacent teeth c) removal of two adjacent teeth d) abnormal size of adjacent teeth erosion a) loss of tooth structure to mechanical forces b) loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution c) prematurely stopped eruption of the tooth d) a condition which results from fused cementum or dentin with the alveolar bone bruxism a) holes in the teeth b) inflammation of gums c) dry mouth d) occasional teeth grinding metacarpi A) upper arm bone; B) five radiating bones to the fingers; C) finger bones; D) wrist bones. craniocerebral A) pertaining to the skull and brain; B) pathologic softening of the skull bones; C) any skull disease; D) the scientific study about skull. proctectomy A) surgical removal of the rectum; B) a special surgical instrument used during proctotomy; C) plastic surgery of the rectum; D) rectum bleeding. cholecystectomy A) the scientific study about gallbladder and liver diseases; B) surgical removal of the gallbladder; C) a malignant tumour of the gallbladder and liver in newborns or children; D) the surgical cutting (incision) of the gallbladder. microdontia a) excessive formation of cementum b) excessive formation of enamel c) condition where teeth are larger than usual size d) condition where teeth are smaller than usual size odontalgia a) gum ache b) toothache c) tooth destruction d) gum destruction ostalgia a) fracture of the bone b) structure of the bone c) pain in the bone d) science that studies bones dentition a) arrangement of teeth b) teeth disorder c) treatment of teeth d) teeth examination melting a) changing a solid substance into a liquid. b) changing a solid substance into steam. c) changing a liquid substance into solid. d) changing a solid substance into powder. liberation a) the process of drug compatibility with other chemicals. b) the process of drug release from the dosage form. c) the process of drug solubility in water. d) the process of drug producing. phytotherapy a) the use of plants for medicinal purposes. b) the use of organisms found in the sea for medicinal purposes. c) the study of plants usage in different cultures for medicinal purposes. d) the study of animal ability to restore their health. antimicrobal drugs a) are used to improve sleeping . b) are used to lose weight. c) are used to combat viral, fungal and parasitic infections. d) are used to treat allergy. oxide a) the amount of present oxygen. b) any compound of oxygen with another element. c) any compound of the air. d) a free atom of oxygen. thermoelectricity . a) the study of relationship between heat and electrical energy. b) the study of heat measurement. c)the study of electrical properties. d) the study of relationship between heat and magnetism. flower a) a flat green organ of photosynthesis on the stem. b) a protective layer of dead cells on the outside of woody plants. c) the reproductive structure of angiosperm plants. d) the organ located in the ground , nourishing the whole plant. arthralgia a)the study and treatment of the joints. b)neuralgic pain in a joint or joints. c)inflammation of the joints. d)surgery on joints. osteoplasty a) plastic surgery of the bone b) plastic surgery of the gums c) plastic surgery of the jaw d) plastic surgery of the tongue abfraction a) correcting of tooth structure from flexural forces b) diagnosis of tooth structure from flexural forces c) treatment of tooth structure from flexural forces d) loss of tooth structure from flexural forces atrial systole A) the elasticity of the arteries; B) the first phase of short contraction of both atria; C) the second phase of a more prolonged contraction of both ventricles; D) the period of rest of the cardiac muscle. tachyarrythmia A) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is lower than 60 beats per minute; B) tachy- and bradycardia attack alternations in the syndrome of sinus nod failure; C) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is higher than 100 beats per minute; D) the heart rhythm that is in the limits of 60 up to 100 beats per minute. periosteum A) each end of a long bone; B) an area of cartilage tissue in the bone; C) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; D) the shaft, or long middle region, of a long bone. lumbar vertebrae A) the first seven bones of the spinal column, forming the neck bone; B) the second set of 12 vertebrae; C) the third set of five vertebral bones; D) a fused bone, having been formed from four small bones. tisane A) herbal extract made from hard parts of plants; B) alcohol extract made of plants; C) herbal infusion made from leaves of the tea bush; D) tincture made from leaves and other parts of plants. pharmacy A) a plant where drugs are manufactured; B) study of physiological effects of drugs on the body; C) science dealing with collection, preparion and standardization of drugs; D) a clinical department where drug addicts are treated. root A) part of a plant keeping leaves and flowers; B) organ that anchors the plant in the ground, absorbs water and mineral salts; C) organ which gives fruit; D) part of the leaf system of the plant. decoction A) a method to brew herbal tea from tougher, denser medicinal herbal materials like roots, bark and berries; B) a method to brew herbal tea from volatile oils, that are readily dissolved in water or release their active ingredients in oil; C) alcohol-based derivative of a fresh herb or another natural plant material; D) concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds. side effects A) efficacy of the medicine; B) the ability of the drug to produce the desired therapeutic effect; C) problems that occur when treatment goes beyond the desired effects; D) the ability of the drug to bind to a receptor. diuretic A) a drug making body sweat; B) a drug making body produce more urine; C) a drug controlling the level of sugar; D) a drug that reduces secretion of acids in the stomach. chemical name A) used in everyday life; B) chosen by the pharmaceutical company; C) assigned by the official body; D) describes atomic and molecular structure of the drug. marine pharmacognosy A) study of chemicals derived from marine organisms; B) medicinal use of plant extracts; C) study of traditional use of plants for medical purposes; D) synthesis of natural bioactive molecules using biotechnology. phalanges A) upper arm bone; B) five radiating bones to the fingers; C) finger bones; D) wrist bones. craniomalacia A) pertaining to the skull and brain; B) pathologic softening of the skull bones; C) any skull disease; D) the scientific study about skull. proctorrhagia A) surgical removal of the rectum; B) a special surgical instrument used during proctotomy; C) plastic surgery of the intestine; D) rectum bleeding. melting a) changing a solid substance into a liquid. b) changing a solid substance into steam. c) changing a liquid substance into solid. d) changing a solid substance into powder. liberation a) the process of drug compatibility with other chemicals. b) the process of drug release from the dosage form. c) the process of drug solubility in water. d) the process of drug producing. phytotherapy a) the use of plants for medicinal purposes. b) the use of organisms found in the sea for medicinal purposes. c) the study of plants usage in different cultures for medicinal purposes. d) the study of animal ability to restore their health. antimicrobal drugs a) are used to improve sleeping . b) are used to lose weight. c) are used to combat viral, fungal and parasitic infections. d) are used to treat allergy. oxide a) the amount of present oxygen. b) any compound of oxygen with another element. c) any compound of the air. d) a free atom of oxygen. cholecyst A) gallbladder; B) urinary bladder; C) surgical removal of the urinary bladder; D) the surgical cutting (incision) of the gallbladder. heart A) the part of the human body linked with the trunk by the neck; B) the upper limb of the human body; C) a hollow muscular organ located in the centre of the chest; D) a hollow bean-shaped organ located in the upper part of the abdomen. bradytachycardia A) the heart rhythm that is in the limits of 60 up to 100 beats per minute; B) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is higher than 100 beats per minute; C) tachy- and bradycardia attack alternations in the syndrome of sinus nod failure; D) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is lower than 60 beats per minute. articular cartilage A) a thin layer of cartilage at the ends of long bones; B) also called spongy bone, found in the epiphyses of long bones and in the middle portion of most other bones an area of cartilage tissue in the bone; C) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones and chiefly around the diaphysis of long bones; D) the cavity containing yellow bone marrow. coccyx A) the first seven bones of the spinal column, forming the neck bone; B) the second set of 12 vertebrae; C) the third set of five vertebral bones; D) a fused bone, having been formed from four small bones. femur A) thigh bone; B) kneecap; C) largest of two lower bones of the leg; D) smaller of two lower leg bones. craniopathy A) pertaining to the skull and brain; B) pathologic softening of the skull bones; C) any skull disease; D) the scientific study about skull. proctotome A) surgical removal of the intestine; B) a special surgical instrument used during proctotomy; C) plastic surgery of the rectum; D) rectum bleeding. hepatopathy A) the scientific study about liver diseases; B) a malignant tumour of the liver in newborns or children; C) any disease of the liver; D) a specialist in liver diseases. otorrhagia A) hemorrhage from the eye; B) hemorrhage from the ear; C) escape of pus from the eye; D) escape of blood from the nose. bradyarrythmia A) normal heart rhythm; B) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is higher than 100 beats per minute; C) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is lower than 60 beats per minute; D) the heart rhythm that is in the limits of 60 up to 100 beats per minute. cortical bone A) a thin layer of cartilage at the ends of long bones; B) also called spongy bone, found in the epiphyses of long bones and in the middle portion of most other bones; C) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones and chiefly around the diaphysis of long bones; D) the cavity containing yellow bone marrow. hip bone A) a large bone that supports the trunk of the body and articulates with the leg bones and sacrum; B) the uppermost and largest portion of the pelvic girdle; C) the posterior part of the pelvic girdle; D) the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. patella A) thigh bone; B) kneecap; C) largest of two lower bones of the leg; D) smaller of two lower leg bones. tisane A) herbal extract made from hard parts of plants; B) alcohol extract made of plants; C) herbal infusion made from leaves of the tea bush; D) tincture made from leaves and other parts of plants. pharmacy A) a plant where drugs are manufactured; B) study of physiological effects of drugs on the body; C) science dealing with collection, preparion and standardization of drugs; D) a clinical department where drug addicts are treated. root A) part of a plant keeping leaves and flowers; B) organ that anchors the plant in the ground, absorbs water and mineral salts; C) organ which gives fruit; D) part of the leaf system of the plant. decoction A) a method to brew herbal tea from tougher, denser medicinal herbal materials like roots, bark and berries; B) a method to brew herbal tea from volatile oils, that are readily dissolved in water or release their active ingredients in oil; C) alcohol-based derivative of a fresh herb or another natural plant material; D) concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds. side effects A) efficacy of the medicine; B) the ability of the drug to produce the desired therapeutic effect; C) problems that occur when treatment goes beyond the desired effects; D) the ability of the drug to bind to a receptor. diuretic A) a drug making body sweat; B) a drug making body produce more urine; C) a drug controlling the level of sugar; D) a drug that reduces secretion of acids in the stomach. chemical name A) used in everyday life; B) chosen by the pharmaceutical company; C) assigned by the official body; D) describes atomic and molecular structure of the drug. marine pharmacognosy A) study of chemicals derived from marine organisms; B) medicinal use of plant extracts; C) study of traditional use of plants for medical purposes; D) synthesis of natural bioactive molecules using biotechnology. craniology A) pertaining to the skull and brain; B) pathologic softening of the skull bones; C) any skull disease; D) the scientific study about skull. enteritis A) inflammation of the stomach and intestine; B) any renal disease; C) any disease of the stomach; D) intestinal inflammation. hepatologist A) any disease of the liver; B) the scientific study about liver diseases; C) a doctor trained to treat gallbladder diseases; D) a specialist in liver diseases. hemorrhage A) escape of blood from the blood vessels; B) escape of blood exclusively from arteries; C) escape of urine from urinary bladder; D) escape of lymph from lymphatic vessels. bradyuria A) pathologic cardiac rhythm that is lower than 60 beats per minute; B) pathologically quick urea discharge; C) pathologically slow urea discharge; D) pathologically painful urea discharge. cancellous bone A) a thin layer of cartilage at the ends of long bones; B) also called spongy bone, found in the epiphyses of long bones and in the middle portion of most other bones; C) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones and chiefly around the diaphysis of long bones; D) the cavity containing yellow bone marrow. ilium A) a large bone that supports the trunk of the body and articulates with the leg bones and sacrum; B) the uppermost and largest portion of the pelvic girdle; C) the posterior part of the pelvic girdle; D) the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. tibia A) thigh bone; B) kneecap; C) largest of two lower bones of the leg; D) smaller of two lower leg bones. scoliosis A) inflammation of the spinal vertebrae; B) normal regular position of the spine; C) a doctor trained to treat people with his spine curved; D) an abnormal curvature of the spine. enteropathogen A) inflammation of the stomach and intestine; B) any intestinal disease; C) microorganism causing intestinal diseases; D) removal of the stomach and intestine. hepatoma A) a tumour of the gallbladder and liver; B) any disease of the liver; C) a specialist in liver diseases; D) a malignant tumour of the liver. thromboplastinopenia A) too large quantity of thrombi in the blood; B) deficiency of red blood cells in the blood; C) lack of any kind of thrombi in the arteries and veins of the human body; D) deficiency of thromboplastin in the blood. inorganic chemistry A) the scientific study of the strucutre of substances and the way they react with other substances; B) the branch of chemistry concerned with the properties and behaviour of inorganic compounds; C) the chemistry of carbon compounds; D) the branch of chemisrty concerned with the properties and behaviour of organic compounds. sodium A) a chemical element that is silver-white metal, usually found combined with other chemicals; B) a metallic element which burns with a bright white flame; C) a red-brown metallic element; D) a heavy grey metallic element. microorganism A) bacteria causing diseases; B) an organism that can be easily seen without a microscope; C) an organism growing on plants or on decaying matter; D) an organism that can be seen only with the help of microscope and that typically consists of only one cell. nonprescription drugs A) drugs which are considered safe for use only under medical supervision; B) drugs which are considered safe for use without medical supervision; C) drugs used for diagnosis, cure, relief, treatment or prevention of the disease or intended to affect the structure or function of the body; D) an organic compound present in food and essential for normal nutrition. pneumonia A) a polygenic disease characterized by abnormally high glucose levels in the blood; B) an acute or chronic disease marked by inflammation of the lungs, especially an infectious disease caused by viruses, bacteria or other pathogens; C) a highly contagious, often epidemic viral disease characterized by fever, muscular aches and pains and inflamation of respiratory passages; D) acute or chronic inflammation of one or more joints, usually accompanied by pain and stiffness. estrogen A) substance making body produce more urine; B) substance produced in the body that controls the level of sugar in the blood; C) a hormone produced in a woman’s body that makes her develop typical female sexual features and prepares her body for having a baby; D) a hormone produced in a man’s body that makes him develop typical male sexual features. homeopathy A) any disease of a human body; B) diseases with similar symptoms; C) a form of medicine which treats body systems with the help of various traditional drugs; D) a well established form of medicine which assists the body is own natural healing system treating the whole person not just the symptoms of the illness or disease. drug development A) a term used to define the entire process of bringing a new drug to the market; B) the ability of the drug to bind to the receptor; C) measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system; D) problems that occur when treatment goes beyond the desired effect. cardiometer A) pain in the heart; B) pathology of the heart muscle; C) an instrument for measuring the heart size; D) a procedure used for evaluating heart rate. osteodystrophy A) a bone disease found chiefly in adult women characterized by bone softening resulting from calcium salts deficiency; B) a tumour composed of bony tissue; C) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition; D) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones. ischium A) a large bone that supports the trunk of the body and articulates with the leg bones and sacrum; B) the uppermost and largest portion of the pelvic girdle; C) the posterior part of the pelvic girdle; D) the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. tendon A) a band or cord of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone; B) a heavy sheet of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone or in some instances to connect muscles; C) the most fixed attachment of a muscle which serves as a basis of action; D) the movable attachment where the effects of movement are produced. enterotome A) the surgical instrument used for intestine incision; B) a doctor qualified to treat intestinal diseases; C) any disease of the stomach and intestine; D) removal of the stomach and intestine. hepatoblastoma A) any disease of the liver; B) a specialist in liver diseases; C) a malignant tumour of the liver in newborns or children; D) the scientific study about liver diseases. leukoderma A) abnormal whiteness of the skin in patches; B) destructive to white blood cells; C) increase in number of white cells in the blood; D) skin covered with leucocytes. eosinopenia A) lack of white blood cells; B) deficiency in the cells of the blood; C) eosinophile cell deficiency in the blood; D) deficiency of red blood cells. cardialgia A) an instrument for measuring the heart size; B) pain in the heart; C) pathology of he heart muscle; D) a procedure used for evaluating heart rate. osteotome A) a tumour composed of bony tissue; B) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition; C) a bone disease found chiefly in adult women characterized by bone softening resulting from calcium salts deficiency; D) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones. pubis A) a large bone that supports the trunk of the body and articulates with the leg bones and sacrum; B) the uppermost and largest portion of the pelvic girdle; C) the posterior part of the pelvic girdle; D) the anterior part of the pelvic girdle. aponeurosis A) a band or cord of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone; B) a heavy sheet of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone or in some instances to connect muscles; C) the most fixed attachment of a muscle which serves as a basis of action; D) the movable attachment where the effects of movement are produced. enteropathy A) any disease of the intestines; B) any renal disease; C) any disease of the stomach; D) removal of the stomach and intestine. hepatology A) a specialist in liver diseases; B) the scientific study about liver diseases; C) the science that deals with gallbladder diseases; D) any disease of the liver. potency a) the amount of the drug needed to produce an effect. b) the amount of the drug needed to test it. c) the amount of the drug needed to solve it . d) the amount of the drug needed to sell it. affinity a) the process of drug compatibility with other chemicals. b) the process of drug release from the dosage form. c) the process of drug solubility in water. d) the process of drug producing. pneumonia a)inflammation of one or more joints. b)chronic inability to fall asleep. c) inflammation of the lungs . d)chronic constipation . sleepping aids a) drugs used to improve sleeping . b) drugs used to lose weight. c) drugs used to combat viral, fungal and parasitic infections. d) drugs used to treat allergy. insuline a) substance produced in the body that controls the level of sugar in your blood. b) substance produced in the body that controls the heart rate. c) substance produced in the body that controls blood pressure. d) substance produced in the body that controls breathing . litmus a)a pigment used to study relationship between heat and electrical energy. b) a pigment used to study solubility. c)а pigment used as a test for acidity and alkalinity. d) a pigment used to study blood. bark a) a flat green organ of photosynthesis on the stem. b) a protective layer of dead cells on the outside of woody plants. c) the reproductive structure of angiosperm plants. d) the organ located in the ground , nourishing the whole plant. drug a) any chemical substance produced by the body. b) any chemical process of the body. c)any chemical substance accumulated in the body . d)any chemical substance that affects the body and its processes. leukotoxic A) destructive to white blood cells; B) a toxin used in medicine for treatment of leukemia; C) abnormal whiteness of the skin in patches; D) increase in number of white cells in the blood. cytopenia A) lack of white blood cells; B) deficiency in the cells of the blood; C) deficiency of red blood cells; D) eosonophil cell deficiency in the blood. cardiodynamics A) the scientific study about heart and blood vessels; B) the scientific study about movements and forces concerning the heart activity; C) pain in the heart; D) an instrument for measuring the heart size. osteoporosis A) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition; B) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones; C) a tumour composed of bony tissue; D) a thinning of bone resulting from excessive loss of minerals in bone. humerus A) upper arm bone; B) medial lower arm bone; C) lateral lower arm bone; D) wrist bones. origin A) a band or cord of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone; B) a heavy sheet of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone or in some instances to connect muscles; C) the most fixed attachment of a muscle which serves as a basis of action; D) the movable attachment where the effects of movement are produced. gastropathy A) inflammation of the stomach and intestine; B) any renal disease; C) any disease of the stomach; D) removal of the stomach and intestine. jaundice A) the so-called epidemic or infectious hepatitis, an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts; B) the destruction of normal liver tissue that leaves nonfunctioning scar tissue surrounding areas of functioning liver tissue; C) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream; D) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells. leukocytosis A) increase in number of white cells in the blood; B) decrease in number of leukocytes; C) abnormal whiteness of the skin in patches; D) destructive to white blood cells. leucopenia A) lack of white blood cells; B) a white blood cell; C) cancer of white blood cells; D) deficiency of red blood cells. cardioangiology A) pain in the heart; B) the scientific study about movements and forces concerning the heart activity; C) the scientific study about heart and blood vessels; D) the science that deals with such a disease as angina pectoris. osteoma A) bad bone development having to do with the process of nutrition; B) a bone disease found chiefly in adult women characterized by bone softening resulting from calcium salts deficiency; C) a tumour composed of bony tissue; D) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones. vaccines A) drugs that are used to prevent many infectious diseases f.e. measles, poliomyelitis; B) drugs that are effective in treating bacterial infections; C) drugs that control blood pressure; D) drugs to control pain. neuropathy A) pertaining to pathology; B) a specialist in pathologies of nervous system; C) a disease or abnormality of the nervous system; D) the branch of medicine that deals with nervous system. placebo A) a drug for schizophrenia; B) toxic substance dangerous for people’s health; C) any prescription drug; D) inactive substance used as a control in an experiment to determine the effectiveness of a medicinal drug. drug dose A) measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system; B) specified quantity of a therapeutic agent, such as a drug or medicine, prescribed to be taken at one time or at stated intervals; C) ability of a drug to produce the desired therapeutic effect; D) process of drug release from the dosage form. insulin A) a drug that reduces the secretion of acid in the stomach; B) substance making body produce more urine; C) substance produced in the body that controls the level of sugar in blood; D) a hormone produced in a woman’s body that makes her develop typical female sexual features. arthritis A) any disease or abnormal condition affecting a joint; B) inflammation of a joint, usually accompanied by pain, swelling and stiffness; C) the study and treatment of the joints; D) neuralgic pain in a joint or joints. over-the-counter drugs A) medicines that may be sold directly to a consumer without a prescription from a health care professional; B) licensed medicines that are regulated by legislation to require a prescription before it can be obtained; C) a copy of a brand name drug whose patent has expired; D) drugs that are patented or controlled by a private organization or manufacturer. essential oil A) an alcohol-based derivative of a fresh herb or other natural plant material, used primarily as an alternative medicine or dietary supplement; B) a herbal infusion made from anything other than the leaves of the tea bush; C) any substance (other, than a food or device) intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, relief, treatment or prevention of disease or intended to affect the structure or function of the body; D) a concentrated, hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants. ulna A) upper arm bone; B) medial lower arm bone; C) lateral lower arm bone; D) wrist bones. insertion A) a band or cord of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone; B) a heavy sheet of white fibrous tissue serving to connect a muscle to a bone or in some instances to connect muscles; C) the most fixed attachment of a muscle which serves as a basis of action; D) the movable attachment where the effects of movement are produced. gastronephritis A) inflammation of the stomach and intestine; B) inflammation of the stomach and kidneys; C) removal of the stomach and intestine; D) any renal disease. cirrhosis A) the so-called epidemic or infectious hepatitis, an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts; B) the destruction of normal liver tissue that leaves nonfunctioning scar tissue surrounding areas of functioning liver tissue; C) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells; D) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream. thrombocytopenia A) decrease in the number of blood platelets below normal; B) increase in the number of blood plateles; C) resembling a blood clot and others hemocytes; D) thrombosis that arises in the arterial inflammation. toxemia A) presence of bile in the blood; B) deficiency of toxins in the blood; C) a doctor trained to treat toxic poisoning; D) presence of toxic products in the blood. vasoconstriction A) removal of vessels and nerves; B) the death of the cells of the walls of blood vessels; C) narrowing of the veins and venules only; D) narrowing of vessels. costovertebral A) pertaining to clavicles and head; B) pertaining to clavicles and ribs; C) pertaining to ribs and vertebrae; D) resection of the rib. radius A) upper arm bone; B) medial lower arm bone; C) lateral lower arm bone; D) wrist bones. palate A) the roof of the mouth; B) the organ for containing food and its digestion; C) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; D) any of numerous hairlike vascular processes in the small intestine. gastrotomy A) inflammation of the stomach and intestine; B) removal of the stomach and intestine; C) incision of the stomach; D) any disease of the stomach. Botkin’s disease A) damage to the liver that results from excessive drinking of alcohol; B) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells; C) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream; D) the so-called epidemic or infectious hepatitis, an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts. thromboarteritis A) thrombosis that arises in the arterial inflammation; B) resembling a blood clot and an artery; C) decrease in the number of blood platelets below normal; D) another word for thrombocyte. cholemia A) bad quality of bile; B) bad bile flow; C) presence of bile in the blood; D) deficiency in the cells of the blood. angionecrosis A) removal of vessels and nerves; B) narrowing of vessels; C) the death of the cells of the walls of blood vessels; D) necrosis of the tissue of the limbs of the human body. costotome A) a tumour composed of bony tissue; B) an instrument for ribs cutting; C) resection of the rib; D) a surgical instrument for cutting or dividing bones. carpi A) upper arm bone; B) medial lower arm bone; C) lateral lower arm bone; D) wrist bones. stomach A) the roof of the mouth; B) the organ for containing food and its digestion; C) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; an important organ in the articulation of speech; D) any of numerous hairlike vascular processes in the small intestine. gastrology A) a scientific study dealing with the diseases of the stomach and intestine; B) removal of the stomach and intestine; C) a scientific study that deals with the gastric diseases; D) inflammation of the stomach and intestine. liver encephalopathy A) the destruction of normal liver tissue that leaves nonfunctioning scar tissue surrounding areas of functioning liver tissue; B) a yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by abnormally high levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream; C) a disorder in which brain function deteriorates because toxic substances, which would normally be removed by the liver, build up in the blood; D) an excessive accumulation of fat (lipid) inside the liver cells. glycemia A) sugar in the blood; B) bad quality of the blood; C) presence of toxic products in the blood; D) deficiency in the cells of the blood. anemia A) presence of sugar in the blood; B) deficient quantity and quality of blood; C) presence of toxic substances in the blood; D) deficiency in the cells of the blood. diabetes A) an acute or chronic inflammation of lungs; B) chronic inability to sleep for an adequate length of time; C) a polygenic disease characterized by abnormally high glucose levels in the blood; D) a sudden loss of brain function caused by a blockage or rupture of a blood vessel of the brain. dystrophy A) a degenerative disorder caused by inadequate or defective nutrition; B) overweight in children; C) a drug for stomachache; D) any disease or abnormal condition affecting gastrointestinal tract. inactive ingredients A) the drug itself; B) products intended to supplement the diet f.e. minerals, vitamins; C) an alcohol-based derivative of a fresh herb or other natural plant material; D) substances added to facilitate the administration of the drug, such as ingredients that provide pleasant taste or colour. phytotherapy A) the study of chemicals derived from marine organisms; B) the medicinal use of plant extracts; C) the synthesis of natural bioactive molecules using biotechnology; D) the study of chemicals derived from plants. microorganism A) a chemical compound that is the basis for one or more derivatives; B) an organism that can be seen with a naked eye and that consists of many cells; C) a dangerous organism that can cause viral, bacterial or fungal infection; D) an organism that can be seen only with the aid of a microscope and that typically consists of only a single cell. metabolism A) the process of release of drug from the formulation; B) the process of a substance entering the blood circulation; C) the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites; D) the elimination of the substances from the body. thermostable A) capable of withstanding moderate heat without loss of characteristic properties; B) having properties of liquid; C) having crystalline components; D) heat-protective. melting A) changing a liquid into vapour; B) changing a solid substance into a liquid; C) changing of a solid substance into powder; D) compression of powder into a solid substance. angioneurectomy A) another term for angina pectoris; B) narrowing of vessels; C) removal of vessels and nerves; D) pain of nerves and vessels. biopsy A) examination of tissues removed from the body; B) vaccine preparation; C) carbon dioxide measuring; D) diagnosis by examination of the blood. narrowed valve A) dilated valve; B) damaged valve; C) constricted valve; D) leaked valve. thrombocyte A) blood platelet; B) red blood cell; C) white blood cell; D) plasma. pepsin A) an enzyme; B) gastric juice; C) a protein; D) a carbohydrate. hard palate A) the floor of the mouth; B) the roof of the mouth; C) the organ of tasting and smelling; D) an unimportant organ in the articulation of speech sounds. auscultation A) tapping of the chest with the fingers to determine if the lungs are filled with air or with fluid; B) listening to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope; C) an electronic, electrical or other equipment for diagnosing heart diseases, such as echocardiogram, electrocardiogram and others; D) laboratory findings, such as blood and urine tests. mandible A) upper front surface of the body; B) lower jaw bone; C) posterior part of the pelvis; D) medial lower arm bone. to percuss A) to tap; B) to palpate; C) to operate on; D) to look at or into. anticoagulant A) drug that affects the brain; B) drug that affects gastric secretion; C) drug that prevents blood clotting; D) drug that prevents bone fracture. to diminish A) to decrease; B) to increase; C) to divide; D) to multiply. erythrocytometer A) increase in the number of red blood cells; B) decrease in the number of white blood cells; C) diagnosis by examination of the blood; D) an apparatus for measuring and counting of red blood cells. indigestion A) pertaining to respiration; B) failure of digestive function; C) excessive formation of gases in stomach; D) the highly acidic stomach contents. breastbone A) the bone down the upper front of the body; B) the column of small bones down the center of the back; C) one of the curved bones round the chest; D) the framework of bones round the body below the waist. leukemia A) the process and result of accumulation of fats and fat-like substances within the walls of arteries; B) a cancer of white blood cells; C) a well-defined round or oval sore where the lining of the stomach or duodenum has been eaten a way by stomach acid and digestive juices; D) an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts. leukemia A) cancer of the lymph nodes; B) cancer of the blood cells; C) cancer of the mammary gland; D) cancer of the stomach. pericardium A) apex of the heart; B) heart valve; C) sac surrounding the heart; D) heart bruit. thrombocyte A) white blood cell without granules in its cytoplasm; B) tiny blood corpuscle, an important agent of hemostases; C) supernatant fluid containing no fibrinogen; D) sticky, pale amber liquid serving as a vehicle for substances. peptic ulcer A) disorder of the teeth; B) the disease of the stomach; C) the inflammation of the heart; D) the disease of the head. aorta A) the smallest capillary in the body; B) the largest vein in the body; C) the smallest artery in the body; D) the largest single artery in the body. bile A) substance made in the pancreas; B) substance made in the liver; C) substance made in the duodenum; D) substance made in the gallbladder. mandible A) upper front surface of the body; B) lower jaw bone; C) posterior part of the pelvis; D) medial lower arm bone. hepatology A) the scientific study about liver diseases; B) any disease of the liver; C) a specialist in liver diseases; D) a malignant tumour of the liver. chronic leukemia A) leukemia beginning very quickly; B) leukemia progressing rapidly; C) leukemia progressing slowly; D) leukemia affecting only one type of leukocytes. catabolism A) burning nutrients in the presence of oxygen; B) pumping action of blood; C) cataract; D) catalyzer. clotting A) coagulation; B) mixture; C) transfusion; D) combination. myocardial infarction A) inflammation of the throat; B) blood disease; C) thrombosis in the coronary artery; D) pulmonary disease. peptic ulcer A) inflammation of the stomach; B) enlargement of the stomach; C) a sore in the lining of the stomach or duodenum eaten away by stomach acid and digestive juices; D) inflammation of the gallbladder wall resulting from a gallstone in the cystic duct. cancellous bone A) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones; B) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; C) a layer of very porous bone, it is sometimes called spongy bone; D) a thin layer of cartilage. Botkin’s disease A) the process and result of accumulation of fats and fat-like substances within the walls of arteries; B) injuries to bones, muscles, and joints, ranging in severity from mild pulled muscles to strained ligaments, dislocated joints, and broken bones; C) a thinning of bone resulting from excessive loss of minerals in bone; D) an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts. vessel A) pain in the heart; B) the movable muscular structure attached to the floor of the mouth; C) a tube that carries blood through the body of a person or an animal, or liquid through the parts of a plant; D) the muscular membranous cavity leading from the mouth and nasal passages to the larynx and esophagus. coccyx A) breastbone; B) hip bone; C) tailbone; D) facial bone. artery A) a large blood vessel which carries blood away from the heart; B) a thin walled vessel which carries blood toward the heart; C) a vessels which carries blood between arteries and veins; D) a valve which prevents the backflow of blood. alleles A) portions; B) versions; C) genotypes; D) agglutinins. chest pain A) sweating, weakness, vomiting; B) discomfort in the neck and throat; C) pain in the abdominal cavity; D) pain in the part of the body containing the heart. gastroduodenitis A) inflammation of the stomach and duodenum; B) removal of the stomach and some portion of duodenum; C) sample of the stomach’s contents; D) a probe for detailed examination of the duodenum and stomach. freezing a) changing a solid substance into a liquid. b) changing a solid substance into steam. c) changing a liquid substance into solid at a low temperature. d) changing a solid substance into powder. drug compatibility a) the process of drug interaction with other chemicals. b) the process of drug release from the dosage form. c) the process of drug solubility in water. d) the process of drug producing. zoopharmacognosy a) the use of plants for medicinal purposes. b) the use of organisms found in the sea for medicinal purposes. c) the study of plants usage in different cultures for medicinal purposes. d) the study of animal ability to restore their health. antiemetic drugs a)are effective against vomiting and nausea. b)are used to lower the level of sugar in the blood. c)are used to combat viral, fungal and parasitic infections. d)are used to treat allergy. nuclear pharmacy a) mixing of drugs by a compounding pharmacist to fit the unique needs of a patient. b) preparing radioactive materials for diagnostic tests and for treating certain diseases. c) meeting the needs of a military health care system. d) pharmacy service to all types of hospital. excretion . a) the process of eliminating waste material from the body. b) the process of accumulating waste material in the body. c) the process of drug release from the dosage form. d) the process of drugs manufacturing . root a) a flat green organ of photosynthesis on the stem. b) a protective layer of dead cells on the outside of woody plants. c) the reproductive structure of angiosperm plants. d) the organ located in the ground , nourishing the whole plant. insomnia a) sleeping difficulties. b)digestive disorder. c)inflammation of joints . d)breathing difficulties . leukemia A) cancer of the lymph nodes; B) cancer of white blood cells; C) cancer of the mammary gland; D) cancer of the stomach. Botkin’s disease A) the process and result of accumulation of fats and fat-like substances within the walls of arteries; B) a bacterial or viral infection affection people whose surname is Botkin; C) a well-defined round or oval sore where the lining of the stomach or duodenum has been eaten a way by stomach acid and digestive juices; D) an acute viral disease affecting hepatic cells and bile ducts. cancellous bone A) a layer of very porous bone, it is sometimes called spongy bone; B) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones; C) a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone; D) a thin layer of cartilage. chemotherapy A) treatment of diseases by mineral water; B) treatment of diseases by X-rays; C) treatment of diseases by massage and exercises; D) treatment of diseases by drugs. auscultation A) tapping the chest with fingers; B) palpation of the abdomen; C) listening to the heart with a stethoscope; D) determining of the heart size. agglutinins A) genes; B) special types of tissue; C) proteins; D) antigenes. histamine A) a vitamin; B) a substance released by the liver; C) a substance released by a stomach; D) a substance released by the kidneys. cardio-vascular disease A) a disease of the respiratory system; B) a disease of the heart and blood vessels; C) a disease of the gastro-intestinal tract; D) a disease of the nervous system. tongue A) the organ of chewing and tasting; B) the roof of the mouth; C) the muscular membranous cavity; D) the largest gland organ. biopsy A) examination of tissues removed from the body; B) vaccine preparation; C) carbon dioxide measuring; D) diagnosis by examination of the blood. plasma A) supernatant fluid which forms when blood clots but contains no fibrinogen or other components; B) sticky, pale amber liquid serving as a vehicle for a number of organic and inorganic substances; C) red viscous fluid tissue of the human body having salty taste and faint odour; D) cells with or without granules in their cytoplasm. coccyx A) breastbone; bone. B) tailbone; C) hip bone; D) facial periosteum A) a small rounded bone resembling a grain of sesame in shape; B) a layer of hard, dense tissue, which lies under the periosteum in all bones; C) an area of cartilage tissue in the bone; D) a strong vascular membrane that covers the surface of long and other bones. bruise A) an injury to tissue resulting from heat, chemicals or electricity; B) the cooling of the whole body to a potentially dangerous temperature; C) a damage of the soft tissue from within by a fractured bone; D) an injury to tissue resulting from a direct violence. tongue A) the organ for containing food and digestion; B) the tube through which food passes from pharynx to the stomach; C) the organ of chewing and tasting; D) the roof of the mouth. erythrocytometer A) an apparatus for measuring and counting red blood cells; B) an apparatus for measuring and counting white blood cells; C) decrease in the number of red blood cells; D) a virus that affects red blood cells. eosinopenia A) deficiency of eosonophil cells in the blood; B) one of the three types of granulocytes; C) cells that are active and elevated in allergic conditions; D) pathologic increase of eosonophil cells in the blood. Вставте пропущене слово чи словосполучення: Homeopathic remedies contain natural substances in ...doses. a) minute b) huge c) enormous d) great A placebo is a pharmacologically … substance that produces an effect similar to drugs. a)inert b)active c)efficient d)effective Examination of a patient’s … may involve placing special paper in the mouth prior to biting to obtain an impression of how the sets of teeth correspond. a) occlusion b) head and neck area c) lymph nodes in the neck d) periodontal tissue … involves visualization of the salivary gland. a) Panoramic X-rays b) Cephalometric projections c) Sialography d) Periapical X-ray … of teeth may result from bacteria stains, tobacco, tea, coffe, and food with an abundance of chlorophyll. a) Eruption b) Loss c) Discolouration d) Complete lack Dilaceration is an abnormall … found on a tooth. a) spot b) bend c) enamel d) bud Dental caries is a disease where bacterial processes damage … . a) soft tooth structure b) pulp c) hard tooth structure d) periodontium The action of drugs on the human body is called … a) pharmacokinetics b)pharmacodynamics c)pharmacognosy d)pharmacoepidemiology Drug abuse can cause physical or psychological …. to the user. a)harm b)benefit c)favour d)advantage Undesired effect produced by drugs is called a(an)….effect. a)valuable b)important c)therapeutic d)adverse Patented drugs are usually sold under a … name . a) trade b)chemical c)popular d)safe …is a condition in which the heart has lost the ability to pump enough blood to the body's tissues. a)Dyspepsia b)Dystrophy c)Dysuria d) Heart failure … is a process of turning steam into a liquid state . a)Fertilization b)Neutralization c)Disintegration d)Condensation A placebo is made to look exactly like a real drug but is made of … . a) chemical substance b) herbal substance c) inactive substance d) active substance The … assigns a generic name to a drug. a) official body b) pharmaceutical company c) seller d) pharmacist Aromatherapy claims that specific aromas carried by essential oils have … . a) damaging effects b) no effects c) adverse effects d) curative effects Most medicines for children are so delicious that they can’t be called … . a) tablets b) remedies c) essential oils d) fish fat Chronic inability to fall asleep is called … . a) stroke b) influenza c) constipation d) insomnia A mild allergic reaction can be treated with an … . a) antibiotic b) antihistamine c) anticoagulant d) antiemetic …is a clear liquid that falls as rain and is used for drinking and washing. a) Water b) Nitrogen c) Oxygen d) Petroleum The extent to which a substance is basic is called … . a) basicity b) neutrality c) pH d) acidity The term … comes from the Latin term, which means “sour”. A) acid; B) vitamin; C) base; D) mineral. A good history is fundamental to accurate … . a) information b) diagnosis c) complaint d) prevention The earliest … of a caries lesion is a spot. a) sign b) cavity c) stain d) plaque Radiographs are needed … less visible areas of teeth. a) to treat b) to remove c) to inspect d) to apply … is an infection of yeast fungi on the mucous membrane of the mouth. a) Oral candidiasis b) Oral cancer c) Dental caries d) Gingivitis The lost tooth structure can not be … . a) stopped b) noticed c) regenerated d) left The chemistry of … is called organic chemistry. A) ionic compounds; B) acids and bases; C) carbon compounds; D) salts. … literary means knowledge of drugs. A) botany; B) pharmacognosy; C) chemistry; D) medicine. The use of essential oils in pregnancy is … . A) beneficial; B) common; C) prescribed by a doctor; D) not recommended. … describes the atomic or molecular structure of the drug. A) The generic name; B) The trade name; C) The chemical name; D) The official name. The main goals of drug development are … . A) efficacy and safety; B) price and form; C) convenience in dosage; D) side-effects. Roots and rhizomes are collected in … after the vegetative processes have finished. A) summer; B) winter; C) autumn; D) spring. … are the two most commonly associated with pharmacy symbols. A) flower and tree; B) mortar and pestle; C) snake and rat; D) cup and test tube. Botanists divide the … into twelve divisions. A) animal kingdom; B) insect kingdom; C) bird kingdom; D) plant kingdom. … describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration. A) Pharmacodynamics; B) Pharmacoepidemiology; C) Pharmacokinetics; D) Pharmaceutical formulation. Inorganic compounds are found in nature as … . A) minerals; B) vitamins; C) aminoacids; D) hormones. The mouth contains a wide variety of … . a) fructose b) bacteria c) folate d) lysine Note any loosening of a tooth because it may be the…of cancer development. a) abnormality b) expansion c) immovability d) sign The diagnosis being made, the appropriate … is prescribed. a) record b) investigation c) treatment d) inspection First of all the history establishes… of the patient. a) available diagnosis b) immediate complaints c) treatment d) background … refers to the fear of dentistry and of receiving dental care. a) Dental treatment b) Dental surgeon c) Dentistry d) Dental fear … is an alcohol-based derivative of a fresh herb or other natural plant material. A) ointment; B) tincture; C) pill; D) tablet. A mild allergic reaction may be treated with … . A) antitussives; B) carminatives; C) decongestants; D) anihistamines. By law, drugs are divided into two categories: …. A) prescription drugs and nonprescription drugs; B) official drugs and generic drugs; C) antimicrobial drugs and antiviral drugs; D) homeopathic drugs and synthetic drugs. Most drugs produce several effects, but only one effect - … - is wanted for the treatment of a disorder. A) placebo effect; B) side effect; C) therapeutic effect; D) prolonged effect. … are more likely to have chronic disorders such as high blood pressure, arthritis. A) Younger people; B) Infants; C) Older people; D) Middle-aged people. … may be dispensed only with a prescription from a licensed professional. a)Non prescription drugs b)Prescription drugs c)Vitamins and minerals d)Dietary supplements The placebo may… the symptoms but not the actual disease. a)effect b)act c)react d)demonstrate Homeopathy is a form of medicine which helps the body to develop its own… a)distributing system b)family system c) natural healing system d)excretion system A sharp point of the … is used to enhance tactile sensation. a) dental drill b) dental engine c) dental explorer d) mouth mirror Occasional teeth …, called bruxism, doesn’t usually cause harm. a) grinding b) clenching c) biting d) loosening … is surgical removal of all or part of the tongue. a) glossolalia b) glossoplegia c) glossoplasty d) glossectomy Xerostomia can cause difficulty in … . a) walking and running b) sitting and working c) writing and reading d) speech and eating … may also accompany stomatitis. a) halitosis b) poor audition c) liver cancer d) impaired vision Drug …date shows the product can’t be used after a particular period of time. a)abuse b)prescription c)dosage d)expiration Digestive disturbances are very common …. drug reactions. a)useful b)helpful c)therapeutic d)adverse The … name describes the atomic or molecular structure of the drug. a)chemical b)natural c)trade d)family …is difficulty in digesting food or an upset stomach. a)Dyspepsia b)Dystrophy c)Dysuria d)Dyscephalia Anaphylaxis is a severe form of allergic reaction, it can be .. a)pleasant b)fatal c) necessary d) successful Commonly encountered techniques in inorganic chemistry are … . A) X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, electron-spin resonance etc.; B) catalysts, superconductors and therapies; C) piezoelectricity, electrical conductivity and non-linear optics; D) liberation, absorption, distribution and excretion. … includes the study of the mechanisms of absorption and distribution of an administered drug, the rate at which a drug action begins and the duration of the effect etc. A) Pharmacodynamics; B) Pharacokinesis; C) Pharmacoepidemiology; D) Pharmaceutical formulation. Neutral organic compounds tend to be … that is they are less soluble in water than in organic solvents. A) insoluble; B) synthesized; C) derived; D) hydrophobic. The botanical name is often followed by a letter which stands for … . A) pharmacological company which uses the plant; B) generic name; C) the botanist who named the plant; D) specific name. Surgical excision of the oral tumour is usually recommended if tumour is … . a) huge b) very big c) small enough d) extremely large … is considered to be the only truly confirmative method for evaluating the cancerous and precancerous nature of a lesion. a) Visual inspection b) Biopsy c) Instrumental examination d) Sailography The goal of glossitis … is to reduce inflammation. a) defection b) diagnostics c) evaluation d) treatment Xerostomia is the medical term for a … due to a lack of … . a) oral cavity / teeth b) mouth / saliva c) oral cavity / tongue d) mouth / tongue papillae Periodontal screening involves visually inspecting the … for redness or swelling. a) gums b) tongue c) pulp d) tonsils An infusion is very similar to a …, but is used with herbs that are more volatile. A) tincture; B) decoction; C) extract; D) suspension. … is any chemical substance that affects the body and its processes. A) a dietary supplement; B) a vitamin; C) a drug; D) a mineral. The difference between the usual effective dose and the dose that produces severe or life-threatening side effects is called … . A) the margin of safety; B) efficacy; C) affinity; D) potency. A drug that cures illnesses and infections caused by bacteria is called … . A) antihistamine; B) diuretic; C) antibiotic; D) insulin. Barbiturates which were commonly used as … can interfere with breathing, dangerously lower blood pressure and even cause death if taken in excess. A) diuretics; B) antihypertensive; C) sleep aids; D) antibiotics. Drug abuse is … use of mind-altering substances without medical need. A) insufficient and intermittent; B) excessive and persistant; C) adequate and temporary; D) average and constant. Pulpitis begins as a … condition. a) permanent b) reversible c) irreversible d) healthy The tongue is divided into … and … . a) movable tongue / immovable tongue b) speakable tongue / eatable tongue c) short tongue / long tongue d) oral tongue / base of the tongue Sensitivity to … on a tooth means that inflammation has spread. a) healing b) tapping c) extracting d) filling If symptoms … root canal therapy is repeated. a) persist b) remove c) determine d) exclude … is a rotary instrument used to remove tooth substance, particularly in the treatment of caries. a) Mouth prop b) Dental syringe c) Dental explorer d) Dental drill Herbal teas are usually consumed for their physical or medicinal effects, especially for their … properties. A) antihypertensive; B) antihistamine; C) anti-inflammatory; D) stimulant, relaxant or sedative. Benefits of certain plants or other materials were worked out by … . A) failure; B) successful experiments; C) trial and error; D) experiments on animals. The symbol “Rx” is usually said to stand for the Latin word “Recipe” meaning …. A) to give; B) to take; C) to label; D) to sign. Organic compounds are structurally … . A) diverse; B) similar; C) identical; D) opposite. Hydrochloric acid is formed by dissolving … . A) oxygen chloride; B) hydrogen chloride; C) oxygen chlorine; D) hydrogen sulfate. Inorganic compounds are found in nature as … . A) animals; B) plants; C) vitamins; D) minerals. Acids taste… . a)sour b)sweet c)bitter d)astringent Basicity shows the extent to which a substance is… a)basis b)busy c)bias d)basic … is important to determine any enlargement, pain, hardness or fixation of the lymph nodes. a) Extraoral palpation b) Visual inspection of the gums c) Intraoral auscultation d) Examination of a patient’s bite Occasional teeth grinding is medically called … a) bruxism b) erythroplakia c) “meth mouth” d) primary herpes … show the entire mouth area on a single X-ray. a) tomograms b) sialography c) panoramic X-rays d) bite-wing x-rays When tooth destruction occurs at the roots of teeth, the process is referred to as …, when caused by cells within the pulp. a) abfraction b) internal resorption c) external resorption d) abrasion Microdontia is a condition where teeth are … than the usual size. a) less brighter b) bigger c) smaller d) normal Botanists divide the plant…into twelve divisions. a)class b)family c)kingdom d)order Drug …is the excessive and persistent use of mind-altering drugs without medical need. a)abuse b)prescription c)dosage d)expiration The ability of drug to produce the desired …effect is called efficacy. a)side b)minimal c)therapeutic d)adverse Homeopathic remedies are made from a wide variety of …substances . a)toxic b)natural c)harmful d)improper …is a condition in which a part of a body gradually becomes weaker. a)Dyspepsia b)Dystrophy c)Dysuria d)Dyscephalia The … reaction of an acid with base will always produce water and a salt. a)fertilization b) neutralization c) disintegration d)condensation A … is a large chair-side appliance found in a dentist’s office. a) dental drill b) dental engine c) dental explorer d) mouth mirror … is an emotional response to threats and danger. a) Mania b) Laugh c) Fear d) Smile …is an abnormal fear of water. a) Hydrophobia b) Gynophobia c) Hydromania d) Monophobia The diagnosis being made, the appropriate … is prescribed. a) information b) case record c) treatment d) hygiene Визначте часову форму присудка: Medicinal chemistry is focused on quality aspects of medicines. a) Present Perfect, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Continuous, Active d) Present Indefinite, Passive Will this patient with allergy be treated with antihistamines? a) Present Continuous,Active b) Future Indefinite, Passive c) Future Perfect, Active d)Future Continuous, Active The medicine has just been dispensed. a) Present Indefinite, Passive b) Present Indefinite, Active c) Present Perfect, Active d) Present Perfect, Passive We do not discuss side effects of medicines during lectures. a) Present Indefinite, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Indefinite, Passive d) Present Perfect, Active A pharmacist advised the customer ibuprofen for relieving headache. a) Past Indefinite, Passive b) Past Perfect, Passive c) Past Indefinite, Active d) Past Perfect, Active I am reading a very interesting article on clinical pharmacy now. a) Present Continuous, Active b) Present Indefinite, Active c) Present Perfect, Active d) Present Perfect, Passive. By 8 o’clock the scientific article on the causes of low bioavailability will have been read. a) Future Indefinite, Active b) Future Indefinite, Passive c) Future Perfect, Passive d) Future Perfect, Active A medicated lollipop containing the drug was being made by the compounding pharmacist at that time. a) Past Indefinite, Passive b) Past Indefinite, Active c) Past Continuous, Passive d) Past Continuous, Active Recently she has been prescribed a homeopathic treatment . a)Present Perfect, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive A chemist was making a cough mixture when a customer came in . a) Present Continuous ,Active b)Present Continuous, Passive c) Past Perfect Continuous, Active d)Past Continuous, Active The homeopathic treatment is based on the on the principle that “like cures like”. a) Present Indefinite, Passive b) Present Indefinite, Active c) Present Continuous ,Active d) Present Continuous, Passive Side effects of the new medicine had been discussed by the end of the seminar. a) Past Perfect Continuous, Active. b)Past Perfect, Passive c) Past Indefinite, Passive d) Past Indefinite, Active I have been taking sepia for ten days. a) Present Continuous, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Perfect Continuous ,Active d) Present Perfect, Active Drugs do not change the basic nature of these functions or create new functions . a) Present Indefinite, Passive b) Present Indefinite, Active c) Present Perfect, Active d) Present Perfect, Passive. This drug will help to protect the digestive tract from stomach acid. a) Present Indefinite, Active b) Future Indefinite, Passive c) Future Indefinite, Active d) Present Indefinite , Passive The doctor left three different medicines in different coloured capsules. a) Past Indefinite, Passive b) Past Indefinite, Active c) Past Continuous, Passive d) Past Perfect, Active Inorganic compounds have been found to be useful as drugs. A) Past Perfect, Passive; B) Present Perfect, Active; C) Present Perfect, Passive; D) Present Perfect Continuous, Active. The distinction of the compounding pharmacy is being explained at the moment. A) Present Continuous, Passive; B) Present Continuous, Active; C) Present Indefinite, Passive; D) Present Perfect, Active. Medical chemistry involves the identification, synthesis and development of new chemical entities suitable for therapeutic use. A) Past Indefinite, Active; B) Present Indefinite, Active; C) Present Indefinite, Passive; D) Present Continuous, Active. She has been reading the article about acids and bases for an hour. A) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; B) Present Perfect, Passive; C) Present Continuous, Passive; D) Present Perfect, Active. Penicillin is used in the treatment of pneumonia. A) Present Indefinite, Active; B) Present Continuous, Active; C) Present Indefinite, Passive; D) Present Perfect, Active. The scientific report of this student was being discussed at that time yesterday. A) Past Continuous, Active; B) Past Continuous, Passive; C) Present Continuous, Active; D) Past Indefinite, Passive. My grandfather had been working at this chemist’s shop for 25 years before retirement. A) Past Perfect Continuous, Active; B) Past Continuous, Passive; C) Past Perfect, Active; D) Present Perfect Continuous, Active. This decoction will be prepared tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite, Active; B) Future Continuous, Active; C) Future Continuous, Passive; D) Future Indefinite, Passive. Chamomile flowers are sometimes added to cosmetics. A) Present Indefinite, Passive; B) Present Indefinite, Active; C) Past Indefinite, Passive; D) Present Continuous, Active. By Monday the scientific experiment will have been finished. A) Future Perfect, Active; B) Future Perfect, Passive; C) Future Indefinite, Passive; D) Future Indefinite, Active. My sister had passed an exam in organic chemisrty by 2 o’clock. A) Present Perfect, Passive; B) Past Indefinite, Active; C) Past Perfect, Passive; D) Past Perfect, Active. The tincture was being made by the compounding pharmacist at that time. A) Past Continuous, Passive; B) Past Continuous, Active; C) Past Perfect, Passive; D) Present Continuous, Active. A young scientist has been waiting for the results of quantitative analysis of this mineral for two days. A) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive; B) Present Perfect, Active; C) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; D) Past perfect Continuous, Passive. Clinical pharmacists provide direct patient care services. A) Present Indefinite, Passive; B) Present Indefinite, Active; C) Past Indefinite, Active; D) Present Perfect, Active. th By the 11 century, techniques and methods of essential oils production hadn’t been known by people. A) Past Indefinite, Active; B) Past Indefinite, Passive; C) Past Perfect, Passive; D) Past Perfect, Active. Next week this patient will be discharged from the hospital. A) Future Continuous, Active; B) Future Perfect, Passive; C) Future Indefinite, Active; D) Future Indefinite, Passive. The professor has been delivering a lecture on oxides and carbonates for half an hour already. a)Present Perfect, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive Homeopathic remedies are usually prepared by experienced chemists . a) Present Indefinite ,Active b)Present Indefinite, Passive c) Present Perfect , Active d)Present Continuous, Active The roots of that plant have just been boiled for preparing herbal tea. a) Present Perfect , Active b) Present Perfect , Passive c) Present Continuous ,Active d) Present Continuous, Passive The pharmacologists enumerated the side effects of the new medicine at the seminar. a) Past Perfect , Active b)Past Perfect, Passive c) Past Indefinite, Passive d) Past Indefinite, Active They are performing the clinical trial of this ointment right now . a) Present Perfect Continuous, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Continuous ,Active d) Present Perfect, Active Cough syrup will be prescribed to the child tomorrow. a) Future Indefinite, Active b) Future Indefinite, Passive c) Future Perfect, Active d) ) Future Perfect, Passive. This drug produces a severe adverse effect ,especialy in elderly people. a) Present Indefinite, Passive b)Present Indefinite, Active c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d) Present Perfect, Passive Sedative drugs were being prescribed to the patient at doctor’s office at this time yesterday. a) Past Indefinite, Active b) Past Indefinite, Passive c) Past Continuous, Passive d) Past Continuous, Active He has been studying the paragraph on acid base neutralization for 2 hours already. A) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; B) Present Continuous, Active; C) Present Perfect, Passive; D) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive. Inorganic compounds are found to be useful as drugs. A) Present Simple, Active; B) Present Continuous, Active; C) Present Simple, Passive; D) Present Perfect, Passive. A medicated lollipop containing the drug was being made by the compounding pharmacist at that time. A) Past Continuous, Active; B) Past Continuous, Passive; C) Past Perfect, Active; D) Past Simple, Passive. The customer has just ordered a cough mixture. A) Present Perfect, Passive; B) Present Simple, Active; C) Past Simple, Passive; D) Present Perfect, Active. By the next week the library-research paper on the scope of pharmacognosy will have been written. A) Future Perfect, Passive; B) Future Simple, Active; C) Future Continuous, Active; D) Future-in-the-Past, Passive. Dietary supplements are products intended to supplement the diet. A) Future Simple, Passive; B) Present Simple, Passive; C) Present Continuous, Active; D) Present Simple, Active. People are returning to the naturals with hope of safety and security. A) Present Simple, Passive; B) Present Continuous, Active; C) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; D) Past Simple, Passive. Will they do this chemical modification tomorrow? A) Future Simple, Active; B) Future Perfect, Passive; C) Present Perfect, Active; D) Past Simple, Passive. Nowadays medicinal plants are used both in traditional and scientific medicine. A) Present Continuous, Active; B) Present Simple, Passive; C) Present Perfect, Active; D) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive. My mother has been working as a pharmacist for 25 years. A) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive; B) Present Perfect, Passive; C) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; D) Present Perfect, Active. The decoction administered by the doctor will have been prepared by 5 o’clock tomorrow. A) Future Continuous, Active; B) Future Simple, Passive; C) Future Perfect, Passive; D) Future Perfect Continuous, Active. We are listening to a very interesting lecture about proprietary names of drugs at the moment. A) Present Perfect, Passive; B) Future Continuous, Active; C) Present Simple, Passive; D) Present Continuous, Active. Were the students ready to speak on the types of drug forms last week? A) Past Continuous, Active; B) Past Simple, Active; C) Past Simple, Passive; D) Past Perfect, Active. Patients had aired their wards by 3 o’clock yesterday. A) Past Perfect, Active; B) Past Simple, Active; C) Past Perfect, Passive; D) Past Continuous, Active. Recently the scientists have developed a new drug for treating diabetes mellitus. A) Past Continuous, Active; B) Present Perfect Continuous, Active; C) Past Simple, Active; D) Present Perfect, Active. Several students of our group will be working at the laboratory at 12 o’clock on Monday. A) Future Simple, Active; B) Future Continuous, Active; C) Future Perfect, Passive; D) Future-in-the-Past, Active. Recently she has done a brilliant report on oxides and carbonates. a)Present Perfect, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d) Present Perfect Continuous, Passive The remedy is being prepared by an experienced chemist now. a) Present Continuous ,Active b)Present Continuous, Passive c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d)Past Continuous, Passive The roots of this plant are used for preparing decoctions. a) Present Indefinite, Active b) Present Indefinite, Passive c) Present Continuous ,Active d) Present Continuous, Passive The pharmacists had enumerated the side effects of the new medicine by the end of the seminar. a) Past Perfect , Active b)Past Perfect, Passive c) Past Indefinite, Passive d) Past Indefinite, Active They have been performing the experiment since nine o’clock. a) Present Perfect Continuous, Active b) Present Perfect, Passive c) Present Continuous ,Active d) Present Perfect, Active Children become often addicted to cough syrups. a) Present Indefinite, Active b) Present Indefinite, Passive c) Present Perfect, Active d) Present Perfect, Passive. The clinical trials of this drug have just been completed successfully. a) Present Perfect, Passive b)Present Perfect, Active c) Present Perfect Continuous, Active d) Past Perfect, Passive The patient’s family insisted on prescribing him sedative drugs. a) Past Indefinite, Active b) Past Indefinite, Passive c) Past Continuous, Passive d) Past Continuous, Active Has the doctor already used chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy for the treatment of this leukemic patient? A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Indefinite. The patient was suffering from asthma attack from 5 till 6 o’clock on Monday. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. The delegation will have visited all of the departments in the regional hospital by 2 o’clock tomorrow. A) Present Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Future Perfect; D) Future Continuous. The caries process doesn’t have an inevitable outcome. a) Past Perfect b) Past Indefinite c) Present Indefinite d) Present Perfect My sister has been ill for a week. a) Past Perfect b) Past Indefinite c) Present Perfect d) Future Indefinite The students will be listening to the lecture on squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue from eight till ten o’clock next Monday. a) Future Indefinite b) Future Continuous c) Future Perfect d) Present Perfect Last year this child grinded his teeth during sleep but he quitted the habit. a) Past Indefinite b) Past Perfect c) Present Perfect d) Present Continuous The whole summer my brother was learning English. a) Past Perfect b) Past Continuous c) Past Indefinite d) Present Perfect I shall not have translated the text “Interproximal Caries” by tomorrow. a) Future Continuous b) Present Perfect c) Future Perfect d) Future Indefinite The stomatologist is examining the mandibular vestibule. a) Present Indefinite b) Past Indefinite c) Present Continuous d) Future Perfect Many people died of tongue cancer in the USA last year. a) Present Perfect b) Past Indefinite c) Past Continuous d) Past Perfect The researchers had finished the experiment by the end of August. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Indefinite; D) Past Perfect. Our body assimilates proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other nutrients. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. Acute lymphocytic leukemia was progressing rapidly. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Perfect; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Continuous. Chromosomal rearrangement disturbed the normal control of cell division. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Perfect. The person receives one gene from mother and one from father. A) Present Continuous; B) Present Indefinite; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Perfect. I shall have done all the exercises by 7 o’clock. a) Past Perfect b) Future Perfect c) Past Indefinite d) Future Indefinite The students had translated the article before the bell rang. a) Past Continuous b) Past Perfect c) Present Indefinite d) Present Perfect Smoking and drinking contribute to the formation of cancer. a) Present Indefinite b) Future Indefinite c) Past Continuous d) Past Perfect Many people died of tongue cancer in the USA last year. a) Future Perfect b) Future Continuous c) Present Indefinite d) Past Indefinite She had prepared the report by the time you came. a) Past Continuous b) Present Indefinite c) Present Perfect d) Past Perfect The young scientist was trying to prove to the professor the necessity of the experiment. a) Present Perfect b) Past Perfect c) Past Continuous d) Future Continuous The scientists will have solved the problem by the end of the year. a) Past Perfect b) Past Indefinite c) Future Indefinite d) Future Perfect I opened the door and went into the ward. a) Present Indefinite b) Past Indefinite c) Present Continuous d) Past Continuous The students are examining the patient suffering from gastritis now. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Continuous; D) Future Perfect. The student had learnt everything about gastritis by Tuesday. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Perfect. This patient has suffered from acute myocardial infarction this year. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Past Indefinite; D) Past Perfect. Now the students are answering the teacher’s question how to strengthen the skeleton. A) Present Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Indefinite; D) Present Continuous. The doctors have already examined the patient’s severe soft tissue trauma. A) Future Perfect; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Perfect. The surgeons had finished the operation on the gallbladder by 3 o’clock. A) Present Perfect; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. Arteries, veins and capillaries form a circulatory system for the flow of blood. A) Present Continuous; B) Present Indefinite; C) Past Indefinite; D) Present Perfect. The cardiologist diagnosed myocardial infarction in this patient last week. A) Past Perfect; B) Past Indefinite; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Perfect. The patient suffering from gastritis will recover soon. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Continuous; C) Future Indefinite; D) Future Continuous. The doctor is applying the splint to the broken bone at the moment. A) Future Perfect; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Indefinite; D) Present Continuous. The Kovalenkos are famous cardiologists. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Indefinite; D) Future Indefinite. The burned tissues have already died. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Perfect. The stomach will begin to secrete the gastric juice soon after the operation. A) Past Indefinite; B) Future Indefinite; C) Past Continuous; D) Future Continuous. The pain starts on its own, but it gets worse. a) Past Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Present Indefinite d) Past Continuous Then we’ll use nitrous oxide which is also known as “laughing gas”. a) Future Continuous b) Future Indefinite c) Present Perfect d) Past Perfect Mary has already bought some anti-inflammatory medicines. a) Present Indefinite b) Present Continuous c) Present Perfect d) Past Perfect We have learnt the main components of a comprehensive dental examination this month. a) Past Continuous b) Past Perfect c) Present Continuous d) Present Perfect This helps dentists easily see the tiniest changes. a) Present Indefinite b) Present Perfect c) Past Indefinite d) Past Perfect Yesterday the medical students discussed the procedure of tooth implantation. a) Present Continuous b) Past Continuous c) Past Indefinite d) Future Indefinite The doctor is prescribing him soft diet right now. a) Present Continuous b) Present Perfect c) Past Continuous d) Past Perfect The physician will have filled in the case history by four o’clock on Monday. a) Present Indefinite b) Present Continuous c) Future Continuous d) Future Perfect The patient suffering from gastritis had left the hospital by Saturday. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The surgeons will have performed the transfusion of the whole blood before the beginng of the operation. A) Future Perfect; B) Present Continuous; C) Future Indefinite; D) Future Continuous. Not all heart diseases cause murmurs. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Continuous. Scientists have carried out experiments with blood transfusions for hundreds of years. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Past Indefinite; D) Past Perfect. Many patients had died by 1901. A) Present Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Indefinite; D) Future Continuous. The doctors suspected people to be infected with contaminated blood. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Perfect; C) Past Indefinite; D) Present Perfect. The stomach will begin to secrete the gastric juice soon after the operation. A) Present Indefinite; B) Future Indefinite; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Perfect. I was reading the article on corticovisceral theory the whole evening yesterday. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Perfect. I will try to enter the Medical University next year. a) Future Perfect b) Future Continuous c) Future Indefinite d) Present Indefinite The doctor will have discharged him from the hospital by Saturday. a) Future Perfect b) Future Continuous c) Future Indefinite d) Present Indefinite The teacher has already entered the room. a) Past Perfect b) Past Continuous c) Present Perfect d) Present Indefinite The student had passed all her exams by the end of December. a) Past Perfect b) Past Indefinite c) Past Continuous d) Present Indefinite The dentist is examining a patient at the moment. a) Past Perfect b) Present Perfect c) Present Continuous d) Present Indefinite Two days ago the doctor identified the problem with her jaw. a) Past Perfect b) Present Perfect c) Past Continuous d) Past Indefinite How long have you known this outstanding dental surgeon? a) Future Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Present Indefinite d) Present Perfect I was reading a scientific article on “Leukoplkia” from 5 till 6 o’clock on Monday. a) Past Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Indefinite d) Past Continuous The scientist has just exposed the rat to radiation to test his theory. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Indefinite. Acute bronchitis was progressing rapidly. A) Present Perfect; B) Past Perfect C) Future Continuous; D) Past Continuous. In 1901 the Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner discovered human blood groups. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Indefinite; C) Past Indefinite; D) Past Perfect. The students are experimenting on mice at the moment. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Continuous. The organism had absorbed the nutrients from the blood by the beginning of the therapy. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Perfect; C) Past Indefinite; D) Present Perfect. The course of the disease is chronic and the symptoms are continuous. A) Present Perfect; B) Future Indefinite; C) Present Indefinite; D) Past Indefinite. The gastrointestinal system includes the stomach, the duodenum, small and large intestines, etc. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. Both surgeons had finished gastrectomy by 11 o’clock last Monday. A) Future Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Present Perfect. Has the physician already examined the patient with knee cap fracture? A) Past Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. The patient has fully recovered after the electric injury. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. The surgeons are inserting a metal rod to keep the child’s spine straight at the moment. A) Present Perfect; B) Future Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Indefinite. The laboratory assistant will have analyzed the blood samples by tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. Have you ever been to London? A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. The surgeons had performed gastrectomy by 2 o’clock. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Has the dentist already examined the patient’s bite. a) Present Indefinite b) Present Perfect c) Present Continuous d) Past Indefinite The patient was suffering from severe toothache from 5 till 6 yesterday. a) Present Continuous b) Past Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Indefinite The scientist obtained much remarkable success in glossitis treatment. a) Present Perfect b) Past Perfect c) Present Indefinite d) Past Indefinite The researchers had finished the experiment by the end of August. a) Past Continuous b) Past Indefinite c) Future Continuous d) Past Perfect Deseased gums swell and detach from the tooth. a) Present Perfect b) Present Indefinite c) Past Continuous d) Past Perfect The students are examining the patient suffering from leukoplakia. a) Present Continuous b) Past Perfect c) Future Indefinite d) Present Perfect The patient suffering from oral herpes infection will recover soon. a) Future Continuous b) Future Indefinite c) Past Perfect d) Present Continuous The dentist will have removed the pulp before filling the tooth. a) Future Continuous b) Present Continuous c) Future Perfect d) Present Indefinite The TV program on the immune system will have finished by 2 o’clock. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Perfect. The nurse is performing electrospinal stimulation at the moment. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Continuous. I shall have taken medicines before the dinner. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The physician revealed neither gastric ulcer nor gastritis in this patient. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The scientists have profoundly investigated the causes and methods of prevention of atherosclerosis this year. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. The dentofacial surgeon will be operating on this patient tomorrow from 9 till 12. a) Present Continuous b) Future Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Continuous People who smoke and drink alcohol usually suffer from dental tartar. a) Present Indefinite b) Present Continuous c) Future Indefinite d) Past Continuous The patient complained both of high temperature and pain in the jaw. a) Present Continuous b) Present Perfect c) Past Continuous d) Past Indefinite Our task will be to investigate either the saliva or the gastric juice. a) Present Perfect b) Past Perfect c) Present Indefinite d) Future Indefinite The district doctor did not administer him either a bed regimen or a diet. a) Future Indefinite b) Past Indefinite c) Present Continuous d) Past Continuous The students will have written the test by two o’clock tomorrow. a) Present Indefinite b) Future Continuous c) Future Perfect d) Past Continuous We have already carried out the investigation. a) Present Perfect b) Past Perfect c) Present Continuous d) Past Continuous The teacher had explained the rule by the end of the lesson. a) Past Continuous b) Past Perfect c) Past Indefinite d) Present Perfect I shall have done all the exercises by 7 o’clock. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. When a long bone has achieved its full growth, an x-ray of the epiphysis has shown no evidence of the epiphyseal plate. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. John is going to the polyclinic at the moment. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Indefinite; D) Future Continuous. The sanitary transport has just delivered an injured in some accident person. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. He had never had nightmares before watching that horror-film. A) Present Continuous; B) Future Continuous; C) Past Indefinite; D) Past Perfect. Have you visited the anatomic museum recently? A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Continuous. He has not wiped the skin around the burn with alcohol yet. A) Present Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Because of pain in the knee Helen was going to the hospital for a long time, from 10 to almost 11 o’clock on Monday. A) Past Continuous; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Indefinite. My brother is a vegetarian. a) Future Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Present Indefinite d) Present Perfect He is having dinner now. a) Future Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Present Perfect d) Present Indefinite I shall have done all the exercises by 7 o’clock. a) Future Perfect b) Future Continuous c) Present Perfect d) Future Indefinite They had fulfilled their research work by Monday. a) Present Perfect b) Past Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Indefinite The tooth stopped aching two hours ago. a) Past Perfect b) Past Continuous c) Present Perfect d) Past Indefinite The dentist hasn’t determined the proper fit of a crown yet. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Present Indefinite I’ll be waiting for you at 9 o’clock tomorrow. a) Present Perfect b) Future Continuous c) Future Perfect d) Future Indefinite It takes me 10 minutes to get to the university. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Present Indefinite The scientist will have solved the problem by the end of the year. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. I was telling my parents about the harmful effect of fats of animals, milk and yolk products and even oleomargarine upon the cholesterol level in the blood for the whole evening yesterday. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Continuous. Beneath the periosteum there is a layer of immature cells, which deposit calcium-phosphorus compounds in the body tissue. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. Last year this patient had a severe fracture of one of sesamoid bones, namely the knee cap. A) Past Perfect; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. The musculosceletal system includes bones, muscles, and joints. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. Because of pain in the thigh Ann will be going to the hospital for a long time, from 11 to almost 12 tomorrow. A) Past Continuous; B) Future Continuous; C) Present Indefinite; D) Future Perfect. I have already massaged the frostbitten parts of the body. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. A dentist’s mirror has a wide range of uses. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Indefinite d) Present Indefinite Last Monday the teacher told us about the possible causes of dental fear. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Indefinite d) Present Indefinite The dentist will be taking the patient’s dental history at this time tomorrow. a) Future Indefinite b) Present Continuous c) Past Continuous d) Future Continuous She has gone to the dentist’s office. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Future Continuous Had you taken the medicines before you had dinner? a) Present Perfect b) Past Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Indefinite The dentist will not have examined the patient by 10 o’clock tomorrow. a) Future Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Future Indefinite d) Future Continuous The doctor is performing the surgery at the moment. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Continuous He hasn’t read the article ”Prevention of Dental Caries” yet. a) Present Perfect b) Present Continuous c) Past Perfect d) Past Continuous He will have finished writing his report on immunoglobulins by Tuesday. A) Future Continuous; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Perfect. The students will have written the test by 2 o’clock tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Will the doctors have discharged you from the hospital by Friday? A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The physician will have conducted medical checkup of this patient by 12.00 o’clock. A) Present Perfect; B) Future Perfect; C) Past Continuous; D) Future Indefinite. These affected tissues haven’t recovered for a long time. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The haematologist is making the morning round now. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Indefinite; C) Future Perfect; D) Present Continuous. Doctor Petrenko is measuring the patient’s blood pressure at the moment. A) Present Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Continuous. The cartilage layer cushions the bones at the place where they meet with other bones (joints). A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Future Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. Yesterday the patient took triparanol, a new drug for reducing blood cholesterol level . A) Past Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Continuous. Within the cortical bone there is a system of small canals containing blood vessels which bring oxygen and nutrients to the bone. A) Present Continuous; B) Future Continuous; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. Tom hasn’t felt well recently. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. The therapeutist will not have examined the patient by 10 o’clock tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Both the therapeutist and the gastroenterologist have come to the conclusion to treat him as an out-patient. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The oncologist will be making the morning round from 8 till 10 o’clock tomorrow. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. The traumatologist will be making the morning round from 8.30 till 10.30 next Monday. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Future Perfect; D) Past Perfect. I shall have taken medicines before dinner. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The researchers have solved the problem of diabetes mellitus. A) Present Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The teacher will have started a lecture on different types of immunity by 9 a.m. A) Past Perfect; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Indefinite. Your cholesterol level in the blood will soon rise. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Continuous. Spaces in cancellous bone contain red bone marrow. A) Future Continuous; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Indefinite; D) Present Indefinite. In an adult, the ribs, pelvic bone, sternum, and vertebrae, as well as the epiphyses of long bones contain red bone marrow within cancellous tissue. A) Past Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. The students will be listening to the lecture on measures for lowering blood cholesterol from eight till ten o’clock next Monday. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Future Continuous. The surgeons had performed gastrectomy by 2 o’clock. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. My aunt had broken her leg before the first of January. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Perfect. We have already carried out the investigation. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The gastroenterologist was making the morning round at this time yesterday. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Past Continuous; D) Future Indefinite. The anaesthesiologist was making the morning round at this time last Tuesday. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Continuous; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Perfect. The red marrow in the long bones is plentiful in young children, but decreases through the years. A) Past Indefinite; B) Future Indefinite; C) Present Indefinite; D) Present Continuous. Neither the doctor nor the nurse were in the consulting room. A) Past Continuous; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. I shall be preparing for the examination in Hematology all day tomorrow. A) Present Perfect; B) Future Continuous; C) Future Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. The doctor hadn’t seen that patient before. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The teacher has just explained the rule. A) Present Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Continuous. The therapeutist will not have examined the patient by 10 o’clock tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The district doctor did not administer him either a bed regimen or a diet. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The nurse was performing electrospinal stimulation at the moment yesterday. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Indefinite; C) Past Continuous; D) Future Continuous. The doctor won’t have discharged John from hospital by Tuesday. A) Future Perfect; B) Future Indefinite; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Perfect. I have known this orthopedist for seven years. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Future Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The doctor hadn’t seen that patient before. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Lately I have read an interesting article concerning muscular system in a popular scientific journal. A) Future Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Present Indefinite. Had you taken the medicines before you had dinner? A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The dentist will have filled in the tooth by 2.15 o’clock. A) Present Continuous; B) Present Perfect; C) Future Perfect; D) Future Indefinite. The nurse will be performing electrospinal stimulation at this moment tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Continuous; C) Future Perfect; D) Past Continuous. Will the doctors have discharged you from the hospital by Friday? A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The patient complained both of high temperature and of pain in the stomach. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Both the therapeutist and the gastroenterologist have come to the conclusion to treat him as an out-patient. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The doctor had given the patient some kinds of medicine by that time. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. The musculosceletal system includes bones, muscles and joints. A) Future Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Indefinite; D) Present Indefinite. This patient is wearing a plaster cast now. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Perfect. The man will have been unconscious by the arrival of the ambulance. A) Future Indefinite; B) Present Indefinite; C) Past Indefinite; D) Future Perfect. Mary has already bought some anti-inflammatory medicines at the chemists. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Past Perfect; D) Present Perfect. The doctor has just examined the patient’s back. A) Past Continuous; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Indefinite; D) Present Perfect. The drug for headache will have eliminated pain by 11 o’clock for sure. A) Future Continuous; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. This patient was wearing a plaster cast from September till November last year. A) Future Continuous; B) Past Indefinite; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Perfect. The students will have written the test by 2 o’clock tomorrow. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. She had prepared the report by that time. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Bones all over the body are of several different types. A) Present Continuous; B) Past Perfect; C) Future Indefinite; D) Present Indefinite. Sesamoid bones are small, rounded bones resembling a grain of sesame in shape. A) Present Continuous; B) Present Perfect; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. Our scientists will have fulfilled their investigation by January. A) Future Indefinite; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Future Continuous. The students had translated the article before the bell. A) Past Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. This patient will be wearing a plaster cast from December till February next year. A) Future Continuous; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Perfect. This volunteer nurse won’t have returned from South Africa by July. A) Future Continuous; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. The nurse has given an injection to a patient today. A) Present Perfect; B) Present Indefinite; C) Present Continuous; D) Past Indefinite. The ambulance has taken this boy to the hospital. A) Present Indefinite; B) Present Perfect; C) Future Perfect; D) Present Continuous. She won’t have told her husband about her disease by his birthday. A) Present Perfect; B) Future Perfect; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. They are learning the information on the disorders affecting the muscles, joints and bones now. A) Present Indefinite; B) Past Perfect; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Continuous. Cartilage cells slowly migrate away from the region of the plate. A) Future Indefinite; B) Past Continuous; C) Present Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. The doctor has just examined the patient suffering from atherosclerosis. A) Present Continuous; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Continuous. The scientists had developed a new affective and safe drug by the end of the year. A) Past Perfect; B) Future Perfect; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Continuous. The surgeons had finished gastrectomy by 12 o’clock yesterday. A) Future Perfect; B) Past Perfect; C) Present Continuous; D) Present Perfect. Atherosclerosis has affected the coronary arteries notably. A) Past Indefinite; B) Present Continuous; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Perfect. Lack of blood supply to the area triggers formation of calcium deposits in the bone. A) Past Continuous; B) Present Continuous; C) Future Continuous; D) Present Indefinite. The students were learning about a variety of disorders affecting the muscles, joints and bones the whole lesson yesterday. A) Past Perfect; B) Past Indefinite; C) Past Continuous; D) Present Continuous. The scientists will have fulfilled this important project by October. A) Future Perfect; B) Future Indefinite; C) Present Perfect; D) Past Indefinite. Виберіть правильну часову форму присудка: Placebos … widely… since the ancient times. a)are used b)are being used c)is used d)have been used Some essential oils …antiseptic effects . a)are produced b)is produced c) produce d) is producing This herbal tincture … ….by a homeopathic practitioner now ,wait a minute, please. a)is prepared b) is being prepared c)is prepare d) is preparing We … ….for the pharmacy manager for an hour already when he appeared. a)had been waiting b)have been waiting c)were waiting d) had been waited The term pharmacognosy … ….by the Austrian physician Schmidt in 1811. a)introduced b)was introduced c)will be introduced d)is introduced Doctor… parents about possible codeine side effects during his last visit. a) warned b)was warned c)warns d)will warn Next week the students … a practical lesson on the functions of the skeletal system. A) will have; B) has; C) shall be having; D) is having. Mixing incompatible blood groups always … to agglutination. A) was leading; B) is leading; C) leads; D) had lead. The surgeons … the operation by 3 o’clock. A) will be finishing; B) is finishing; C) will have finished; D) will finish. The physician … full physical examination of the patient suffering from heart disease at this time tomorrow. A) shall perform; B) will be performing; C) will have performed; D) was performing. The teacher … the results of the test on soft tissue traumas before the bell. A) is announcing; B) had announced; C) has announced; D) announced. The course of ulcer … already … to vary with age and sex, location of ulcers. A) shall … have proved; B) has … proved; C) were … proving; D) are … proving. The anatomy teacher … the students about the structure of the skull at the moment. A) were telling; B) is telling; C) will be telling; D) tells. Next week the doctor … a bone marrow biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. A) will perform; B) was performing; C) shall be performing; D) will have performed. He … to become a pharmacist since childhood. A) was dreaming; B) dreamed; C) has been dreaming; D) is. Nowadays medicinal plants … both in traditional and scientific medicine. A) is used; B) are used; C) were used; D) will be used. Studies to identify and quantify adverse drug effects … already. A) have been performed; B) were performed; C) are being performed; D) performed. Somebody … this pharmaceutical laboratory in 1963. A) building; B) builded; C) build; D) built. The report on deontology … at 3 o’clock yesterday. A) was being discussed; B) was discussed; C) will be discussed; D) discussed. A herbal tea or tisane … a herbal infusion made of the leaves of the tea bush. A) are; B) was; C) is; D) were. After 1901 blood transfusions … safer. A) became; B) become; C) becomes; D) was becoming. The surgeon … the operation on appendicitis yet. A) has not performed; B) was not performing; C) is not performing; D) did not perform. I … the paragraph on exacerbation of ulcers in the book which I … from you. A) had read; borrowed; B) read; borrowed; C) had read; had borrowed; D) read; had borrowed. The lecturer … the structure of the chest now. A) shows; B) is showing; C) showed; D) will be showing. Another type of soft tissue trauma … cold injury which includes hypothermia. A) are; B) is; C) shall be; D) were. The transfusion … if a person doesn’t have any antibodies against the donor blood’s antigens. A) worked; B) will work; C) is working; D) has worked. The students … anything about gastritis yet. A) did not learn; B) have not learnt; C) were not learning; D) are not learning. The scientist … his research work by October. A) finish; B) will finish; C) will have finished; D) will be finishing. James Herrick … myocardial infarction in 1912. A) described; B) will describe; C) was describing; D) has described. Investigation based on the effects of … (2500) medicinal plants found in the Carpathians is carried out by this young botanist. A) twenty five nought nought; B) two hundred five thousand; C) twenty-five hundred; D) two thousand five hundred. The patient suffering from the severe form of hepatitis was hospitalized yesterday. He is in … (ward № 2). A) ward two; B) the second ward; C) the ward number two; D) the ward second. The book which is widely used by the students of all farmaceutical faculties was published on … (January, 25, 1990). A) the twenty-fifth of January, one thousand nine hundred and ninety; B) January twenty-five, nineteen ninety; C) the twenty-fifth of January, nineteen ninety; D) the January twenty-fifth, nineteen-ninety. To receive the desired sedative effect one must take … (1/3) of the tincture and wait nearly … (1/2) an hour. A) one third, one second; B) one third, half; C) third, second; D) one three, half. If this medicine contains more than … (7,55) mg of an active substance, it will be more effective. A) seven point five five; B) seven point fifty five; C) seven five five; D) seven point half. The doctor … this patient at 3 p.m. tomorrow. A) shall examine; B) will have examined; C) examined; D) will be examining. A physician … for sounds of turbulent blood flow (called bruits) yet. A) doesn’t listen; B) hasn’t listened; C) listened; D) will not listen. Karl Landsteiner … two distinct chemical molecules on the surface of the red blood cell many years ago. A) observes; B) will observe; C) observed; D) is observing. They … the alimentary tract before they began performing gastroenteroscopy. A) have studied; B) has studied; C) had studied; D) studied. New methods of treatments …usually… on study groups. a)are… tested b)are… being tested c)is…being test d)is… tested Some tinctures …antiseptic effects . a) produce b)is produced c)has produced d) is producing This herbal tea …. just… . a)is… prepared b) is ..being prepared c)has been… prepared d)is… preparing The pharmacy manager …….. on the phone now. Wait a minute, please. a)has been talking b)have been talking c)is talking d)are talking The Austrian physician Schmidt …the term pharmacognosy in 1811. a)introduced b)was introduced c)will be introduced d)were introduced Baby’s parents… about possible addiction to codeine at their visit to the doctor tomorrow . a)has warned b)was warned c)warns d)will be warned The cardiologist … all his patients by the end of his working day. A) will examine; B) will be examining; C) will have examined; D) don’t examine. Cardio-vascular diseases … mainly in people over 45. A) was occurring; B) occurs; C) is occurring; D) occur. The traumatologist … this patient with broken bones , when I entered the ward. A) was examining; B) examined; C) is examining; D) will be examining. The blood … salty taste and faint odour. A) is possessing; B) possesses; C) possessed; D) had possessed. The second year students … Anatomy last year. A) has studied; B) was studying; C) studied; D) had studied. My friend … English before he entered the University. A) is studying; B) has studied; C) studied; D) had studied. The surgeons … on the patient today. A) haven’t operated; B) didn’t operate; C) wasn’t operating; D) operated. My sister … from the sanatorium by the end of the week. A) returned; B) will be returning; C) will have returned; D) will return. Use of drugs … unless the expected benefits outweigh the possible risks. A) are not justfied; B) is not justfied; C) don’t justfied; D) doesn’t justfied. Helen … for her examination in organic chemistry for two hours. A) is preparing; B) was preparing; C) has been preparing; D) prepares. We … a chemist’s shop for 10 minutes before we found it. A) had been looking for; B) have been looking for; C) were looking for; D) looked for. Different symbols used to represent the pharmacy profession … by the lecturer now. A) show; B) are showed; C) are being shown; D) is being showed. By 8 o’clock the surgical operation … . A) will be finished; B) will have been finished; C) will finish; D) shall have been finished. This pharmaceutical plant … in 1980. A) was built; B) was build; C) is built; D) has been built. Last week we … a test paper on bone structure. A) had written; B) has written; C) wrote; D) have written. He … as a gastroenterologist since 1996. A) is working; B) will be working; C) has worked; D) worked. The nurse said that the doctor … him soft diet. A) prescribes; B) had prescribed; C) has prescribed; D) is prescribing. The physician … you about the circulation of blood tomorrow. A) will tell; B) was telling; C) is telling; D) tells. The doctor … just … the patient’s back. A) was … examining; B) did … examine; C) has … examined; D) is … examining. Students … already … an interesting article about homeopathic medicine. A) had discussed; B) discussed; C) are discussing; D) have discussed. Phytomedicines … increasingly in Western Europe now. A) were used; B) are being used; C) have been used; D) is used. Pharmacodynamics … the physiological effect of drugs on the body. A) studies; B) study; C) is studying; D) has studied. By 2 o’clock medicines prescribed by a doctor … . A) will be dispensed; B) will have been dispensed; C) had dispensed; D) were dispensed. Thousands of plant and animal products used in treatment of various diseases … in books of ancient physicians. A) will be described; B) is described; C) were described; D) have been described. Peppermint oil … in insomnia. A) is used; B) are used; C) were used; D) has been used. The pain … worse on deep breathing in and coughing. A) become; B) becomes; C) have become; D) are becoming. The blood … a viscous fluid tissue possessing many various functions. A) shall be; B) were; C) are; D) is. The physician … the case history of the patient suffering from gastritis by the end of the week. A) shall fill in; B) will be filling in; C) will fill in; D) will have filled in. Neither the doctor nor the nurse … where the patient … . A) had known, shall go; B) knew, had gone; C) is knowing, go; D) were knowing, have gone. I … never … a hematologist before. A) was … visiting; B) have … visited; C) shall … visit; D) will … have visited. The patient … acute stomachache after he … the prescribed analgesics. A) won’t feel, will take; B) won’t feel, has taken; C) won’t have felt, will take; D) won’t be feeling, will have taken. When the doctor entered the ward, he … that the nurse … the patient’s blood pressure. A) has seen, is measuring; B) had seen, measured; C) saw, was measuring; D) saw, has measured. The musculoskeletal system … bones, muscles, and joints. A) were including; B) include; C) is including; D) includes. Only natural substances… for making homeopathic remedies. a)are used b)are being used c)is used d)have been used Many synthetic drugs… side effects . a)are produced b)is produced c) produce d) is producing The pharmacist …your mixture. Wait a minute, please . a)is prepared b) is being prepared c)is prepare d) is preparing The patients …for their doctor at the ward from 9 till 10 o’clock yesterday . a)had been waiting b)have been waiting c)were waiting d) had been waited Samuel Hahnemann … some methods of homeopathic treatment 200 years ago. a)introduced b)was introduced c)will be introduced d)is introduced Baby’s parents …about this drug side effects during their next visit. a)warns b)was warned c)was warning d)will be warned We … the formation and structure of bones during the whole lesson yesterday. A) was learning; B) were learning; C) learned; D) learns. … you … the doctor recently? A) Did … see; B) Have … seen; C) Are … seeing; D) Do … see. When he … the operating room, the surgeon … already … the operation. A) was entering, is … finishing; B) will enter, will … have finished; C) entered, had … finished; D) had entered, didn't … finish. I … from the hospital by 6 o’clock. A) shall have returned; B) will return; C) shall be returning; D) am returning. We … different investigation last term. A) are making; B) have made; C) made; D) had made. At the moment a young scientist … the distinction of the compounding pharmacy. a) are explaining b) are being explained c) is explaining d) have been explained Yesterday some prescription drug … without a prescription from a licensed professional . a) dispensed b) is dispensed c) were dispensed d) is dispending She … some information about inorganic chemistry when her friend entered the room. a) looked for b) was looking for c) had been looking for d) had looked for This postgraduate student … properties of some hard material for a whole year. a) has been investigating b) have been investigating c) was investigating d) had investigated Drugs … only the rate at which existing biological functions proceed. a) affected b) was affected c) will affect d) affect Parents usually … the instructions on the medication bottle before giving it to their child. a) learn b) learned c) was learning d) will have learned Yesterday the student … the teacher’s questions how to strengthen the skeleton. A) doesn't answer; B) hasn't answered; C) didn't answer; D) hadn't answered. - Where were you at 2 p.m. yesterday? - I … to the hospital at that time. A) was going; B) had gone; C) will have gone; D) went. The doctor … just … large blisters. A) was … opening; B) has … opened; C) is … opening; D) will … open. Now he was glad he … to be operated on the esophagus. A) did not agree; B) has not agreed; C) had not agreed; D) was not agreeing. They … their research work by Monday. A) will have fulfilled; B) will fulfill; C) will be fulfilling; D) fulfils. We … anatomy and physiology of the liver at the next lesson. A) shall study; B) shall be studying; C) shall have studied; D) won't be studying. … the doctor … this patient with broken bones tomorrow? A) Did … examine; B) Will … examine; C) Has … examined; D) Will … have examined. - May I call you tomorrow at 10 a.m.? - You’d better call me in the afternoon, because I … the morning round from 9.00 till 11.00 o’clock. A) makes; B) shall be making; C) made; D) will make. … you ever … novocaine solution in burns? A) Did … use; B) Have … used; C) Was … using; D) Had … used. After the doctor … the patient all over, he advised him to visit gastroenterologist as he suspected some serious liver and gallbladder problems. A) was examining; B) had examined; C) examined; D) has examined. We … the report by 4 o’clock in the afternoon. A) shall discuss; B) shall be discussing; C) shall have discussed; D) discusses. The dentist … the proper fit of a crown yet. a) will have determined b) isn’t determining c) hasn’t determined d) determined At the moment the dental surgeon … on the maxilla. a) is operating b) operated c) operates d) was operating What procedure … the dentist … now? a) will perform b) has performed c) is performing d) had performed Last week we … a test paper on the pharmacological techniques of managing dental fear. a) will write b) wrote c) has written d) write The dentist … my tooth when I suddenly felt acute pain. a) was drilling b) had drilled c) is drilling d) drilled … you ever … to Chicago? a) had been b) have being c) have been d) have be Because of mistake we … the patient to additional radiation. a) have exposed b) is exposing c) exposes d) will have exposed My friend … Biology and Chemistry before he entered the university. a) studied b) had studied c) is studying d) studies I … to enter the Medical University next year. A) will be trying; B) shall have tried; C) shall try; D) won't have tried. Last week we … a test paper on bone structure. A) wrote; B) have written; C) had written; D) was writing. The student … for the exam the whole day tomorrow. A) will prepare; B) will be preparing; C) is preparing; D) will have prepared. The traumatologist … just … the child with sports trauma. A) has … examined; B) had … examined; C) was … examining; D) will … examine. Last week he had gastro- and enterocolitis because the unabsorbed and undigested components of food … from his body for almost three days. A) hadn't evacuated; B) weren't evacuating; C) haven't evacuated; D) hasn't evacuated. The student … a test yesterday. A) has written; B) had written; C) were writing; D) wrote. The teacher … the function of bile by the end of the lesson. A) will be explaining; B) will explain; C) won't be explaining; D) will have explained. … the lecturer … the structure of the chest yesterday? A) Was … explain; B) Did … explained; C) Has … explained; D) Did … explain. We … to the orthopaedist explaining us the difference between gout and pseudogout for almost an hour on Monday. A) listened; B) have listened; C) were listening; D) had listened. She … these bites and swellings today. A) saw; B) has seen; C) was seeing; D) had seen. Yesterday the medical students discussed the procedure of appendectomy which they … the day before yesterday. A) had watched; B) were watching; C) watched; D) has watched. The investigator … this problem last month. A) has solved; B) solved; C) had solved; D) were solving. The patient … fully … by the end of the month. A) will … recover; B) will have … recovered; C) will … be recovering; D) was … recovering. When they entered the ward the doctor … the patient’s face and neck. a) is examining b) have examined c) was examining d) examines Smoking and drinking … to the formation of cancer. a) contribute b) was contributing c) will becontributing d) has contributed The whole lesson yesterday they … the main rules of dental history taking. a) is learning b) had learned c) was learning d) were learning … you … to the doctor today? a) Have spoken b) Did speak c) Do speak d) Does speak Yesterday the dentist … computed tomography to identify a tumour. a) have used b) has used c) used d) uses She … just … the nurse in the hall. a) has seen b) was seeing c) sees d) have seen I … TV when she arrives tonight. a) am watching b) will be watching c) was watching d) will watch … you … English before you moved to New York? a) Have studied b) Had studied c) Did study d) Do study Last Monday the teacher … us about the structure of the skull. A) tells; B) told; C) will tell; D) has told. I … my district doctor from 2 till 7 o'clock. At last he … at eight o'clock in the evening. A) had rung, answered; B) was ringing, answered; C) had rung, was answering; D) was ringing, was answering. The boy … soft tissues injury this week. A) had; B) has had; C) was having; D) have. The patient … fully … after the operation on duodenum by November. A) had … recovered; B) has … recovered; C) was … recovering; D) didn't … recover. The liver … aching two hours ago. A) has stopped; B) had stopped; C) stopped; D) will have stopped. I … the text "The Liver" into Ukrainian by the time my mother comes home. A) shan't have translated; B) will be translating; C) shall translate; D) won't be translating. We … the skeletal structure in Anatomy. A) learn; B) learns; C) is learning; D) has learned. The doctor … him from the hospital by Saturday. A) will be discharging; B) will have discharged; C) shan't discharge; D) will discharge. … you … to the doctor today? A) Did … speak; B) Was … speaking; C) Have … spoken; D) Had … spoken. At the moment the dental surgeon … on the maxilla. a) operates b) is operating c) were operating d) operated Tomorrow from 8 till 9 o’clock the doctor… the patient’s delicate items with an ultrasonic cleaner. a) is cleaning b) was cleaning c) will be cleaning d) will have cleaned The nurse … just … analgesics to the patient suffering from toothache. a) was … giving b) is … giving c) had … given d) has … given Ann is busy. She … the methods of salivary gland. a) studies b) is studying c) studied d) was studying Two days ago the doctor … the problem with her jaw. a) will identify b) has identified c) identified d) was identifying I’m sorry. I … the thermometer. a) have broken b) broke c) was breaking d) am breaking Yesterday the dentist … computed tomography to identify the tumour. a) was using b) used c) has used d) had used … you … to the doctor today? a) Are…speaking b) Did … speak c) Have … spoken d) Were … speaking He … the Medical University last year. A) has entered; B) had entered; C) entered; D) were entering. He … me that he … his exam in Anatomy at three o'clock. A) told, was passing; B) tell, had passed; C) had told, was passing; D) have told, passed. … you … the textbook which you … in the morphological academic building before? A) Did … find, had lost; B) Were … finding, were loosing; C) Has ... found, has lost; D) Had … found, lost. These drugs … blood vessels to bring oxygen and nutrients to the bone in an hour. A) is helping; B) has helped; C) will help; D) had helped. I … this doctor for 5 years. A) knew; B) had known; C) was knowing; D) have known. When we entered the ward, we saw that the nurse … an injection to the patient suffering from some stomach disease. A) made; B) has made; C) was making; D) were making. The doctor … him soft diet right now. A) prescribes; B) will have prescribed; C) is prescribing; D) don’t prescribe. … he still … this article “Hepatic Diseases”? – No, he … just … it. A) Did … read, was … reading; B) Is … reading, has … read; C) Are … reading, have … read; D) Shall … be reading, will … read. My friend … Biology and Physics very persistently before he … the Medical Institute. A) had studied, entered; B) has studied, has entered; C) was studying, was entered; D) studied, had entered. The students … everything ordered by the anaesthetist. Now they can leave the hospital. A) has done; B) was doing; C) did; D) have done. The doctor … a sample of joint fluid now. A) was taking; B) will be taking; C) is taking; D) take. The surgeon … on this patient tomorrow from nine till twelve. A) will be operating; B) operates; C) will have operated; D) was operating. The dentist … the patient at 3 p.m. tomorrow. a) shall examine b) will have examined c) examined d) will be examining The oncologist … treatment to the patient suffering from tongue cancer yet. a) doesn’t administer b) hasn’t administered c) administered d) will not administer Survival rates for oral cancer … on the precise site, and the stage of the cancer diagnosis. a) depends b) is depending c) depend d) was depending The scientist … his research work by October. a) finish b) will finish c) will have finished d) will be finishing In the 1890s W.D. Miller … a series of studies to propose an explanation for dental caries. a) was conducting b) conducted c) has conducted d) had conducted I … the article on bruxism in the book which I … from you. a) had read; borrowed b) red; borrowed c) had read; had borrowed d) read; had borrowed I … my friends about the harmful effect of smoking and drinking upon oral health for the whole evening yesterday. a) was telling b) told c) had told d) am telling The doctor … me from the hospital by 3 o’clock tomorrow. a) will discharge b) will be discharging c) will have discharged d) have discharged I … the text “The Liver” yet. A) didn’t read; B) haven’t read; C) am not reading; D) hadn’t read. I … an excellent mark in anatomy tomorrow, if I … the main principles of bone formation. A) shall get, know; B) shall get, shall know; C) gets, knows; D) have got, have known. The ambulance … when some doctor passing by … already … him the first aid. A) had arrived, didn’t … give; B) arrived, were … giving; C) will have arrived, has … given; D) arrived, had … given. The periosteum … a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane. A) shall be; B) have been; C) were; D) is. At the moment the surgeon … on the patient suffering from the knee cap fracture. A) were operating; B) is operating; C) has operated; D) operated. The doctors … on the patient today. A) hasn’t operated; B) haven't operated; C) wasn’t operating; D) operated. The doctor … that the patient … the medicines. A) knew, hadn't taken; B) knows, weren't taking; C) had known, took; D) was knowing, had taken. The professor … us many interesting things concerning alimentary tract he had heard at the conference of gastroenterologists. A) has told; B) told; C) had told; D) were telling. Next week the dental hygienist … him to reduce consumption of carbohydrate food. a) will be advising b) have advised c) will advise d) will have advised The teacher … already … the room. a) have entered b) had entered c) has entered d) will have entered The investigator … this problem last month. a) has solved b) have solved c) solves d) solved They … their research work by last Monday. a) fulfilled b) had fulfilled c) will fulfill d) will have fulfilled I … all the exercises by 7 o’clock. a) shall have done b) is doing c) did d) has done There … many types of medicines in that drug cabinet. a) has b) are c) was d) being … dental fear … to the fear of dentistry and of receiving dental care? a) Do … refers b) Does …. refer c) Was … refer d) will … have referred This patient … about his immediate complaints now. a) is telling b) was telling c) tells d) told He … the text about gastritis before they come back. A) will translate; B) will have translated; C) is translating; D) had translated. Tomorrow from eight till nine o'clock the doctor … the patient suffering from pain in his joints. A) shall examine; B) was examining; C) will be examining; D) will have examined. As you … older, small bones … together to make big ones. A) grows, joins; B) has grown, shall join; C) will grow, will join; D) grow, will join. The nurse … just … analgesics to the patient suffering from pain in his muscles. A) will … give; B) had … given; C) has … given; D) is … giving. I … the nurse in the ward when I was passing by. A) was seeing; B) saw; C) had seen; D) has seen. My friend … English before he … the University. A) will study, had entered; B) is studying, was entering; C) has studied, has entered; D) had studied, entered. The physician … the case history by four o’clock on Monday. A) fills in; B) have filled in; C) were filling in; D) will have filled in. Next week we … a practical lesson dealing with the functions of the skeletal system. A) have had; B) had had; C) shall have; D) is having. The nurse … electrospinal stimulation at this time tomorrow. A) will perform; B) will be performing; C) are performing; D) will have performed. Now he was glad he … to be operated on the mandible. a) have not agree b) has not agreed c) had not agreed d) will not agree After the dentist … the patient, he advised him to visit dentofacial surgeon as he suspected oral cancer. a) will examine b) was examining c) examines d) had examined The professor … just… us many interesting things concerning dental abnormalities. a) has … told b) have … told c) had … told d) will … have told Last Monday the teacher … us about the possible causes of dental fear. a) tells b) told c) was telling d) had told Next week we … a practical lesson on the methods of dentophobia treatment. a) have b) had c) will have d) have had Yesterday the student … the teacher’s question. a) was not answering b) has not answered c) had not answered d) did not answer We … the instruments dentists use in their everyday practice during the whole lesson yesterday. a) are learning b) were learning c) learned d) have learned These drugs … bad toothache in a quarter of an hour. a) relive b) will relive c) are reliving d) were reliving How long … you … this outstanding physician? A) did … know; B) do … know; C) have … known; D) are … knowing. When … they … the operation? A) did … finish; B) have … finished; C) was … finishing; D) did … finished. The doctors … the decision before I … . A) has taken, came; B) had taken, came; C) are taking, comes; D) took, had come. My sister … from the sanatorium by the end of the week. A) will have returned; B) returns; C) will return; D) returned. This nurse … an injection to the patient now. A) make; B) is making; C) made; D) has made. We … an individual muscle. A) isn't contracting; B) wasn't contracting; C) doesn't contract; D) don't contract. … you … in hospital this month? What … ? A) Have … been, has happened; B) Had … been, had happened; C) Were … being, happened; D) Did … were, happened. I … the temperature 10 minutes ago. A) have taken; B) took; C) had taken; D) was taking. They … to the University at 8 o’clock, the lesson … already…. A) doesn't get, didn't … start; B) weren't getting, was … starting; C) didn't get, had … started; D) hadn't got, has … started. We … the physiological functions of the stomach by the end of the lesson. A) shall learn; B) shall have learnt; C) are learning; D) will be learning. When they entered the ward the doctor … the patient’s back. A) is examining; B) will be examining; C) was examining; D) has examined. Nelly … never … a dentist yet. A) did … visit; B) has … visited; C) had … visited; D) was … visiting. I … the nurse in the ward when I was passing by. a) was seeing b) saw c) will see d) had seen She … just … the nurse in the hall. a) has … seen b) was … seeing c) will … see d) had … seen The students … everything ordered by the dentist. Now they can leave the clinic. a) have done b) were doing c) has done d) will have done He … the text before they come back. a) will translate b) is translating c) will have translated d) was translating My sister … from the sanatorium by the end of the week. a) will have returned b) returns c) will return d) returned We … different investigations last term. a) have made b) had made c) were making d) made He … him since January. a) did not see b) has not seen c) was not seeing d) had not seen I … the text “Prevention of Dental Caries” yet. a) have not read b) did not read c) will not read d) do not read … each striated muscle … of a body and two attachments? A) Does … consist; B) Is … consisting; C) Has … consisted; D) Had … consisted. She … those bites and swellings yesterday. A) saw; B) has seen; C) was seeing; D) had seen. The ambulance … when we … already … him. A) arrived, had … helped; B) arrive, didn't … help; C) was arriving, has … helped; D) have arrive, were … helping. She … the prescribed drugs for diarrhea before she … stomachache. A) will have taken, feels; B) took, felt; C) is taking, will feel; D) will take, will be feeling. The doctor’s assistant … a brace on my back when suddenly I felt acute muscular pain. A) put; B) puts; C) was putting; D) had put. How long … you … sick? A) were … being; B) had … been; C) have … been; D) are … be. Two days ago she … serious injuries. A) has got; B) had got; C) got; D) gets. Personal hygiene care … of proper brushing and flossing daily. a) is consisting b) consists c) have consisted d) had consisted The dental surgeons … on the patient today. a) have operated b) will have operated c) had operated d) has operated I … this dentist for 10 years. a) know b) knew c) have known d) is knowing … he still … the article “Dental Pathologies”? a) was … reading b) does … read c) did … read d) is … reading If you … smoking, your risk of oral cancer development … . a) won’t quit … will rise b) don’t quit … will rise c) won’t quit … rise d) didn’t quit … will rise The students … the article before the bell rang. a) had translated b) have translated c) translated d) will have translated We … benign tumours of the oral cavity the whole lesson yesterday. a) are discussing b) were discussing c) will be discussing d) discussed My brother … to enter the university next year. a) tried b) has tried c) will try d) will have tried Ann … the main principles of food digestion by that time. A) are learning; B) were learning; C) have learnt; D) had learnt. People who smoke and drink alcohol usually … from peptic ulcer. A) is suffering; B) will have suffered; C) suffer; D) has suffered. Our group-mate … from the seaside before the academic year … . A) will have returned, begins; B) returned, have begun; C) is returning, will begin; D) will return, will be beginning. Look, the surgeon … a metal rod to keep the spine straight. A) insert; B) had inserted; C) shall have inserted; D) is inserting. The gastroenterologist … him to keep to a diet. A) will be advising; B) will have advised; C) shan't have advised; D) will advise. Yesterday I … up to my district doctor but nobody… . A) had rung, had answered; B) have rung, has answered; C) was ringing, was answering; D) rang, answered. Helen … English well because she … in the USA. A) speak, lived; B) is speaking, had lived; C) are speaking, lives; D) speaks, has lived. The gastroenterologist … that he … everything possible to prevent proctorrhagia in this patient. A) ensured, had done; B) have ensured, have done; C) had ensured, did; D) was ensuring, were doing. The patient … acute stomachache after he … the prescribed analgetics. A) won’t feel, has taken; B) won’t have felt, will take; C) doesn’t feel, will have taken; D) will be feeling, will be taking. … the shoulder girdle … the upper extremity with the trunk? A) Do … connect; B) Are … connecting; C) Have … connected; D) Does … connect. They … the information on a variety of disorders which affect the muscles, joints and bones the whole lesson yesterday. A) learnt; B) was learning; C) has learned; D) were learning. Вставте пропущене модальне дієслово чи еквівалент: … you retell this text? A) has; B) can; C) is; D) have. The blood in the veins of the liver … attain the temperature of 39,7°C. A) may; B) was permitted; C) can to; D) ought. Your grandmother … visit a cardiologist at 10 o’clock tomorrow. A) has; B) could; C) won’t be able; D) is to. I … to get an excellent mark in Anatomy if I learn the main principles of bone formation. A) wasn’t allowed; B) will be able; C) must; D) have. My friend … speak English perfectly well. a) can b) may c) ought d) is I … play the guitar. a) am b) have c) can d) ought She … be at the laboratory now. a) have b) ought c) must d) are You … take my English textbook. a) may b) have c) will be able d) had My daughter … to be examined by an odontologist. a) must b) should c) ought d) may … he play the piano? A) ought; B) is; C) must to; D) can. He … be an experienced haematologist. A) must; C) will be able; B) need; D) doesn’t have. The rate of heartbeat … increase depending on different emotions. A) wasn’t able; B) should to; C) may; D) has. Dr. Kovalchuk … meet the famous professor from London at 7 a.m. at the railway station. A) might to; B) is; C) is to; D) has. The doctor … discover mild scoliosis during a routine physical examination. A) is; B) may; C) has; D) will be able. The students … read and translate the article about digestion without dictionary. A) can’t; B) don’t have; C) mustn’t; D) oughtn’t. You … to follow the doctor’s advice. A) can; B) may; C) must; D) ought. He … be at the university now. A) need; B) is; C) must; D) has. You… follow the doctor’s advice. a) have b) must c) are d) ought The lecturer… speak so fast. a) is b) have c) has d) shouldn’t Children … sleep nine hours a day. a) must b) ought c) have d) will be able She … to see the dentist yesterday. a) has b) must c) is d) was I … believe it’s finally happening, can you? a) could b) can’t c) can d) couldn’t I … come to the polyclinic tomorrow. I’ll be busy. A) won’t be able to; B) am able; C) can’t; D) will be permitted. The doctor … insert a metal rod during surgery to keep the patient’s spine straight. A) is; B) ought; C) should; D) was able. This student … operate a tomography computer very well. A) can; B) may to; C) was; D) is allowed. You … follow the doctor’s advice. There is no other way out for you. A) can; B) must; C) may; D) should. The patient … feel fatigue in the back after prolonged sitting or standing. A) has; B) will be able; C) may; D) is. The man … be afraid , but he … undergo the operation. A) may, must; B) must, oughtn’t; C) is, is; D) must to, may to. A doctor … listen to the breathing sound, using a stethoscope. A) can; B) has; C) is; D) was allowed. An orthopedist … to examine the child with scoliosis at 2 o’clock tomorrow. A) should; B) must; C) is; D) shall be permitted. We … see a filterable virus through a usual microscope. A) mustn’t; B) shouldn’t; C) can’t; D) oughtn’t to. The doctor … be ready to answer all the patient’s questions. A) must; B) need; C) ought; D) have. I am sorry I am late. … I come in? A) Can; B) May; C) Could; D) Ought. You … to visit your cardiologist more often. A) must; B) ought; C) can; D) may. In jaundice the skin and the sclerae take on a yellowish colour which … vary in its intensity. A) ought; B) should; C) is; D) may. The students … translate this article without a dictionary. A) have; B) can; C) need; D) was able. In six months we … to read English medical journals. A) must; B) shall be able; C) can; D) should. … I ask you to do me a favour?. a) May b) Will be able c) Ought d) Am The dentist… be ready to answer all the patient’s questions concerning oral candidоsis. a) need b) must c) ought d) have No matter how hard he tried, the doctor… help the patient. a) can’t b) mustn’t c) couldn’t d) may not We… wait for the nurse any longer. a) can b) must c) can’t d) should … the surgeon start operating immediately? a) Have b) Must c) Are d) Ought You … fill in the tooth, otherwise you’ll lose it. A) must; B) ought; C) should to; D) can. The doctor … determine many cardiac diseases by heart sounds. A) can; B) ought; C) are allowed; D) must to. She … to see a district doctor at 2 o’clock yesterday. A) is; B) were; C) may; D) was. You … see a doctor tomorrow. a) can b) should c) could d) ought … I ask you a question? a) Can b) May c) Have d) Should … you help me with this report, please? a) Can b) May c) Could d) Should The medicine … to be kept in a cool dark place. a) are b) could c) can d) is I have some free time. I … help her now. a) can b) may c) could d) should The leukemic cells … also invade different organs, including liver, spleen, lymph nodes, kidneys and brain. A) may; B) was allowed; C) need; D) could to. She … be an experienced therapeutist. A) ought; B) must; C) is; D) has. You … to visit a dentist twice a year. A) should; B) was; C) ought; D) must. This sportsman … run 100 m in 13 seconds. A) was; B) ought; C) is; D) can. Ann … go to the polyclinic with her sister. A) may; B) must to; C) cannot to; D) should. You … talk aloud in the hospital. A) must not; B) must to; C) aren’t; D) has to. This medicine … to be kept in a cool dark place. A) will be able; B) can; C) could; D) is. In six months he … to read English medical journals. A) can; B) must; C) will be able; D) should. … you jump so high? A) Must to; B) Can; C) Is; D) Ought. She … be in the library now. A) are to; B) must to; C) may; D) could to. … you retell this text? a) has b) can c) is d) have Your grandmother … to visit a dentist at 10 o’clock. a) have b) could c) can d) is I … to get an excellent mark in Anatomy if I learn the structure of teeth. a) wasn’t allowed b) will be able c) must d) have He … be an experienced dentist. a) must b) need c) will be able d) doesn’t have You … to follow the doctor’s advice. a) can b) may c) must d) ought You … be very tired. A) may to; B) must; C) can to; D) is able. … the surgeon start operating immediately? A) Have; B) Can; C) Are; D) Ought. Heparin … be dangerous to use. Yet it … to be used in clinical practice. A) can, has; B) may not, have; C) may, must; D) must, can. I … to shake the medicine before using. A) am; B) must; C) can; D) has. … I trouble you for a glass of water? a) Must b) May c) Am d) Ought I…swallow the pill. a) didn’t have b) can’t c) haven’t d) will be able … I ask you to do me a favor? a) May b) Will be able c) Have d) Am He … be an inexperienced stomatologist. a) must b) should c) need d) has The patient … go anywhere. a) need b) is c) mustn’t d) hasn’t He … be a very good doctor. A) was to; B) is able; C) must; D) are to. We … read and translate English texts. A) ought; B) is to; C) may to; D) can. … I cross the street when the light is red? A) Were to; B) Is able to; C) Must to; D) May. I … speak Chinese when I was a kid. a) can b) should c) could d) must This … be the right restaurant. There are no other restaurants on this street. a) ought b) should c) could d) must People with high cholesterol … eat low-fat foods. a) are b) should c) could d) have Margaret … to exercise more so she will be better prepared for the marathon. a) ought b) can c) could d) must You … drink so much. It's not good for your health. a) can not b) might not c) couldn’t d) mustn’t The slide agglutination test … seem unnecessary in this case. But you … do it. A) may, must; B) might, have; C) may not, can; D) could, had. My sister … play the violin. A) ought; B) may to; C) must to; D) can. A sick person … spread the infection by personal contact from the last days of the incubation period during the entire course of the disease. A) may; B) were to; C) hadn’t to; D) mustn’t to. They … know the symptoms of gastric ulcers. A) were permitted; B) may not to; C) can to; D) must. Women … to lift heavy things. A) has; B) are not allowed; C) is not; D) must not. The two types of blood … seem alike. But they … belong to different groups. A) may, can; B) might, are; C) can to, ought; D) ought, couldn’t. The sick man … to go out. A) must; B) were allowed; C) was not allowed; D) should. Her husband … speak German very well. a) can b) may c) could d) should John … take my dictionary. a) could b) may c) are d) ought … I smoke here? a) can b) ought c) might They … disrupt the work more than necessary. a) couldn’t b) may not c) can d) mustn’t I think we … check everything again. a) ought b) may c) could d) should You … pay more attention to your health. A) must; B) ought; C) is to; D) are able. Even a small dose of 0.1 ml of infected blood … be dangerous for a person. A) cannot; B) ought; C) must to; D) may. The scientists … solve this problem. A) can; B) must to; C) may to; D) ought. Many drugs…produce adverse effect in elderly people. a)may b)must c)should d)have to You …to stop using the drugs if you develop some allergic reactions to it. a)mustn’t b)must c)can’t d)will have ….you remind these difficult chemical names of remedies? a)Can b)Ought c)Have to d)Are able The patient … be afraid a little, but he … undergo the operation. A) may, must; B) must, oughtn’t; C) is, is; D) must to, may to. … he go there by trolley-bus? A) Is; B) Can; C) Were; D) Must to. In advanced cases of jaundice nervous symptoms … develop. A) am to; B) must to; C) may; D) was to. Students … take anything whithout teacher’s permission. A) don’t have to; B) can’t; C) mustn’t; D) weren’t to. In six month you … read English medical journals. A) can; B) will be able to; C) should; D) must. She … to see a doctor yesterday. A) has; B) was; C) is; D) must. You … take vitamins, otherwise you’ll fall ill A) may to; B) must; C) must not to; D) may not to. You … to come at eight sharp. A) is able; B) can; C) must; D) are. You … follow the doctor’s advice. There is no other way out for you. A) may; B) can; C) must; D) ought. If a doctor … detect the allergen he … administer a skin test. A) may not; has to; B) had to; can; C) might; should; D) cannot; must. You … consult a doctor if the symptoms appear again. A) should; B) would; C) could; D) is. The patient … recover. But the doctor isn’t sure he … to lead active life. A) may to, shall be able; B) may, will be able; C) ought, can; D) must, must. Leukaemia … be fatal. But some patients suffering from it … stay alive long. A) can, may; B) can to, may to; C) should, ought to; D) ought to, should. Many elderly people …take drugs because of some chronic conditions. a)has to b)was able to c)is able to d)have to You… take drugs without doctor’s prescription. a)is not to b)mustn’t c)isn’t able to d)is to This substance… react with oxygen. a) have to b)ought c)can d)are able to He … be an inexperienced haematologist. A) must; B) should; C) need; D) has. The surgeons … to finish the operation in 20 minutes. A) are; B) was permitted; C) must; D) may. In toxic jaundice the stools … be of normal colour or deeply bile-coloured. A) must to; B) may; C) ought; D) is able. The laboratory assistant … see the filterable virus under a usual microscope. A) mustn’t to; B) cannot; C) may not to; D) oughtn’t. According to the symptoms it … be the flue. A) can; B) should; C) may; D) ought. … I borrow your pen? A) Am; B) Could; C) Have; D) Must. I … visit my dentist yesterday as I felt a severe toothache. A) had to; B) can; C) might; D) must. In jaundice the bile … pass to the intestines. A) cannot; B) shouldn’t to; C) mustn’t to; D) were to. Occasionally, the person … cough up or vomit large amounts of blood. A) may; B) cannot to; C) were to; D) ought. This medicine … be used only after meal according to signature. A) may; B) is to; C) is able to; D) can. You look as if you are ill. You … consult a doctor as soon as possible. A) can; B) may; C) could; D) should. I don’t know where he is. But he … be at the hospital now. A) may not; B) must not; C) cannot; D) ought. I … to make endoscopy at 15.30 next Tuesday. A) must; B) am; C) has; D) is able. The doctor … be ready to answer all the patient’s questions. A) need; B) must; C) ought; D) have. Heparin … be dangerous to use. Yet it … to be used in clinical practice. A) can, has; B) may not, have; C) may, must; D) must, can. Many drugs…be prescribed to the elderly people because of chronic conditions. a)is not to b)mustn’t c)has not to d)is not able to Antibiotics …allow the body to repair damage caused by the infection. a)mustn’t b)shouldn’t c)can d)will have You …enjoy massage and aroma therapy at this health centre. a)may b)hadn’t to c)has to d)is able to The patient … go anywhere. A) need; B) should; C) mustn’t; D) hasn’t. We … to discuss the methods of treatment of duodenal ulcers on Monday. A) can; B) is; C) were; D) must. We … wait for the pharmacist any longer. a) can b) mustn’t c) shouldn’t d) can’t You … tell your doctor that you have allergy to penicillin before he prescribes medicines for you . a) must b) shouldn’t c) can d) may You …dress well if you don’t want to catch cold again. a) may b) hadn’t to c) should d) are able to Kidney failure and liver encephalopathy … develop in patients suffering from liver diseases. A) shouldn’t to; B) must to; C) can to; D) may. Leukaemia … be fatal. But some patients suffering from it … stay alive long. A) can, may; B) can to, may to; C) should, ought to; D) ought to, should. The slide agglutination test … seem unnecessary in this case. But you … do it. A) may, must; B) might, have; C) may not, can; D) could, had. The student … answer the teacher’s question. A) was able; B) should to; C) can; D) must to. John … take my dictionary. A) were to; B) was; C) have to; D) may. You … worry about the operation, it’s minor surgery. A) isn’t to; B) shouldn’t; C) are able to; D) may not to. We … to meet near the hospital. A) could; B) was; C) are; D) must. No matter how hard he tried, the doctor … help the patient. A) can’t; B) mustn’t; C) couldn’t; D) may not. All the students of our group … read and speak English. A) can; B) is to; C) must to; D) ought. … I call you on Sunday? A) Must to; B) May; C)Are; D) Ought. You … be at the polyclinic at nine. A) has to; B) are able; C) ought; D) must. You … smoke as you suffer from gastric ulcer. A) shouldn’t; B) oughtn’t; C) should; D) ought. … I trouble you for a glass of water. I … swallow the pill. A) Must, could; B) May, can’t; C) Am, hadn’t; D) Ought, will be able. You … follow the doctor’s advice. There is no other way out for you. A) can; B) must; C) may; D) ought. You … to eat more fruit. A) must; B) shouldn’t; C) should; D) ought. They … get up early in the morning. A) must; B) is to; C) ought; D) should to. The patient … soon recover. A) is; B) were to; C) may; D) have to. You … use dictionaries. A) may not to; B) can’t; C) is able to; D) has to. She … be in hospital now. A) weren’t to; B) mustn’t to; C) cannot; D) oughtn’t. … I use your phone? A) Am; B) Should to; C) Must to; D) May. The students … work in the reading-hall. A) ought; B) must; C) should to; D) is to. You … to consult a doctor. A) may; B) shouldn’t; C) ought; D) should. The lecturer … speak so fast. A) should to; B) must to; C) has; D) shouldn’t. Children … sleep nine hours a day. A) must; B) ought; C) have; D) will be able. The doctor … stay in the hospital. A) are to; B) have to; C) must; D) may to. Why … I stay in the hospital? A) could to; B) oughtn’t; C) ought; D) should. He … come home later tonight. A) have to; B) were to; C) may; D) must to. … you speak English? A) Ought; B) Was; C) Can; D) Must to. … he play the piano? A) May to; B) Has; C) Ought; D) Can. … I use your methodical guide? A) May; B) Is to; C) Am; D) Ought. He … to wait for the doctor for an hour. A) must; B) are able; C) had; D) were. She … be in the chemist’s now. A) ought; B) are to; C) have to; D) must. She … to see the doctor yesterday. A) has; B) must; C) is; D) was. I … believe it’s finally happening, can you? A) could; B) can’t; C) can; D) couldn’t. According to the symptoms it … be gangrenous cholecystitis. A) must to; B) may; C) ought; D) is able. He … be ill now. A) must; B) can to; C) is able; D) may to. Where … we buy this journal? A) should to; B) was permitted to; C) can; D) must to. The patient … recover. But the doctor isn’t sure he … to lead active life. A) may to, shall be able; B) may, will be able; C) ought, can; D) must, must. Вставте пропущені прийменники, де це необхідно: Long bones are found … the thigh, lower leg, upper and lower arm. A) into; B) in; C) on; D) at. Yellow bone marrow is chiefly composed … fatty connective tissue. A) of; B) by; C) with; D) in. The bases … all modern developments in chemistry were laid … the Russian scientist Mendeleyev. a) from, to b) of,c) of, by d) -, by She looked … the surgeon and understood that her life depended … his skilful hands. a) at, on b) on, from c) on, by d) at, from The dentist listened … a woman suffering … dental fear with sympathy. a) -, of b) to, from c) -, by d) by, with As I was looking … the papers I came … this paragraph. a) after, around b) -, across c) over, to d) over, across Where have you come …? a) of b) c) from d) to He has known … this doctor … 5 years. A) -; in; B) to; from; C) -; for; D) with; for. A burn is an injury … tissue resulting … heat, chemicals or electricity. A) in; by; B) on; with; C) to; from; D) on; by. Frostbite is more likely to occur … people who have poor circulation because … arteriosclerosis. A) on; of; B) in; of; C) with; -; D) in; from. All the students listened … the lecturer … great interest. a) about, with b) - , with c) to, with d) to, at The treatment … stomatitis is based … the problem causing it. a) from, on b) from, in c) of, in d) of, on W. D. Miller conducted a series … studies that led him … propose an explanation … dental caries. a) of, to, for b) - , towards, for c) about, towards, about d) of, to, … Sunday I usually get up … nine o’clock. a) At, on b) - , at c) In, on d) On , at The students are looking forward … graduating … the Medical University. a) to, from b) about, from c) to, d) of, on Further digestion and absorption … food … the blood takes place in the small intestine. A) of; into; B) -; in; C) by; on; D) with; at. Students go … the University 5 days a week. A) to; B) in; C) on; D) into. Can you finish examining the patient … 2 o’clock? A) before; B) by; C) in; D) on. The products … digestion are absorbed … the blood and lymph. A) of, into; B) in, through; C) before, by; D) to, in. Jaundice is a symptom common … many disturbances and diseases … the liver. A) in, to; B) on, by; C) into, to; D) to, of. The liver is a soft plastic organ located … the right upper quadrant … the abdominal cavity. A) into, from; B) in, of; C) with, by; D) before, in. The process of digestion is completed ... the large intestine … the absorption of water. A) on, with; B) in, by; C) into, of; D) to, since. … summer I like to go … bed late. a) In, to b) At, to c) In, at d) On, to The young scientist was trying to prove … the teacher the necessity … the experiment. a) for, of b) into, for c) from, to d) to, of The academic year begins … the first … September. a) in, in b) on, of c) of, on d) at, of He put his hand … his pocket and took out a letter … the famous dentist. a) into, to b) in, with c) to, for d) at, for He was taken … hospital … an ambulance. a) to, by b) at, with c) into, by d) to, after I don’t go to the university … Saturdays and Sundays. A) on; B) at; C) in; D) into. Leukemia is a cancer … blood cells. A) in; B) of; C) into; D) by. The scientists are to be congratulated … producing such a clear and authoritative work. a) with b) to c) on d) This patient suffers … some unusual disease, and his life depends … quick and accurate work. a) from; on b) in; on c) -; from I was afraid … the operation, but knowing that my life depended … it, I agreed … surgery immediately. a) -; from; to b) of; on; to c) -; to; on d) of; -; to “What do you complain … ?”, asked the doctor. a) of b) on c) to d) from Don’t enter … the operating room. The surgeons are operating … the patient suffering … tongue cancer. a) -; on; from b) to; -; on c) into; -; for d) in; at; in This doctor entered … medical university in 1960 and graduated … it in 1966. A) to, - ; B) - , from; C) into, from; D) in, - . Exposure … radiation increases the risk … developing leukemia. A) from, in; B) -, from; C) by, of; D) to, of. He was waiting … her … his friend. A) for, with; B) on, by; C) by, with; D) for, - . The teacher was looking … him … great surprise. A) on, in; B) at, with; C) with, in; D) on, with. After a week or two the doctor sent the bill … his visits. A) from; B) with; C) for; D) of. Alice sang a song … the concert. A) to; B) at; C) with; D) into. We played … football … the lessons. A) in, by; B) in, after; C) at, at; D) -, after. What are the molecules composed …? a) from b) of c) with d) Then we looked … the knife to open the tin … . a) for, with b) from, to c) - , with d) for, -. Translate this sentence … English … Ukrainian, please . a) with, in b) from, into c) after, at d) from, on The energy …water is transformed … electric energy … means of hydraulic turbines. a) from, in, with b) by, to, after, c) of, into, by d) of, under, Gingivitis causes … much discomfort … glossitis that is inflammation … the tongue. a) as ... as, of b) as … as, with c) as … as, to d) neither … nor, of The doctor looked … the patient’s blood test and realized that he suffered … leukemia. A) at, from; B) in, with; C) on, by; D) into, from. … Sunday I usually get up … 9 o’clock. A) In, at; B) Into, by; C) On, at; D) At, with. The academic year begins … September and is over … July. A) in, by; B) in, on; C) at, at; D) on, at. The lessons begin … 8 o’clock. A) in; B) at; C) by; D) before. The girl … long dark hair is Alice Colton. A) with; B) in; C) at; D) of. The doctor had cured this patient … gastritis … October. A) with, to; B) from, by; C) of, with; D) by, by. The person receives one gene … mother and one … father. A) of, from; B) from, of; C) from, from; D) of, of. My sister is fond … listening … classical music. A) from, -; B) with, at; C) of, to; D) to, in. Landsteiner observed two distinct chemical molecules present … the surface … the red blood cells. A) on, of; B) in, by; C) into, to; D) at, with. He has worked at this dispensary … the graduating from the medical university. A) with; B) from; C) since; D) at. The professor was pleased … the intern’s work. A) with; B) of; C) to; D) at. Panoramic X-ray is useful … detecting the position … fully emerged as well as emerging teeth. a) of, in b) for, of c) of, of d) for, from She looked … the surgeon and understood that her life depended … his skilful hands. a) at, on b) on, from c) on, by d) at, from The frequency … which teeth are exposed … cariogenic environments affects the likelihood … caries development. a) -, by, of b) with, -, of c) of, to, of d) in, at, The student explained … the teacher that by the end … the lesson he hadn’t finished the task. a) by, of b) to, on c) of, at d) to, of … Sunday I usually get up … 10 o’clock. a) In, at b) On, at c) At, at d) On, in The polyclinic is open … 8 a.m. … 7 p. m. A) since, till; B) at, to; C) in, till; D) from, to. The rate … heart contractions is regulated … two groups of nerve fibers. A) from, with; B) for, into; C) of, by; D) in, by. … an adult the heart makes from 60 … 72 beats per minute. A) On, to; B) In, to; C) - , to; D) With, before. The young scientist was trying to prove … the professor the necessity … the experiment. A) - , of; B) with, to; C) to, from; D) before, with. The polyclinic is open … 8 … 7 o’clock. a) since, in b) from, to c) by, till d) before, to Local factors … stomatitis can be corrected … a dentist. a) from, to b) of , with c) of, by d) with, by All the students listened … the lecturer … great interest. a) to, with b) for, to c) with, of d) with, to The treatment … stomatitis is based … the problem causing it. a) from, on b) of, by c) at, on d) of, on The nurse will return … a few minutes. a) at b) by c) in d) to One must not laugh … a disabled person. A) of; B) at; C) with; D) - . The patient complains … severe pain in the stomach. A) from; B) in; C) of; D) to. The nurse will return … the hospital … a few minutes. A) - , on; B) from, in; C) from, at; D) to, - . Oxygen-rich blood enters the left side … the heart … the pulmonary veins. A) at, from; B) of, with; C) before, in; D) of, from. The causes and methods … prevention of atherosclerosis have been under study … many decades. A) of, for; B) with, of; C) on, at; D) of, into. The student likes to be praised … the presence … his fellow-students. A) -, in; B) at, - ; C) in, of; D) with, with. There are many patients … the hospital. A) in; B) into; C) after; D) on. I opened the door and went … the ward. a) into b) on c) after d) with … Saturday and Sunday I usually get up … 10 o’clock. a) at/in b) in/at c) at/on d) on/at The doctor is devoted … his patient. a) of b) to c) with d) in He was treated … very effective drugs. a) with b) to c) in d) by This patient suffers … some unusual disease, and his life depends … quick and accurate diagnosis. a) from/on b) in/on c) -/from d) by/Hemoglobin combines readily … oxygen. A) from; B) into; C) with; D) at. Translate this sentence … Ukrainian, please. A) on; B) by; C) into; D) at. He closed the door and took his seat … the desk … the window. A) at, at; B) at, in; C) on, with; D) to, into. Though I was afraid … the operation, I entered the operating room … hesitation. I knew that my life depended … it. A) of, without, on; B) -, with, from; C) in, -, with; D) of, without, to. Columbus made his first voyage … Europe … America … 1492. A) with, to, at; B) from, in, in; C) from, to, in; D) from, to, at. The ABO blood type classification system was discovered … K. Landsteiner. A) by; B) with; C) -; D) after. The scientists are to be congratulated … producing such a clear and authoritative work. A) with; B) to; C) on; D) -. A doctor listens … the heart … a stethoscope. A) to, with; B) to, by; C) in, with; D) on, for. This patient suffers … some unusual disease, and his life depends … quick and accurate diagnosis. A) from, on; B) in, on; C) -, from; D) by, -. I was afraid … the operation, but knowing that my life depended … it, I agreed to surgery immediately. A) -, from; B) of, on; C) of, with; D) by, from. The nurse, who takes care … my younger brother, insisted … going … bed … 10 p.m. A) of, in, to, at; B) for, in, in, at; C) of, on, to, at; D) of, on, in, at. She became a hematologist as her father had … her. A) by; B) in front of; C) -; D) before. Vegetable diet is inferior … protein diet. A) with; B) to; C) in; D) -. The doctor isn’t satisfied … the results … the course of treatment. A) -, by; B) with, of; C) by, with; D) by, -. My grandparents congratulated me … leaving … school and entering … the medical university. A) on, -, -; B) with, -, to; C) of, from, -; D) on, from, to. Doctors have access … a wide array … tests and procedures … making rapid, precise diagnoses. A) to, of, for; B) to, of, from; C) in, on, for; D) on, with, by. This old man didn’t have enough money to pay … his treatment, he died … tuberculosis … Monday. A) for, from, in; B) for, of, on; C) of, from, by; D) for, from, at. The doctor could tell … the look that something terrible had happened. A) in; B) at; C) by; D) before. “What do you complain …?”, asked the doctor. A) of; B) on; C) to; D) from. Echocardiography is one … the most widely used techniques … diagnosing heart disease. A) of, in; B) at, in; C) in, with; D) on, to. Don’t enter … the operating room. The surgeons are operating … the patient suffering … renal calculi. A) -, on, from; B) to, -, on; C) into, -, for; D) in, at, in. We called the doctor … because Tom was complaining … pain … his stomach. A) in, of, in; B) at, for, - ; C) in, at, after; D) into, - , at. The doctor looked … the patient’s physique, listened … his lungs and heart … a stethoscope and took … his blood pressure. A) at, to, with, -; B) on, -, -, -; C) on, at, by, out; D) into, -, by, off. They are both doctors … profession. A) in; B) by; C) before; D) behind. The nurse will return … a few minutes. A) at; B) on; C) into; D) in. This student is very good … human anatomy, yet totally incapable … understanding the main rules of blood transfusion. A) in, of; B) at, -; C) on, in; D) with, at. They laughed … me because I am afraid … dogs. A) from, of; B) at, from; C) of, of; D) at, of. The pediatrician smiled … the young mother. He knew her child was well looked … and cared … . A) at, after, for; B) with, for, -; C) from, for, after; D) of, -, of. Arteriosclerosis is a general term … several diseases … which the wall … an artery becomes thicker and less elastic. A) for, in, of; B) for, to, with; C) in, with, of; D) of, to, by. Has the doctor … the USA already arrived? A) since; B) with; C) to; D) from. The doctor really sympathized … the patient. A) -; B) to; C) with; D) at. The students are looking forward … graduating … the Medical University. A) -, -; B) at, -; C) to, from; D) -, to. The risk … developing atherosclerosis increases … high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol levels, cigarette smoking, diabetes, obesity, lack … exercise and advancing age. A) of, with, of; B) of, into, by; C) in, on, before; D) with, of, from. This man is famous … his brilliant translation … Latin … Ukrainian. A) of, from, into; B) from, of, to; C) for, from, into; D) for, from, to. Arteriosclerosis is a general term … several diseases … which the wall … an artery becomes thicker and less elastic. A) for, in, of; B) for, to, with; C) in, with, of; D) of, to, by. He’s been working in this dispensary … leaving the medical university. A) from; B) by; C) -; D) since. Last year I entered … medical university. A) to; B) -; C) into; D) in. The doctor looked … the patient’s blood test and realized that he suffered … leukemia. A) on, with; B) at, from; C) on, by; D) into, from. I am looking … glasses. I suffer … presbyopia, so in sunny weather I can’t do … them. A) after, with, with; B) for, from, without; C) -, on, out of; D) for, in, -. The blood type is established … the person is born … specific genes inherited … parents. A) before, by, from; B) before, to, with; C) with, for, in; D) in, by, from. I usually go … home … bus. But today I’ll go … foot. A) to, by, with; B) -, by, on; C) -, by, in; D) to, on, by. The polyclinic is open … 8 to 7 o’clock. A) by; B) with; C) from; D) -. It is difficult for old people to climb … high mountains. A) on; B) to; C) -; D) at. All the students listened … the lecturer … great interest. A) to, with; B) -, with; C) at, -; D) in, by. The station platform was crowded … people waiting … the train. A) of, for; B) with, for; C) of, to; D) with, to. The patients … ruptures, fractures, various wounds and different surgical diseases are treated … surgeons … surgical department. A) of, with, in; B) with, by, in; C) to, with, at; D) by, by, by. The successes … modern medicine are inseparably linked … the tremendous achievements made … transfusiology. A) of, with, in; B) of, by, on; C) from, with, into; D) for, by, in. He was blind … birth. A) in; B) from; C) of; D) with. The surgeon answered … all the patient’s questions. A) on; B) to; C) at; D) -. The doctors will have discharged him … hospital … Monday. A) from, by; B) with, before; C) in, on; D) -, at. According … their functions different organs are divided … several systems. A) of, in; B) with, -; C) to, into; D) -, in. Chemotherapy … combination … radiotherapy is used … the treatment … leukemic patients. A) in, with, for, of; B) on, with, for, of; C) to, by, for, in; D) on, by, from, before. I’m sorry … shouting … you yesterday, I was so tired … waiting … you. A) for, at, of, for; B) - , - , for, of; C) - , for, - , for; D) of, at, at, at. The academic year begins … the first of September. A) in; B) at; C) -; D) on. The scientists have arrived … an interesting conclusion. A) to; B) at; C) in; D) -. I bought this book and it belongs … me. A) -; B) by; C) at; D) to. She usually gets up … 10 or … 11 o’clock … Saturdays. A) at, at, on; B) at, at, in; C) with, from, on; D) at, in, on. The patient who suffered … gastritis was discharged … the hospital. He went … home. A) of, from, -; B) from, from, -; C) from, from, to; D) of, from, to. The patient has been waiting … the doctor … half an hour already. It’s turned out that he is speaking … the nurse … the moment. A) for, for, to, at; B) on, -, with, in; C) -, -, with, by; D) at, for, to, in. The doctor is devoted … his patients. A) with; B) to; C) of; D) -. As a doctor, you will be interested … the patient’s ESR. A) in; B) into; C) with; D) -. Inflammation may be combined … a small part … the body. A) to, of; B) to, in; C) at, into; D) with, on. These photos were taken … my friend … a very good camera. A) by, with; B) by, by; C) with, by; D) with, with. The patient has been waiting … the doctor … half an hour already. It’s turned out that he is speaking … the nurse … the moment. A) for, for, to, at; B) on, -, with, in; C) -, -, with, by; D) at, for, to, in. The student explained … the teacher that by the end … lesson he hadn’t finished the translation … the text “Blood Groups” and that’s why he hadn’t handed it … her. A) to, of, of, to; B) -, of, of, -; C) before, -, -, before; D) to, in, in, to. He was taken to hospital … an ambulance. A) into; B) with; C) by; D) from. Blood platelets are also referred … as thrombocytes. A) -; B) to; C) with; D) at. He dedicated his life … medical sciences. A) to; B) in; C) -; D) on. The young scientist was trying to prove … the professor the necessity … the experiment. A) -, in; B) -, by; C) to, of; D) at, to. Treatment depends … the type … musculoskeletal disorder. A) on, of; B) in, with; C) on, to; D) in, of. Do you go … the University … bus or … foot? A) to, by, by; B) at, by, on; C) at, by, by; D) to, by, on. He was treated … very effective drugs. A) by; B) with; C) -; D) at. He has a high fever. I must send … the doctor immediately. A) in; B) with; C) at; D) for. This doctor entered … medical university in 1960 and graduated … it in 1966. A) to, -; B) -, from; C) in, from; D) into, -. A burn is an injury … tissue resulting … heat, chemicals or electricity. A) to, from; B) to, of; C) in, from; D) on, with. … Sunday I usually get up … nine o’clock. A) On, at; B) At, in; C) In, by; D) On, it. I was angry … the doctor … his unprofessional work. A) with, for; B) with, by; C) about, with; D) at, after. He was cured … a very skilful doctor. A) by; B) with; C) at; D) -. Do you know what rhesus incompatibility may lead … during pregnancy? A) in; B) with; C) to; D) at. I get up … six o’clock or … a quarter past six. A) in, in; B) at, at; C) at, in; D) in, at. … Saturday and Sunday I usually get up … 9 o’clock. A) On, at; B) In, in; C) In, at; D) On, in. The products … digestion are absorbed … the blood and lymph. A) of, into; B) of, in; C) at, on; D) in, into. She was so tired … waiting … the nurse who was responsible … morning procedures. A) of, to, for; B) for, for, of; C) to, of, to; D) of, for, for. The doctor wrote the prescription … a pen. A) -; B) in; C) by; D) with. Blood may be tested … presence of pathogenic microorganisms or a series of biochemical substances. A) in; B) for; C) at; D) to. Almost everybody is very afraid … operations, and one must not laugh … it. A) by, from; B) of, with; C) of, at; D) -, at. … winter I usually go … bed at ten o’clock because I study … the university and have to get up early. A) At, in, to; B) Into, into, into; C) In, to, at; D) In, in, in. Don’t be so proud … the research work written … you. It is full … mistakes. A) by, by, of; B) for, of, of; C) of, by, of; D) of, of, of. The process … digestion is completed … the large intestine … the absorption … water. A) of, in, by, of; B) in, of, by, before; C) from, in, by, of; D) since, in, of, with. A little girl was taken to hospital … an ambulance. A) - ; B) with; C) of; D) by. The boy cut his finger … a knife. A) of; B) -; C) with; D) by. One must not laugh … a disabled person. A) at; B) from; C) of; D) on. There is no water … the glass. Pour some water … my glass; I want to take some water after my medicine. A) on, on; B) to, to; C) into, in; D) in, into. The remains … the digesting fluids are evacuated … the body. A) of, from; B) of, with; C) from, to; D) in, from. Let’s go … the club … Shevchenko street, we can listen … our favourite music there. A) to, on, for; B) at, at, - ; C) to, in, to; D) in, in, - . The professor was pleased … the interns’ work. A) of; B) with; C) -; D) on. Are you aware … the fact that fibrinogen is responsible … blood clotting? A) in, - ; B) with, in; C) at, by; D) of, for. I have already sent … the doctor and now I am looking forward … his arrival. A) for, to; B) by, for; C) -, in; D) by, to. The doctor operated … the patient suffering … renal calculi yesterday. A) -, for; B) with, with; C) on, from; D) -, -. Even a small dose … 0.1 ml … infected blood may be dangerous … a person. A) of, of, for; B) of, in, into; C) with, in, on; D) before, on, for. I have been waiting … my friend, who had left Kyiv … London … a long time. A) for, to, for; B) to, to, for; C) to, for, for; D) for, for, for. Вставте пропущений числівник: Each erythrocyte lives about …(125) days. A) one hundred twenty five; B) one hundred and twenty five; C) one hundred and twenty-five; D) one hundred twenty-five. I usually get up at … (645) a.m. A) a quarter to six; B) a quarter to seven; C) a quarter to seventh; D) half past six. He was born on … (19.05.1960). a) the nintenth of March, nineteen sixty b) the nineteenth of May, nineteen sixty c) the nineteenth of May, nineteen sixteen d) ninteenth of March, nineteen sixty The population of our city is … (36, 294). a) thirty-six thousands two hundreds and ninety-four b) thirty six thousand and two hundreds and ninety four c) thirty six thousand two hundred ninety four d) thirty-six thousand two hundred and ninety-four Next week, we are going to study … . a) Lesson Nine b) Lesson Ninth c) Lesson Nineth d) the Nineth Lesson About … (3/5) of workers are young people. a) third fifths b) three fifth c) three fifths d) third fifth (7. 067) … is his average score. a) seven point nought sixty-seven b) seven point nought seven six c) seven point nought six seven d) seven nought point six seven This doctor is … (44), he was born on … (31.01.1963). A) fourty-four, thirty-one of January nineteen sixty-three; B) forty four, thirty first of January one thousand nine hundred and sixty three; C) fifty-four, the thirty-oneth of January nineteen fifty-three; D) forty-four, the thirty-first of January nineteen sixty-three. In the UK, there were … (7,697) cases of oral cancer. a) seven hundred six hundred ninety-seven b) seven thousand six hundred and ninety-seven c) seven thousands six hundreds and nineteen seven d) seven hundreds six hundred ninty-seven The … programme is more interesting than the … one. a) one … second b) firsth … secondth c) first … second d) one … two More than … (78%) of teachers in our university are young or middle-aged. a) seventy eight percents b) seventy- eighth percentage c) seventeen eighth per cent d) seventy-eight per cent It’s … (18. 35) o’clock a) twenty-five minutes past seven b) twenty-five minutes to seven c) twenty five minutes past seven d) a quarter to nineteen The floorspace of this flat is … (65.45) m2. a) sixty-five point forty-five b) sixty-five nought foruty-five c) six five point four five d) six five nought four five This ward is quite large: its floor space is … (23.07) m2. A) two three point nought seven; B) twenty-three and seven; C) twenty-third and seventh; D) two three point seven hundredths. I can swim … (3 ¾) km at a time. A) three three four; B) three and three fourths; C) three three forths; D) three and three fourth. The number of bones in the adult skeleton is over … (201). A) two hundreds and one; B) two hundred and one; C) two hundred one; D) two hundreds and one. There are … (120) students in the classroom. a) one hundred-twenty b) one hundred and twenty c) a hundred twenty d) a thousand- twenty How much is … (56) divided by … (7)? a) fifty six, seven b) fifty six, seventh c) fifty-six, seven d) fifty-six, sevens Today he works … (2/5) of the day but receives … (1/2) of his salary a) two-five, one-second b) two and five, one and two c) two fifth, one twoth d) two fifths, half This famous oncologist was born on … (26.07.1959). a) the twenty-sixth of July, nineteen fifty-nine b) twenty-six of July, nineteen fifty-ninth c) the twenty sixth of June, ninety fifty nine d) the twenty-sixth of July, one thousand nine hundred fifty-nine 64. It is … (13.30) now, but you were to come at … (12.45). a) half to one, fourty-five minutes past twelve b) half past one, a quarter to one c) thirteen and half, fifteen minutes to first d) half past thirteen, a quarter past twelve I usually come to the university at …(745) a.m. A) a quarter to seven; B) a quarter past seven; C) a quarter to eight; D) half past seven. This teacher is … (32), she celebrates her birthday on … (24.05.1975). A) thirty two; twenty fourth of May, one thousand nine hundred and seventy five; B) thirteen and two; twenty-four of May, nineteen seventy-five; C) thirty-two; the twenty-fourth of April, nineteen seven five; D) thirty-two; the twenty-fourth of May, nineteen seventy-five. That operating room is not very large: its floor space is … (15.03) m2. A) fifteen and three; B) one five point nought three; C) one five and nought third; D) fifteen point three hundred. On the … (21.06.2008) a patient suffering from oral cancer, aged … (48), was hospitalized. a) twenty-first of June\ two thousand and eight / forty-eight b) twenty first of June, two thousand and eight / fourty-eight c) twenty one of July, too thousand and eight / forty eight d) twenty-first of July, twenty zero eight / fourty eight My brother has already prepared … (3/5) his thesis on the methods of leukoplakia treatment. a) three fiveth b) three fifths c) third fifth d) free five Don’t phone him up to … (12.30) o’clock. He’ll be busy receiving patients. It’s better to phone him at … (12.45) or … (12.55) when he is free for sure. a) half past twelve, a quarter to one, five minutes to one b) a quarter past twelve, a half to one, five minutes to one c) thirty minutes to first, fifteen minutes to first, fifth minutes to first d) half after twelfth, a quarter before first, five minutes before first Every year in Europe about … (100, 800) people are diagnosed with head and neck cancer. a) one thousand and eighty b) one hundred thousand eight hundred c) one thousand hundred and eight hundred d) one thousand eight hundreds Age is also a risk factor - … (95) per cent of oral cancer occur among persons over the age of … (40). a) nineteen five, fourteen b) ninety-five, forty c) ninety five, fortieth d) ninety-fifth, fourty Read Paragraph … (18) on the structure of bones. A) eighteen; B) eighty; C) eighteenth; D) eightieth. This sportsman can jump in … (1 4/7) m height. A) one and four seventh; B) one for sevenths; C) one and four sevenths; D) one four seven. Red blood cells are small, pale-red, biconcave discs about … (0.07) of a millimeter in diameter. A) zero point seven; B) point nought seven; C) nought comma nought seventeen; D) zero comma zero seventh. He has been to the USA for … (1 1/2) year. a) a year and a half b) one year and one quarter c) one year and two halves d) half a year "C" is (3) … letter of the English alphabet. a) a three b) the threeth c) the third d) the first Our last meeting was on … (24.03.1982). a) the twenty-fourth of March, nineteen eighty-two b) twenty-fourth of May, nineteen and eighty-two c) the twenty-four of March, ninety eighty-two d) twelve fourth of March, nineteen and eighty-too About … (2, 458, 120) old people died of flu last winter. a) two millions four hundred and fifty-eight thousands one hundred and twenty b) too million for hundred and fifty-eight thousands one hundred and twelve c) two million and four hundred fifty-eight thousand one hundred twenty d) two million four hundred and fifty-eight thousand one hundred and twenty Can you multiply … (0.052) by … (18.6) without electronic calculator. a) point nought five two / one eight point six b) zero point zero fifty-two / eighteen point six c) nought point nought fifty two / one eight point six d) nought point nought fifty-two / eighteen point six 15 At … (7 ) a.m I was called to see a man aged … (23), who was admitted to the hospital the night before. A) seven fifteen; two three; B) seven and quarter; twenty-third; C) a quarter past seven; twenty-three; D) a quarter to seventh; twenty-three. The patient’s temperature was … (104)°F. A) a hundred four; B) a hundred and four; C) one hundred fourteen; D) one hundred and fourth. Saliva consists of … (99.5) per cent water and … (0.5) per cent total solids. A) double nine point five; five ten; B) nine nine comma five; zero comma five; C) nine nine point five; point five; D) ninety nine comma five; zero comma five. Fermentations held Pasteur’s attention up to … (1863). A) one thousand eight hundred sixty three; B) one thousand and eight hundreds and sixty-three; C) eighteen sixty-third; D) eighteen sixty-three. Only … (1/2) of the number of persons with oral cancer are alive … (5) years after the diagnosis. a) one seconds, fifth b) first second, five c) half, five d) half, fifth Tobacco use is increased among women compared with rates in … (1950)s. a) nineteen fifties b) nineteen fiftieth c) one thousand nine hundred and fifteen d) one hundreds nine thousands and fifty How much is … (23) plus … (45)? a) twenty three , fourty five b) twenty third, fourty fifth c) twenty-third, forty-fifth d) twenty-three, forty-five The dentist starts to receive patients at … (12.15) and finishes at … (18.35). a) a quarter to one thirty-fifth to seven b) a quarter to twelve / twenty-fives to seven c) a quarter past one / thirty-five to seven d) a quarter past twelve / twenty- five to seven My father was born on … (18.05.1961). a) the eighteenth of March, nineteen sixty one b) the eighteenth of May, nineteen sixty-one c) the nineteenth of May, nineteen sixteen-one d) the ninteenth of March, nineteen sixty one Incubation period of grippe is short, usually … (24) to … (72) hours. A) twenty four; seventy two; B) twenty fourth; seventy second; C) twenty-four; seventy-two; D) two four; seventy-second. The reaction of the gastric juice is acidic, pH … (0.9) to … (1.5). A) point nine; one point five; B) zero point nine; fifteen; C) zero comma nine; one comma five; D) point eight; one point five. Body temperature may be generally fatal at … (107)°F. A) one hundred-seven ; B) a hundred seven; C) one hundred zero seven; D) one hundred and seven. The pulse rate in typhus often remains … (125). A) one hundred twenty-five; B) a hundred and two five; C) a hundred and twenty-five; D) a thousand and twenty-five. The floor space of this department is 248 m2. a) two and forty-eight b) two hundred – forty eight c) two hundreds forty eight d) two hundred and forty-eight The working day begins at 8.15 here. a) half to eight b) a quarter to nine c) a quarter past eight d) half past nine More than 5,600 students study at this university. a) five thousand six hundred b) five thousands six hundreds c) five-thousand six-hundred d) fifth thousand sixth hundred How much is 245 minus 17? a) two hundred forty five, seventeen b) two hundreds and forty-five, seventeenth c) two hundreds forty-five, seventy d) two hundred and forty-five, seventeen You have coped with 1/6 of the test. a) first six b) one sixth c) first sixth d) one sixths The operation lasted for … (2 2/3) hours. A) two and two thirds; B) two and two three; C) two two third; D) two and two threeths. … (25.11.1810) is M. Pirogov’s birthday. A) Twenty-fiveth of December, nineteen ten; B) The twenty-five of November, one thousand eight hundred and tenth; C) The twenty-fifth of April, eighteen ten; D) The twenty-fifth of November, eighteen ten. The child was given … (1,500) units of antitoxin and … (300,000) units of penicillin. A) one thousand five hundreds; three hundreds thousands; B) one thousand five hundred; three hundred thousand; C) one comma five hundred; three hundred comma three zeroes; D) one hundred and five thousand; three thousand hundred. The blood in the veins of the liver may attain the temperature of … (39.7)°C. A) three nine point seven; B) three nine comma seven; C) thirty-nine point seventeen; D) three eight point seven. If the disease is uncomplicated, the temperature falls on the … (16) day. A) sixteen; B) sixty; C) sixth; D) sixteenth. The incubation period of tetanus varies on an average from … (5) to … (15) days. A) fifth, fifteenth; B) fifth; fiftieth; C) five; fifteenth; D) five; fifteen. … (1/3) of the procedure was performed by the professor, and then, as he went out, his assistant finished it. A) one three; B) one threeth; C) one third; D) two thirds. The lecture will take place in classroom … (40). A) forty; B) fourteen; C) fourtieth; D) fourth. S.P. Botkin was born on … (17.09.1832). A) seventeen of September, eighteen thirty-two; B) the seventeenth of September, nineteen thirty-two; C) the seventeenth of September, eighteen thirty-two; D) the seventeenth of October, one thousand eight hundred and thirtytwo. The pharmacist prepared … (0.2)% solution, which costs … (3.05$). A) two, three point five dollars; B) point two, three point nought five dollars; C) zero point zero two, zero three point zero five dollars; D) nought comma two, three comma nought fifteen dollars. S.P. Botkin was born on … (17.09.1832). A) seventeen of September, nineteen thirty-second; B) the eighteenth of September, eighty thirty two; C) the seventeenth of August, one eight three two; D) the seventeenth of September, eighteen thirty-two. In the … (XX) century a small outbreak of plague occurred in … (1910) in Suffolk. A) twentieth, nineteen ten; B) twelve, nineteen ten; C) twenty, nineteen tenth; D) twentieth, one thousand nine hundred and one zero. Physical examination of the woman aged … (38) showed a carcinoma of the breast of about … (2 2/3) cm in diameter. A) thirty-nine, two two three; B) thirty eight, two two third; C) thirty-eight, two and two thirds; D) fifty-eight, two and two threeths. About … (34,150) deaths occur yearly in the USA from cancer of the stomach. A) thirty for thousand one hundred thirty; B) thirty-four thousand one hundred and fifty; C) thirty-for thousands one hundred and fifty; D) thirty-four hundred one thousand and fifty. The nurse makes injections at … (615) a.m. and at (1430) p.m. A) a quarter past six, half past two; B) fifteen minutes past six, thirty minutes to two; C) a quarter to six, a half to three; D) fifteen minutes past the sixth, thirty minutes to the third. Blood temperature in the vessels of fingers and nose may be only … (36.1)°C. A) thirty-three point one tenth; B) three six point one; C) sixty-three point one; D) three six comma one. On … (15.02.1997) a woman with diabetes mellitus, aged … (42), was hospitalized. A) the fiftieth of February, ninety nineteen seven; forty-two; B) the fifteenth of September, nineteen ninety-seven; fourty-two; C) the fifteenth of February, a thousand nine hundred ninety-seven; fourty-two; D) the fifteenth of February, nineteen ninety-seven; forty-two. The most prominent point of each eyeball is about … (1 1/4) inches from the middle line of the face, so that both eyes are (2 1/2) inches apart. A) one one four; two one two; B) one one fourth; two one twoth; C) one and a quarter; two and a half; D) first and a quarter; second and one second. The “Great Plague” occurred in London in the … (XVII) century when … (70,000) people died. A) seventeenth, seventy thousand; B) seventeen, seventy thousands; C) seventy, seventeen comma zero; D) seventieth, seventeen thousand. The students usually get up at … (625) a.m. on weekdays. A) twenty five seconds past six; B) twenty-five minutes past six; C) twenty five minutes after the sixth; D) twenty-five minutes to six. The average length of a baby at birth is about … (52) cm and the average weight is about … (3,500) g. A) thirty-two, three thousand and five hundred; B) fifty-two, three hundred five thousand; C) fifty second, three thousands five hundreds; D) fifty-two, three thousand five hundred. The number of bones in the adult skeleton is over … (200). A) too hundred; B) two hundreds; C) two thousand; D) two hundred. The head of the gastroenterological department celebrated his … (55) anniversary of the … (21.06.1998). A) fifty-fifth, twenty-first of June, nineteen ninety-eight; B) fivety-fiveth, twenty-one of June, nineteen ninety-eighth; C) fifty fifth, twenty first of July, nineteen and ninety eight; D) fiftieth fifth, twentieth first of June, nineteen ninetieth eighth. The amount of gastric juice secreted in the stomach within … (24) hours is … (1.5) – … (2) liters. A) twenty-four, one point five, two; B) twenty four, one point five tenth, two; C) two four, one comma five, two; D) too four, fifteen, too. Cardiac muscle works about … (1/3) the time a person lives. A) one threeth; B) one third; C) one and three; D) first thirds. 45 At … (11 ) a.m. the nurse entered Ward … (3). A) fifteen minutes to eleven, three; B) a quarter to twelve, three; C) forty-five minutes past eleven, third; D) half to twelve, three. Exercise testing has a … (1) in … (5,000) risk of heart attack or death. A) one, five hundreds; B) first, fifth thousand; C) one, five thousands; D) one, five thousand. Hepatitis C virus causes at least … (80%) of the hepatitis cases arising from blood transfusion. A) eight zero; B) eighteen; C) eightieth; D) eighty. This surgeon is … (55), he was born on the … (23.02.1953). A) fifty-five, twenty-third of February, nineteen fifty-three; B) fivety five, twenty three of March, nineteen fifty three; C) fifteen fifth, twelve hreeth of February, nineteen and fifty three; D) fifty five, twenty third of February, one thousand nine hundred and fifty-third. … (34.56) minus … (0.09) equals … (34.47). A) three four point five six, point nought nine, three four point four seven; B) thirty-four and fifty-six, and nine, thirty-four and forty-seven; C) thirty-four comma five six, comma nought nine, thirty-four comma four seven; D) three four point fifty-six, comma nought nine, three four comma forty-seven. Only about … (½) the people with duodenal ulcers have typical symptoms: gnawing, burning, aching, soreness, an empty feeling, and hunger. A) halves; B) a quarter; C) a half; D) first second. You are to read Paragraph … (8) on respiratory disorders by … (1440). A) eighth, forty minutes past two; B) eighth, twenty minutes before three; C) eight, twenty minutes to three; D) eight, twelve minutes to third. Leukemic children between ages of … (3) and … (7) have the best prognosis. A) thirty, seventy; B) free, sex; C) third, seventh; D) three, seven. The heart contracts from the … (1) moment of life until the last one. A) one; B) oneth; C) second; D) first. Among people ages … (45) to … (65), cirrhosis is the … (3) most common cause of death, after heart disease and cancer. A) fourteen five, sixteen five, three; B) forty-five, sixty-five, third; C) four five, six five, threeth; D) forty fifth, sixty fifth, second. … (17.09) plus … (0.046) equals … (17.136). A) one seven point nought nine, point nought four six, one seven point one three six; B) one seven paint not nine, paint not for sex, one seven paint one free sex; C) seventeen comma ten hundredth, comma forty-six thousandth, seventeen comma one hundred and thirty-six thousandth; D) seventy point nine, point fourteen six, seventy point one thousand and thirteen six. About … (½) the bile secreted between meals is diverted through the cystic duct and into the gallbladder. A) a quarter; B) a half; C) one seconds; D) first second. Drinking milk, eating, or taking antacids generally relives stomach pain, but it usually returns … (2) or … (3) hours later. A) first, second; B) second, third; C) too, free; D) two, three. Everyone produces stomach acid, but only … (1) in … (10) people develops ulcer. A) first, tenth; B) second, tenth; C) one, ten; D) one, one zero. On the … (21.06.2008) a child suffering from scoliosis, aged … (12), was hospitalized. A) twenty-first of June, two thousand and eight, twelve; B) twenty first of July, two thousands and eight, twenty; C) twenty one of July, too thousands end eighth, twelfth; D) twenty oneth of June, twenty zero eight, twelve. This ward is large: its floor space is … (21.07) m2 and the area of the hospital is … (0.098) acres. A) two one point nought seven, point nought nine eight; B) too one paint knot seven, paint knot nein eight; C) twenty-one comma seven hundredth, comma ninety-eight thousandth; D) twelve one point seventy, comma nineteen eight. My brother has already prepared … (3/5) his thesis on the methods of treatment of marginal ulcers. A) three fiveth; B) three fifths; C) third fifth; D) free five. Don't phone him up to … (1230) o'clock. He'll be busy receiving the patients. It's better to phone him at … (1245) or (1255) when he is free for sure. A) half past twelve, a quarter to one, five minutes to one; B) a quarter past twelve, a half to one, five minutes to one; C) thirty minutes to first, fifteen minutes to first, fifth minutes to first; D) half after twelfth, a quarter before first, five minutes before first. Albumins constitute about … (60)% of all plasma proteins. A) six zero; B) six nought; C) sixteen; D) sixty. The chest is composed of … (12) thoracic vertebrae, the breastbone and … (12) pairs of ribs. A) eleven, eleven; B) twenty, twenty; C) twelve, twelve; D) twelfth, twentieth. On the … (3.03.2007) a child suffering from frostbite, aged … (11), was hospitalized. A) third of March, two thousand and seven, eleven; B) three of May, two thousands seven, eleventh; C) threeth of May, two hundred and seven, ten-one; D) second of March, twenty zero seven, eleven. This ward is not large: its floor space is … (12.01) m2 and the area of the hospital is … (0.0989) acres. A) one two point nought one, point nought nine eight nine; B) twelve and one, and nine hundred eighty-nine; C) twenty point one hundredth, point nine hundred and eighty-nine ten thousandth; D) eleven comma nought one, nought comma nought eight nine eight. The district doctor has received only … (1/4) the patient up to now. A) half; B) one fifth; C) first four; D) a quarter. I get up at … (550) on weekdays, but on weekends I get up at … (830). A) ten minutes before six, half before nine; B) ten minutes to six, half past eight; C) ten minutes before sixth, thirty minutes past eighth; D) tenth minutes to six, a quarter past eigth. Milk products contain about … (100) substances useful for men. A) one thousand; B) first hundred; C) first thousands; D) one hundred. The stomach measures about … (21) - … (25) cm in length, … (8) - … (9) cm in its greatest diameter. A) twenty-one, twenty-five, eight, nine; B) twelve one, twelve five, seven, eight; C) twenty-first, twenty-fifth, eighth, ninth; D) twentieth first, twentieth fifth, seventh, eighth. On the … (31.08.2003) a woman suffering from gastric ulcer, aged … (33), was hospitalized. A) thirty-first of August, two thousand and three, thirty-three; B) thirty first of September, two thousands and three, thirty three; C) thirty-one of July, two hundreds and three, thirty-third; D) thirteen first of August, twenty zero third, thirteen three. This operating room is quite large: its floor space is … (24.03) m2 and the floor space of the surgical department is 0.062 acres. A) twenty-four comma three, comma sixty-two; B) too for paint knot free, paint knot sex too; C) two four point nought three, point nought six two; D) twelve four and zero three, zero and zero sixteen two. I have already bought … (1/4) the medicines prescribed by the doctor. A) a half; B) first fourth; C) one and four; D) a quarter. Though I am to be at work at … (800) o'clock, at … (735) I am already on the spot. A) eighth, twenty five minutes to eighth; B) eight, twenty-five minutes to eight; C) eighth, thirty-five minute past seventh; D) eight, thirty five minutes after seven. Hepatitis C has the greatest likelihood of becoming chronic – about a … (75)% chance; though usually mild it is a serious problem because about … (20)% of the affected people eventually develop cirrhosis. A) seventy-fifth, twentieth; B) seventeen five, twenty; C) seventy five, twelve; D) seventy-five, twenty. The life span of an erythrocyte is roughly … (120) days. A) a hundred twentieth; B) one hundred and twenty; C) one hundred and twelve; D) one hundred two zero. I have to hand in my report on unsaturated fatty acids on the … (23.05.2008). A) twenty-third of May, two thousand and eight; B) twenty third of March, two thousands and eighth; C) twenty-three of March, two hundred and eight; D) twenty threeth of May, twenty zero eight. The blood in the veins of the liver may attain the temperature of … (39.8)°C, while that in the vessels of the fingers, nose and cheeks may have a temperature of only … (35.9)°C. A) thirty-nine comma eighth, thirty-five comma ninth; B) three nine point eight, three five point nine; C) thirteen nine point nine, thirteen five point nine; D) thirty nine and eight, thirty five and nine. A friend of mine can spend … (2 1/2 ) days without sleep. A) too end one too; B) two one second; C) second and first second; D) two and a half. The working day of a doctor starts at … (800) o'clock. The doctor's morning round lasts from … (810) up to … (855). A) eighth, ten minutes past eighth, five minutes to ninth; B) eight, ten minutes past eight, five minutes to nine; C) eighth, ten minutes after eighth, five minutes to nine; D) nine, ten minutes after eight, five minutes before nine. Hepatitis A rarely becomes chronic; hepatitis B becomes chronic in … (5) to … (10)% of the infected people. A) fifty, one zero; B) fifteen, ten; C) fifth, tenth; D) five, ten. The count of leukocytes in the blood of a healthy person is … (4,500) to … (9,500) per cu mm. A) four thousand five hundred, nine thousand five hundred; B) four hundred five thousand, nine hundred five thousand; C) four thousands five hundreds, nine thousands five hundreds; D) fourteen thousand and five hundred, nineteen thousand and nine hundred. The … (1) set of … (7) bones of the spinal column, forming the neck bone, are the cervical vertebrae. A) oneth, seven; B) second, seventh; C) one, seventeen; D) first, seven. The capacity of the stomach is from … (2.13) to … (2.49) litres. A) too paint one free, too paint for nein; B) two point thirteen hundredth, two point forty-nine hundredth; C) two point one three, two point four nine; D) two comma thirty, two comma fourteen nine. A friend of mine can live … (6 1/2) days without food. A) sixth and one second; B) six one second; C) six and a half; D) six and a quarter. This patient has to measure his blood pressure … (10) times a day starting at … (615) a.m. and ending at … (1045) p.m. A) ten, a half past six, a half to eleven; B) ten, a quarter past six, a quarter to eleven; C) tenth, fifteen minutes past sixth, fifteen minutes to tenth; D) ten, fifteen minutes after six, fifteen minutes before ten. A person with acute viral hepatitis usually recovers after … (4) to … (8) weeks. A) forty, eighty; B) fourth, eight; C) for, eighth; D) four, eight. It is estimated that erythrocytes are the most numerous cellular elements, ranging from … (4,000,000) to … (5,000,000) per cubic millimeter. A) forty million, fifty million; B) fourteen million, fifteen million; C) four million, five million; D) four-millions, five-millions. The … (3) set of … (5) vertebral bones are the lumbar vertebrae. A) threeth, fifth; B) second, fifty; C) third, five; D) first, fifteen. The amount of gastric juice secreted in the stomach within … (24) hours is … (1.4) – … (2.01) liters. A) twelve for, one point for, two point one; B) twenty-four, one point four, two point nought one; C) twenty four, one and four, two and nought one; D) two four, one comma four, two comma nought one. A friend of mine can live … (2 1/4) without water. A) two and a quarter; B) two one fourth; C) second one fourth; D) two and a half. The surgeons are getting ready in the scrub-up room, so, the operation will begin not later than at … (1035) or even at … (1025). It will last for about … (3 1/2) hours. A) twenty five minutes to eleventh, twenty five minutes past tenth, three and one second; B) twenty-five minutes to eleven, twenty-five minutes past ten, three and a half; C) a quarter to eleven, a quarter past ten, three a half; D) twenty-five minutes before eleven, twenty-five minutes after ten, three one two. The coccyx is a fused bone, having been formed from … (4) small bones. A) forty; B) fourth; C) for; D) four. The spinal column is composed of … (26) bone segments, called vertebrae, which are arranged in …(5) divisions from the base of the skull to the tailbone. A) two six, fifth; B) twenty seven, six; C) twenty-six, five; D) twelve six, five. Did prof. Shevchenko celebrate his … (60) anniversary on the … (11) or …(31.08.1999)? A) sixtieth, eleventh, thirty-first of August, nineteen ninety-nine; B) sixteenth, eleventh, thirty first of August, nineteen nineteen nine; C) sixty, twelfth, thirty-one of August, nineteen and ninety-nine; D) sixtyth, eleven, thirty-oneth of September, nineteen ninety-nineth. The stomach has a capacity from … (2.14) to … (2.48) litres. A) too point fourteen, too point forty-eight; B) two comma fourteen hundred, two comma forty-eight hundred; C) two point one four, two point four eight; D) two comma forty, two comma fourteen eight. I can swim … (3 4/7) km at a time. A) three four seventh; B) three and four sevenths; C) free end for seven; D) third fourth sevenths. The surgeon entered Operating Room … (2) at … (1030). A) two, half to twelve; B) two, half past ten; C) second, thirty minutes to eleven; D) two, a quarter past ten. With cardiac catheterization and angiography, the chance of a major complication – such as stroke, heart attack, or death – is … (1) in … (1,000). A) first, one hundredth; B) one, one hundred; C) first, first thousand; D) one, one thousand. The thoracic vertebrae articulate with the … (12) pairs of ribs. A) one too; B) twelve; C) eleven; D) twenty. On the … (14.06.1998) a man suffering from leukemia, aged … (53), was hospitalized. A) fourteenth of June, nineteen ninety-eight, fifty-three; B) fourteenth of July, nineteen ninety and eight, fifty and three; C) fortieth of June, nineteen and ninety-eight, fifty-third; D) fourteen of July, one thousand nine hundred and ninety-eight, fifty three. The average human blood volume is not less than … (7.5)% but not more than … (10)% of the body weight, i. e, about … (5) litres in adults. A) seven point five tenth, tenth, five; B) seven point five, ten, five; C) seven comma fifth, ten, fifth; D) seventh and five, ten, fifty. I can eat … (1 5/7) kg bananas at a time. A) one five seventh; B) one and five sevenths; C) first and five sevenths; D) one fifth seventh. 15 At … (10 ) the anesthesiologist and the surgeon left Operating Room … (1). A) half past ten, one; B) fifteen minutes past ten, first; C) a quarter past ten, one; D) a quarter after ten, first. The heart makes from … (60) to … (72) beats per minute in adults but in children the rate of heartbeat is much higher. A) sixteen, seventy two; B) sixty, seventeen two; C) sixtieth, seventy-second; D) sixty, seventy-two. When scoliosis develops, no cause can be found in … (75) percent of the cases. A) seventy-five; B) seventy fifth; C) seven fifth; D) seventeen five. I've just spoken to the builders. They'll have managed to fix the cardiologic department by the … (1.08.2008). A) second of August, twenty eight; B) first of August, two thousand and eight; C) one of September, twenty zero eight; D) oneth of July, two thousand nine. Erythrocytes are round, biconcave discs, … (7.2) microns in diameter. A) seven and two; B) seven point two; C) seven point and too; D) seven comma two tenth. My friend can eat … (2 3/8) kg oranges at a time. A) too end free eight; B) two and three eighths; C) second and third eighth; D) two three eight. At about … (1130) a.m. the nurse brought me a cap and a white gown Size … (38). A) half to twelve, thirty eight; B) a quarter after eleven, thirty-eighth; C) half past eleven, thirty-eight; D) thirty minutes before twelve, thirteen eight. The weight of a healthy heart is about … (300) grams in an adult man and about … (220) grams in a woman. A) three thousands, two thousands twelve; B) three thousand, two thousand twenty; C) three hundreds, two hundreds and twelve; D) three hundred, two hundred and twenty. The skeletal muscles number over … (400) in the human body. A) for hundreds; B) four thousand; C) forty hundred; D) four hundred. The … (2) set of … (12) vertebrae are known as the thoracic vertebrae. A) two, twelfth; B) second, twelve; C) first, twenty; D) tooth, one too. The blood in the veins of the liver may attain the temperature of … (39.7)°C, while that in the vessels of the fingers, nose and cheeks may have a temperature of only … (36.1)°C. A) thirty-nine comma seven tenth, thirty-six comma one tenth; B) three nine point seven, three six point one; C) three nine comma seventh, three six comma first; D) three nine and seven, three six and one. Our teacher of physical training went on foot … (15 7/9) km a day last week. A) fifteen seven ninth; B) fifteen and seven ninths; C) fifty and seventy ninths; D) fifteenth seventh ninth. The human heart makes from … (60) to … (72) beats per minute. a) sixty/seventy two b) sixteen/seventy-two c) sixty/seventy-two d) sixteen/seventy two The dentist is … (44), he was born on the … (23.02.1967). a) fourty-four/ twenty three of February/ nineteen sixty seven b) forty-four/ twenty three of December/ nineteen sixty-seven c) forty-four/ twenty-third of February/ nineteen sixty-seven d) forty-four/ twenty-third of April/ nineteen sixty seven 62. You are to read unit … (8) on dental caries by … (1440). a) the eighth/ forty minutes past two b) the eighth/ twenty minutes before three c) eight/ twenty minutes to three d) eight/ twelve minutes to third … (17.09) plus … (0.046) equals … (17.136). a) one seven point nought nine/ point nought four six/ one seven point one three six b) one seven paint not nine/ paint not for sex/ one seven paint one free sex c) seventeen comma ten hundredth/ comma forty-six thousandth/ seventeen comma one hundred and thirty-six thousands d) seventy point nine/ point fourteen six/ seventy point one thousand and thirteen six My brother has already prepared … (3/5) his thesis on the methods of treatment of dental caries. a) three fiveth b) three fifths c) three fifth d) third fifths You can take Trolley-bus … (8) and at … (1245) you'll be at the hospital. A) eighth, a quarter to first; B) eight, fifteen minutes before one; C) eight, a quarter to one; D) eighteen, forty-five minutes past twelve. There are … (3) versions of the blood type gene: А, В and O. Since everybody has … (2) copies of these genes, there are … (6) possible combinations: AA, BB, OO, AB, АО and BO. A) thirty, twenty, sixty; B) third, second, sixth; C) free, too, sex; D) three, two, six. This sportsman can run … (100) m in … (13) seconds. A) one hundred, thirteen; B) one thousand, thirteenth; C) one hundreds, thirty; D) one zero zero, one three. This nurse is … (22), she was born on the … (11.07.1986). A) two two, one one of June, one nine eight six; B) twenty two, eleven of June, nineteen and eighty six; C) twenty-two, eleventh of July, nineteen eighty-six; D) twelve too, ten first of July, one thousand nine hundred and eightysixth. Could you give me your calculator for a minute? I can't multiply … (0.081) by… (45.92). A) point zero eight one, four five point nine two; B) zero eighty-one thousandth, forty-five ninety-two hundredth; C) zero comma zero eighty-one, forty-five comma ninety-two; D) zero and zero eight first, four five and nine second. The Chinese used…(350)herbal remedies in 3000 BC. a)three hundred and fifty b) three and fifty c) thirty and five d)third hundred and fifty Our chemist’s shop is open from…( 8.30) till…( 21.00). a)half past eight/twenty-one b) half past nine/twenty-one c) half past eight/nine p.m. d) ) half past nine/nine p.m. 45. The discovery of penicillin is attributed to Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming in …(1928). a)nineteen thousand twenty-eight b) nineteen twenty-nine c)one thousand nine hundred and twenty-eight d) nineteen twenty- eight A…(75)-year- old lady had a sudden heart attack after having taken…(2/3)of her daily dose. a) seventy-fifth/two-third b) seventeen-five/ two-thirds c) seventy-five/two-third d) seventy-five/two-thirds Molecular weight of Chlorine is …(35,5) . a)thirty-five and five b) thirty-five and fifth c) three five point five d) thirty- fifth point five My physical condition is rather good. Last summer I went … (8 5/7) km a day uphill. A) eight five seventh; B) eight and five sevenths; C) eighth and fifth seventh; D) eighteen five seventieths. If I take Bus … (13), I'll have been at the polyclinic by … (930). A) thirteenth, half to ten; B) thirteen, half past nine; C) thirteenth, thirty minutes after nine; D) thirty, thirty minutes before ten. The most significant part of the red cell is its red colouring substance or hemoglobin which on an average forms about … (36)% of its mass. A) three six; B) thirty sixth; C) thirteen six; D) thirty-six. More than … (21 000) kinds of medicinal plants are used in the world nowadays. A) twenty-one thousands; B) twenty-first thousand; C) twenty-one thousand; D) twenty-one hundred. The patient starts taking medicines for diabetes at … (630). A) half to seven; B) thirty minutes past six; C) half past five; D) half past six. When Carl Linné was … (28), in … (1735) he published his main work “Systema Naturae” which made him famous all over the world. A) twenty-eight; seventeen thirty-fifth; B) twenty-eight; seventy thirty-five; C) twenty-eight; seventeen thirtieth-fifth; D) twenty-eight; seventeen thirty-five. To normalize patient’s blood pressure, the doctor prescribed him to take … (1/3) of the glass of medicinal species. A) one three; B) one third; C) first three; D) three first. This drug contains … (0,725) mg of ibuprofen. A) nought point seven two five; B) nought point seven thousand and twenty five; C) nought point seven two fifths; D) nought point seven too five. The movement of food in the intestines of a healthy person may last from … (12) to … (72) hours. A) twelve, seventy-two; B) twenty, seventy two; C) eleven, seven two; D) twelfth, seventeen two. Do you know when the famous Ukrainian scholar of the … (XIX) century was born? A) nineteen; B) ninety; C) ninetieth; D) nineteenth. Can I take your calculator? I can't divide … (0.056) by … (13.5) without it. A) point zero five six, one three point five; B) zero point fifty-six, thirteen point five; C) zero comma fifty-six thousandth, thirteen comma five tenth; D) zero and zero five six, thirteen and five. The most prominent point of each eyeball is about … (1 1/4) inches from the middle line of the face. A) one one fourth; B) one and a quarter; C) one and a half; D) first and first four. If you take Tram … (9), you'll manage to be at the maternity home at … (810) a.m. A) ninth, ten minutes after eight; B) nine, ten minutes past eight; C) nineteen, ten seconds past eighteen; D) ninth, ten minutes to eighty. The liver is the largest gland in the body consisting of … (2) principal lobes. The lobules of the liver are elongated, polygonal structures, having … (5, 6 or 7) sides. A) two, fifth, sixth, seventh; B) second, five, six, seven; C) too, fifth, sex, seventh; D) two, five, six, seven. Gastric and duodenal ulcers are found to develop more frequently in men than in women, mainly at ages of … (25) to … (40) years. A) twelve and five, forty; B) twenty fifth, fourteen; C) two five, four zero; D) twenty-five, forty. The most common blood type classification system is the ABO system, discovered by an Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner in the early … (20) century. A) twelfth; B) twentyth; C) two hundred; D) twentieth. … (0.067) multiplied by … (54.09) equals …(3.62403). A) point nought six seven, five four point nought nine, three point six two four nought three; B) knot point knot sex seven, five for point knot nine, free point sex too for knot free; C) comma zero sixty-seven, fifty-four comma zero nine, three comma sixty-two thousand four hundred and three; D) not and sixty-seven, fifty-four and nine, three and sixty-two thousand four hundred and three. Both eyes are … (2 1/2) inches apart. A) too and one too; B) two and a half; C) two one second; D) second and a quarter. Will you be able to visit my office at … (1305)? – Sorry, Doctor, I'll be busy then. May I visit you at … (1355). A) five minutes past first, five minutes to second; B) five minutes past one, five minutes to two; C) five minutes after one, five minutes before two; D) five seconds after first, five seconds before second. There are more than 20 genetically determined blood group systems known today. A) twelve; B) twelfth; C) twentieth; D) twenty. About … (80) percent of the cholesterol made by the liver is used to make bile. A) eight zero; B) eighteen; C) eightieth; D) eighty. This doctor is … (44), he was born on the … (22.01.1964). A) fourteen four, twelve two of December, nineteen sixteen four; B) four four, two two of January, one thousand nine hundred and sixty-four; C) forty-four, twenty-second of January, nineteen sixty-four; D) fourty four, twenty second off February , nineteen and sixty fourth. We have a doctor’s appointment at …(14.30) . a)half past two p.m. b) half past three p.m. c) two-thirteen p.m. d)two-thirty a.m. There are about …(49)pharmaceutical companies in Ukraine, producing more than…(160)drugs of a synthetic and natural origin . a)forty-nine/one hundred and sixteen b) forty and nine/one hundred sixteen c) forty-nine/one hundred and sixty d)fourteen-nine/one hundred and sixty There is only …(2/3) of natural juice in this tincture. a)two and three b) two-thirds c) second-third d)two-third Molecular weight of Ferrum is about …(55,85). a)fifty-five point eight five b)five five point eight five c)fifty-five koma eight five d)fifty-five point eighty- five The seminar on homeopathic drugs was being held in Germany from September …(1) to… (5),…(1988). a)the first/the fifth/nineteen eighty eight b)one/five/ nineteen eighty eight c) the first/the fifth/eighteen ninety nine d) the first/the fifth/one thousand nine hundred and eighty eight … (21.06) divided by … (0.092) equals … (238.91). A) two one point nought six, point nought nine two, two three eight point nine one; B) twenty-one and six, and ninety-two, two hundred thirty-eight and ninety-one; C) twenty-first point sixth, point ninety-second, two hundred and thirty-eighth point ninety-first; D) twenty-one comma zero six, comma zero nine two, two hundred and thirty-eight comma and nine one. I have already written about … (½) the report on the stress ulcers. A) a quarter; B) a half; C) one twoth; D) first second. May I visit the patient from Ward … (15) at … (1420)? A) fifteen, twenty minutes past second; B) fifteen, twenty minutes past two; C) fifteenth, twelve minutes after second; D) fifteenth, twenty minutes after fourteen. The total weight of the blood pumped by the heart daily is about … (9-11) tons. A) ninth - eleventh; B) ninetieth - twelfth; C) nineteen - oneteen; D) nine - eleven. (275)… participants who took part at the international conference in France. a) too hundred and seventy-five b) two thousand and seventy five c) two hundred seventy five d) two hundred and seventy-five The patient with incurable disease was given the first placebo … (June 29, 1999). a) on the twenty-nineth of June, nineteen ninety-nine b) on the twentieth-ninth of June, nineteen ninety-nine c) on the twenty-nine of June, nineteen ninety-nine d) on the twenty-ninth of June, nineteen ninety-nine As the child was only 1 year old the pediatrician prescribed only … (1/3) of the expectorant medicine two times per day. a) first three b) one three c) one third d) one point third This tablet contains … (0.45) mg of active substance, the rest is starch. a) nought point four five b) zero point forty five c) nought point forty-five d) nill point forty-fifth The lecture is being delivered in …(#6 room). a) the sixth room b) room sixth c) room six d) room number six (50%)… of clinical trial participants who had taken the placebo improved. a) fifty per cent b)fifty per cents c) fifteen per cents d) fiftieth per cent That chemist’s shop was opened on… (12th April ,1961). a)on the twentieth of April, nineteen hundred and sixty-one. b)on the twelve of April, nineteen hundred and sixty-one. c) on the twelfth of April, nineteen sixty-one. d) on the April twelve, nineteen hundred and sixty-one. (2/3)… of this medicine must be taken at once. a)two point tree. b)two and three. c) two thirds. d)two point thirds . Here is a list containing more than …(3 587) medicinal plants used in homeopathy. a)three point five hundred and eighty seven. b) three thousands five hundreds and eighty seven. c) thirty- five hundred and eighty seven. d) three thousand five hundred and eighty seven. The lecture on the use of medicinal plants starts at …(15.30). a)fifteen- thirty. b) thirty past fifteen. c) half past three p.m. d) three o’clock and thirty minutes. In … (1909) the pH scale for measuring acidity was invented. A) one thousand nine hundred nought nine; B) one thousand nine hundred and nine; C) one nine nought nine; D) nineteen nought nine. This community pharmacy usually opens at … (830) a.m. A) thirty minutes past eight; B) half past eight a.m.; C) half to nine; D) thirty minutes to nine. Multiply … (0,58) by … (3,69). A) nought point five eight / three point six nine; B) nought point fifty-eight / three point sixty-nine; C) point fifty-eighth / three point sixty-ninth; D) nought five eight / three six nine. This prominent pharmacologist was born on … (02.10.1962). A) second of October nineteen sixty-two; B) October, two, one thousand nine hundred sixty-two; C) the second of October nineteen sixty-two; D) the second of the tenth one nine six two. … (1/2) of these medicines are sedatives. A) half; B) a half; C) one-second; D) first-two. On … (26.07.1997) my grandfather celebrated his … (50) anniversary. A) twenty-six of June twenty twelve / fifty; B) the twenty-sixth of July nineteen ninety-seven / fiftieth; C) the twenty sixth of July twenty twelve / the fiftyth; D) twenty-six of July two nought one two / fiftieth. Let’s meet near the chemist’s at … (1915). A) fifteen past nineteen; B) quarter past seven a.m.; C) a quarter past seven p.m.; D) fifteen minutes past seven hour. … (2/3) of all the medicines sold at this pharmacy cost more than … (30) hryvnias. A) second-third / thirtieth; B) two-third / thirty; C) two-thirdes / threety; D) two-thirds / thirty. Divide … (6,46) into … (2,81). A) six point four six / two point eight one; B) six point forty six / two point eighty one; C) six point forty-six / two eighty-one; D) six four six / two eight one. You should take … (1½) of glass of this decoction a day. A) one one two; B) one one second; C) one point one second; D) one and a half. Вставте артиклі, де це необхідно: Her father is … chemist, and her two elder sisters are…doctors. a)a ,b)-,c)the,a d)an, a In… Carpathians people have been using medicinal plants for…long time. a)-, a b)the, a c)-, d)the, This is … herb I told you about in …Crimea. a)the, the b) a, c)the, d)-, …most common allergic reactions are …hives, itching, swelling of tissues. a)the, the b)the, c)-, the d)the, a Should I bring this medicine to …ward 5,...nurse? a)the, a b)an, c)-, d) -, a Could you have … look at … report which I gave you yesterday. A) -; the; B) a; the; C) the; a; D) -; -. My friend is … surgeon. She is … best surgeon in our town. A) a; -; B) the; the; C) a; a; D) a; the. It is rather … difficult operation. … 6 surgeons will be performing it. A) a; -; B) -; -; C) -; the; D) a; the. … cow is … domestic animal. A) a; a; B) the; a; C) the; the; D) -; the. Is there … hospital or … polyclinic in … Shevchenko Street. A) -; -; -; B) a; a; the; C) the; -; -; D) a; a; -. Doctor Petrenko is … most experienced gastroenterologist in the hospital. A) a; B) an; C) the; D) -. My brother is … hematologist and my parents are … cardiologists. A) a; an; B) a; the; C) a; -; D) the; the. … doctor you need is in … operating room 2 now. A) The; the; B) The; - ; C) A; an; D) -; an. … wolf is … wild animal. A) The; a; D) The; -. B) A; a; C) -; a; It was … difficult task to get to the top of …Hoverla , especially for those who was in …Carpathians for …first time. a)a, -, the, the b)-, -, -, c)the, the, -, d)the, the, the, the .… British museum is one of … most famous among the others. a)-, a b)The, a c)-, d)The, the 50. They will establish …Union of Pharmacists in …Ukraine next year. a)-, b)a, an c)-, the d)the, She had…terrible time after taking …medicine prescribed by her doctor. a)a, the b)an, a c)-, the d)the, a Ann was … third in .. long line at … chemist’s counter. a)the, a, an b)an, -, the c)the, a, the d) -, a, the … Smiths visited many foreign countries namely… United Kingdom, … Netherlands, … Germany and other. A) -; the; -;, -; B) The; -; -; -; C) -; a; a; the; D) The; the; the; -. The ambulance arrived in … minute. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. I haven’t seen him for … long time. A) an; B) the; C) a; D) - . No … mistake was made while writing final test on … Modulus 2. A) an, - ; B) -, the; C) a, - ; D) -, - . My elder sister is … botanist and my parents … chemists. A) a / the; B) the / the; C) - / -; D) a / -. It’s … plant our teacher told us about. A) a; B) -; C) the; D) an. This is … herbal tea. A) a; B) an; C) the; D) -. … wild chamomile is one of … most widely used flowers. A) a / a; B) the / the; C) - / -; D) - / the. Last year Mr. Dupon delivered lectures in … Canada and … USA. A) - / ; B) - / the; C) the / the; D) the / -. It is … scientific journal. It’s … journal I told you about. A) an, the; B) -, the; C) a, the; D) -, a. … Mr. Petrenko is … most experienced doctor in the hospital. A) - ,- ; B) -, a; C) the, the; D) -, the. … Lake Baikal is … deepest lake in … world. A) -, the, the; B) the, the, the; C) -, the, - ; D) the, the, a. Surgeons have already started … operation. … operation will last for … hour. A) the / The / a; B) an / The / an; C) the / An / -; D) the / - / an. Yesterday … Volkovs went to … theatre. A) - / a; B) - / the; C) the / -; D) the / the. Would you like … tea or … coffee? … water will boil soon. A) - / - / the; B) a / a / a; C) the / the / the; D) - / - / -. – Where is Mr. Smith, … nurse? – He is in … ward five. A) a / the; B) - / -; C) - / the; D) - / a. He is … famous herbalist. He receives … patients on … Fridays. A) the / the / the; B) - / - / -; C) a / - / -; D) a / - / the. Epidemics of influenza usually occur in … winter. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. This doctor is … very kind man. A) a; B) the; C) an; D) - . … Chicago is on … Lake Michigan. A) a,- ; B) the, a; C) the, the; D) - , - . There is … lamp above … operating table. A) the, - ; B) a, the; C) the, the; D) the, a. … third section of a drug label includes common … side effects. a)a, b)-, c)the, d)a, a We always have …good time during our holidays at …Black Sea. a)a, the b)the, a c)-, d)-, the This is …new phone number of …doctor I told you about. a)the, the b) a, the c)a, - d)the, a He is …musician, he plays … the piano. a)the, the b)a, the c)a, d)the, a Do you often go to …polyclinic?-Once or twice…month. a)the, a b)a, c)the, the d) -, a There was … door opposite me. I went in and locked … door. A) the, an; B) the, the; C) a, a; D) a, the. … highest peak of … Carpathian Mountains is … Hoverla. A) the, the, a; B) a, the -; C) the, the, -; D) a, the, a. In … summer of 2006 he was hospitalized because of stomachache and nausea. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. By … mistake he was made a diagnosis of acute lymphocytic leukemia. A) - ; B) the; C) a; D) an. I was … fifth patient the doctor examined on … Monday. A) the, the; B) the, a; C) the, - ; D) -, - . … Labour Party is very popular in … United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. A) The, the; B) a, the; C) the, - ; D) - , - . … first heart sound is … longest one. A) The, - ; B) A, - ; C) - , -; D) The, the. Both my… sister and her … husband are …therapeutists. a) a, -, b) -, -, the c) -, -, d) a, a, a I was … fifth patient … doctor of our clinic examined on Monday. a) a, the b) -, a c) the, the d) -, the … patient who had been operated before was allowed to go for … walk. a) The, b) A, the c) A, d) The, a This … doctor makes his … morning rounds every … day. a) the, the, the b) a, the, a c) -, -, d) the, a, Once … year students of our university go to .. UK or other countries of … Europe to improve and share their knowledge. a) a, the, b) a, -, c) the, the, a d) -, a, the Two … ambulances drove up to … hospital in … Main Street. A) - , the, - ; B) - , the, the; C) - , - , - ; D) -, a, - . My aunt is … ophthalmologist. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. I can play … piano. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. For … long time … problem of blood transfusion wasn’t solved. A) a, the; B) an, a; C) - , -; D) the, -. This is … hospital. … hospital was built five years ago. A) the, - ; B) a, The; C) - , The; D) the, The. Is there … polyclinic in … Chornovil street? A) a, - ; B) the, a; C) - , the; D) - , - . … Nile flows across … Northeastern part of … Africa. A) The, the, - ; B) A, the, - ; C) - , the, - ; D) - , - , an. My aunt is … ophthalmologist. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. This is … hospital. It is … hospital I work at. a) a, the b) the, a c) the, the d) -, the … Doctor Kovaliuk is … best oncologist in our town. a) a, the b) the, a c) -, the d) the, the Lat year my parents went to … France and ... Netherlands. a) a, the b) the, c) -, the d) the, the … Baikal is … deepest lake in … world. a) the, the, the b) the, -, the c) -, the, a d) the, the, What … clever student you are! a) a b) the c) an d) – I can play … piano. A) a; B) the; C) - ; D) an. For … long time … problem of blood transfusion wasn’t solved. A) a, the; B) an, a; C) - , -; D) the, -. … earth revolves around … sun once every 365 days. a) an, the b) the, a c) the, the d) a, the Eugene’s lunch consisted of … sandwich, two cookies, and ... can of soda. a) an, an b) the, the c) a, a d) a, the … wool that is produced in Scotland is used to make … sweaters. a) An, the b) The, a c) The, d) A, the I'm … David Appleyard that lives in … Japan. a) the, b) the, a c) -, d) a, the Many Chinese still believe … Englishman always carries … umbrella. a) the, the b) the, a c) an, an d) a, the This is … hospital. … hospital was built five years ago. A) the, - ; B) a, The; C) - , The; D) the, The. Is there … polyclinic in … Chornovil street? A) a, - ; B) the, a; C) - , the; D) - , - . She felt …severe tongue swelling on … tenth day. a) a, the b) a, a c) the, - d) -, a Last summer I planned to go to … UK or … France but went to … Netherlands. a) -, the, the b) the, - ,the c) -, -, the d) the, the, the There are… lot of rest homes in … Carpathians. a) -, b) a, c) a, the d) the, … head of … Svoboda Party is … O. Tyahnybok. a) The, the, b) -, -, c) The, -, d) -, the, … cow is … domestic animal. a) The, the b) A, c) The, a d) A, the … Nile flows across … Northeastern part of … Africa. A) The, the, - ; B) A, the, - ; C) - , the, - ; D) - , - , an. The patient has already taken this treatment for … week. A) an; B) a; C) the; D) - . What … clever student you are! a) the b) a c) an d) In … winter of 2005 he was hospitalized because of tongue cancer. a) an b) a c) the d) … Petrenkos is … dynasty of oncologists. a) a ; the b) The; c) The; a d) -; It is … scientific journal. It’s … journal I told you about. a) the; a b) a; the c) the; the d) a; a He told us about … relief he felt after the physiotherapy. a) b) a c) the d) an … highest mountains are in … Asia. A) the, the; B) - , - ; C) the, - ; D) a, the. … Smiths usually visit their grandmother in … Netherlands. A) The, the; B) - , - ; C) The, - ; D) - , the. … human heart contracts from … first moment of life until … last one. A) The, a, a; B) The, the, the; C) - , a, - ; D) An, - , the. This is … ointment. This is … ointment I bought for you to relieve … herpes labialis. a) an, the, b) the, a, the c) the, the, the d) a, the, There is … blister in … the baby’s mouth. a) an, the b) the, a c) the, the d) a, the … sun rose but remained hidden behind … dark grey clouds. a) the, b) the, a c) -, the d) a, the … patient asked … doctor to tell him … truth. a) the, -, the b) the, a, c) the, the, the d) a, the, a No … mistake was made while writing the final test on … Module 2. a) the, b) the, a c) -, the d) -, The doctor saw … patient in … ward 4. … patient was very weak. A) the, the, The; B) a, - , The; C) an, a, - ; D) a, the, The. … Sechenov became … professor at … Medical and Surgical Academy in … Moscow. A) - , - , - , the; B) The, the, a, a; C) The, an, - , -; D) - , a, the, - . … Baikal is situated in … Russia. a) -, the b) The, c) The, the d) -, … Kovalenkos are…famous dentists. a) The, b) -, the c) -, d) -, a Have you ever been to … Philippines or … Malaysia?. a) the , the b) -, c) the, d) -, the In … south of our country … different sanatoriums and health resorts are located. a) a, b) the, c) -, a d) -, the I got into … bus 23 by … mistake. a) the, b) a, a c) -, a d) -, She is still quite … child. A) an; B) the; C) -; D) a. This is … apparatus for blood transfusion. This is … apparatus I told you about. A) an, an; B) a, -; C) the, the; D) an, the. His mother is … doctor who treated me … last year. a) -, a b) a, the c) -,d) the, This is … most painful procedure I have ever had. a) a b) the c) – d) an We visit … British Museum from … time to … time. a) -, -, the b) a, the, c) the, -, d) -, -,What is … highest peak of … Alps? a) -, b) the, the c) a, the d) the,Neither … doctor nor … nurse knew where … patient had gone. a) -,-,the b) a, a, a c) the, the, the d) a, a, the There is … nurse in … ward. A) the, the; B) a, a; C) a, the; D) the, a. … capillaries are … tiniest blood vessels. A) A, -; B) A, a; C) The, the; D) A, the. … Hoverla is … highest peak of … Carpathians. A) a, -, -; B) the, the, -; C) -, the, the; D) a, the, -. … my son always goes to … bed at 10 o’clock. a) -, a b) -, the c) -,d) The, the … Neva flows into … Gulf of … Finland. a) The, the, b) -, -, the c) -, the,– d) The, -, the I was operated on in … summer. a) a b) c) an d) the There was … long silence on hearing … diagnosis. a) a, the b) -, c) the, a d) a,… dental clinic you told me about is situated in … Mazepa street. a) The, b) -, c) -, a d) The, the Last year I went to … France and … Netherlands, this year I have visited … United Kingdom and … Germany, and next year I shall go to … USA. A) the, -, -, the, -; B) -, the, the, -, the; C) a, the, the, a, the; D) the, a, a, the, a. He is … hematologist who treated my granny. A) a; B) an; C) the; D) -. The nurse is in … ward ten. A) a; B) an; C) -; D) the. … my son always goes to … bed at 10 o’clock. A) -, a; B) -, the; C) -, -; D) The, the. There is … lamp above … operating table. A) the, an; B) a, an; C) a, the; D) the, the. … Neva flows into … Gulf of … Finland. A) The, the, -; B) -, -, the; C) -, the, -; D) The, -, the. … traumatologist wants … surgeon to have … look at … wound. A) The, the, a, the; B) A, a, the, a; C) -, the, -, the; D) a, -, a, -. … most important systems for blood transfusions are the ABO and Rh systems. A) A; B) An; C) -; D) The. I was operated on in … summer. A) a; B) -; C) an; D) the. Olga is … cleverest student in … group. A) a, a; B) the, the; C) an, an; D) the, -. There was … long silence on hearing … diagnosis. A) a, the; B) -, -; C) the, a; D) a, -. – Of which country is … Washington … capital? – … United States of America. A) -, -, -; B) the, the -; C) -, the, the; D) the, the, the. … doctor allowed … patient to go for … walk to … park. A) The, the, a, the; B) A, a, -, a; C) -, -, a, -; D) -, the, -, the. … most important systems for blood transfusions are the ABO and Rh systems. A) A; B) An; C) -; D) The. I was operated on in … summer. A) a; B) -; C) an; D) the. Olga is … cleverest student in … group. A) a, a; B) the, the; C) an, an; D) the, -. There was … long silence on hearing … diagnosis. A) a, the; B) -, -; C) the, a; D) a, -. – Of which country is … Washington … capital? – … United States of America. A) -, -, -; B) the, the -; C) -, the, the; D) the, the, the. … doctor allowed … patient to go for … walk to … park. A) The, the, a, the; B) A, a, -, a; C) -, -, a, -; D) -, the, -, the. He is … patient of our clinic. A) the; B) an; C) -; D) a. … mistake was made while diagnosing the patient with acute leukemia. A) -; B) an; C) the; D) a. For … long time … problem of blood transfusion wasn’t solved. A) the, a; B) a, the; C) -, a; D) the, -. … hospital you told me about is situated in … Mazepa street. A) The, - ; B) -, -; C) A, a; D) The, the. Drinking … coffee is not recommended to … people suffering from … hypertension. A) -, -, -; B) the, a, -; C) the, the, the; D) a, a, a. … proctologist asked … patient not to be … shy and tell … truth. A) The, the, -, the; B) A, a, -, a; C) The, the, -, -; D) -, -, the, the. … floor in this ward has been just washed. A) A; B) -; C) The; D) An. … blood type is established before … person is born. A) a, the; B) the, -; C) -, a; D) -, -. This severe chromosomal disease runs in … his family. A) an; B) a; C) the; D) -. I would have … coffee and … cake. A) -, -; B) a, a; C) the, the; D) the, -. This is … ointment I bought for you to relieve … pain in … joints. A) the, -, the; B) a, a, a; C) a, -, a; D) the, a, a. … doctor allowed … patient to go for … walk. A) The, the, a; B) A, a, the; C) -, -, -; D) A, the, the. The ambulance arrived in … minute. A) -; B) the; C) a; D) an. On … Mondays the hematologist usually receives patients in his consulting room. A) an; B) a; C) the; D) -. I was … fifth patient the doctor examined on … Monday. A) a, a; B) -, -; C) the, - ; D) a, a. … Ivano-Frankivsk is situated on … Bystrytsya River. A) -, -; B) the, -; C) -, the; D) the, the. Though I am not … doctor I decided to have … look at his … wound. A) a, a, -; B) -, the, the; C) -, -, -; D) a, a, a. “… Fire Destroys … Plane” was … article which stoke me most of all. A) -, -, the; B) The, the, -; C) A, a, -; D) -, -, a. What … clever student you are! A) the; B) a; C) an; D) -. In … winter of 2005 he was hospitalized because of weakness, shortness of breath, and bleeding. A) an; B) a; C) the; D) -. It is … scientific journal. It’s … journal I told you about. A) the, a; B) a, the; C) the, the; D) a, a. … Chicago is on … Lake Michigan. A) the, -; B) -, -; C) -, the; D) the, the. … Petrenkos is … dynasty of doctors. A) A, the; B) The, -; C) The, a; D) -, -. “… Helicopter Saves … Man” was … largest article in this newspaper. A) -, -, the; B) The, the, -; C) A, a, a; D) The, the, the. This doctor is … very kind man. A) -; B) the; C) an; D) a. When will you make me an injection, … nurse? A) a; B) -; C) an; D) the. … carp is … fish. A) -, -; B) a, a; C) the, a; D) a, the. … prominent anatomist-microscopist … O. Shumlyansky was born in 1748. A) The, -; B) The, the; C) A, the; D) A, -. While being in … London I visited … Royal Opera House. A) the, the; B) -, -; C) -, the; D) the, -. … patient asked … doctor to tell him … truth. A) -, the, a; B) A, a, a; C) -, -, -; D) The, the, the. His father is … doctor. A) -; B) the; C) a; D) an. … nurse can make intravenous injections. A) an; B) -; C) the; D) a. … hour had passed before they finished … operation. A) A, an; B) The, -; C) An, the; D) The, the. Helen, without … word, left … classroom. A) -, a; B) the, a; C) a, the; D) the, -. There’s … very good drugstore in … Shevchenko Street. You can easily walk there in … few minutes. A) a, the, the; B) a, the, -; C) -, a, -; D) a, -, a. I have to buy … syringe, … medicine dropper and … some drugs. Perhaps you can tell me where I can find … chemist’s shop? A) the, a, the, a; B) the, the, the, a; C) a, a, -, a; D) -, -, -, the. What … beautiful day! A) an; B) the; C) -; D) a. I haven’t seen him for … long time. A) an; B) -; C) the; D) a. I saw … ambulance at my house. … ambulance was rather new. A) an, The; B) the, An; C) an, An; D) -, The. There was … door opposite me. I went in and locked … door. A) a, a; B) the, a; C) a, the; D) the, the. Is there … polyclinic or … hospital in … Chornovil Street? A) -, -, the; B) the, the, a; C) the, the, -; D) a, a, -. … well-known physician … Mr. White will visit … Italy, … Israel and UK … next year. A) A, -, -, -, the, -; B) A, -, the, the, the, -; C) A, -, -, -, -, the; D) The, the, -, -, -, the. It is rather … difficult operation. A) -; B) the; C) an; D) a. He understood … mistake he made. A) -; B) an; C) a; D) the. … wolf is … wild animal. A) A, the; B) The, a; C) The, the; D) A, a. … newborn must be cared for with … great responsibility. A) The, the; B) A, -; C) A, the; D) -, -. … first and … second cardiac sounds are heard over all portions of … heart. A) -, -, the; B) a, a, -; C) A, the, a; D) The, the, the. … well-known physician … Mr. Smith has visited … France, … Germany and … Philippines … this year. A) A, -, -, -, the, -; B) -, -, the, the, the, the; C) The, the, -, -, the, the; D) a, -, the, the, -, a. … sun rose but remained hidden behind dark gray clouds. A) -; B) An; C) A; D) The. Though I am not … musician I can play … piano very well. A) a, the; B) the, a; C) the, the; D) a, -. No … mistake was made while writing the final test on … Modulus 1. A) the, the; B) -, -; C) a, a; D) an, an. … Kovalenkos are … famous cardiologists. A) a, -; B) The, a; C) -, -; D) The, -. … Khreshchatyk Street is … most famous street in … Kyiv. A) -, the, -; B) the, the, the; C) the, -, the; D) -, -, -. … well-known physician … Mr. Cabot visited … Netherlands and … Poland … last year. A) A, -, -, -, the; B) The, the, the, the -; C) A, -, the, -, -; D) -, -, the, -, the. His father is … doctor I told you about. A) a; B) the; C) an; D) -. I can play … piano. A) an; B) -; C) a; D) the. This is … hospital. … hospital was built five years ago. A) The, a; B) A, the; C) An, a; D) -, the. He is … therapeutist who treated me in … autumn of 1999. A) a, a; B) the, the; C) an, an; D) -, -. … Labour Party is very popular in … United Kingdom of … Great Britain and Nothern Ireland. A) -, -, -; B) The, the, -; C) The, the, the; D) -, the, the. … great surgeon and scientist … M. V. Skliphosovsky liked … Ukraine and often visited … Odesa. A) -, -, the, the; B) The, -, -, -; C) A, -, the, -; D) -, the, -, the. He is … best surgeon in our town. A) a; B) the; C) -; D) an. My parents are … doctors. A) a; B) an; C) the; D) -. Mr. Smith is … most experienced doctor in … hospital. A) a, a; B) the, the; C) -, -; D) a, the. … some students were not prepared for … lesson. A) a, a; B) the, -; C) -, the; D) a, -. … Baikal is … deepest lake in … world. A) The, the, the; B) -, -, -; C) -, the, -; D) -, the, the. … Nile flows across … northeastern part of … Africa to … Mediterranean Sea. A) The, the, -, the; B) -, -, -, the; C) The, a, the, the; D) -, the, the -. She didn’t answer … third question. A) an; B) -; C) the; D) a. My father is … doctor. A) -; B) the; C) an; D) a. … person with Rh+ blood can receive blood from … person with Rh- blood without any problems. A) The, - ; B) A, a; C) A, the; Am I to go to … Ward 8, … doctor? A) the, the; B) -, -; C) a, a; From … time to … time … Mr. Smith feels nausea and fatigue. A) -, -, -; B) -, -, the; C) the, the -; … highest peak of … Carpathian Mountains is … Hoverla. A) The, -, the; B) The, the, -; C) The, the, the; My sister is … anesthetist. A) a; B) -; C) the; D) -, -. D) a, the. D) a, a, -. D) A, the, a. D) an. At what time may I visit you, … doctor? A) an; B) a; C) the; D) - . … cow is … domestic animal. A) A, the; B) The, a; C) -, -; D) The, the. I am going to visit … physician on … Monday. A) the, the; B) a, -; C) a, a; D) -, the. … head of … Batkivshchyna Party is … Yuliya Tymoshenko. A) The, the, -; B) a, the, the; C) -, -, -; D) a, -, -. In … this newspaper there is … article with … headline “… Man was Cured of … Leukemia”. A) -, the, the, -, -; B) a, the, the, a, -; C) -, a, a, the, a; D) the, a, a, -, the. Трансформуйте наступні речення у пасивний стан: The students were discussing electro-optical properties of organic compounds when I entered the room. The doctor will prescribe him some antibiotic to combat the infection. Doctors prescribe cortisone, aspirin or ibuprofen for treating inflammations. Recently researches have tested the new medicine on large study groups. He will prepare a suitable drug formulation next week. The lecturer has already explained the difference between official names of drugs and their brand names. The students had already discussed the benefits of homeopathic remedies when I entered the room. Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to combat the infection. We are discussing his report on galenics now. This student has just finished his summer practice at the community pharmacy. The scientists have just finished the investigation of side effects of new medicine. Yesterday the whole lesson our teacher was explaining us the aims and principles of pharmaceutics. The students discussed the use of organic compounds in pharmacology last week. They haven’t prepared decoction of the dandelion roots yet. He will repair the drug cabinet where poisonous medications are stored tomorrow. Pharmacists collect medicinal plants every summer. The nurse checked the blood pressure of the patient before the operation. They were carrying the injured person to the hospital. The patient has lost teeth because of severe gum disease. Some individuals or animals produce antibodies against infectious agents. The teacher will have told the students about strategies for preventing the transmission of HIV by the next week. The doctor and the patient were carrying out their experiments to identify an allergen at 4 o’clock yesterday. The students usually study symptoms of different diseases at the lessons. Protestor Smirnov delivers lectures in Chemistry every morning. I have learnt most information about the endodontic treatment from this book. The denturist will have made a new denture by the next week. The teacher hasn’t explained us the etiology of the respiratory tract diseases yet. The doctor is performing the spinal puncture during the operation now. The new virus particles destroy lymphocytes. The students have already studied the organs of the respiratory system. He was learning internal and external respiration from 3 till 4 yesterday. We use the term “atopic disease” to describe a group of often inherited Ig Emediated diseases. Look! The dentist is pulling the patient`s tooth with forceps. Then the stomatologist gave my sister anesthesia. Before he went to bed he had brushed his dentures. Doctor Petrenko was examining the patients the whole morning yesterday. The students haven’t filled in the case history yet. Bony cage protects lungs and other organs in the chest. Root canal treatment provides desirable curing effect. The dentist has just performed the process of cleansing patient’s teeth . Last week the dentist placed veneers on the patient’s stained teeth. The doctor was examining this patient at 10 o’clock yesterday. This student had studied sense organs by 7 o’clock last night. Nurses keep medical instruments sterile. The doctor was investigating the etiology of this disease during the whole day on Friday. They had translated the text by 7 o’clock yesterday. Veneers provide desirable aesthetic effect. A dentist will perform the process of cleansing patient’s teeth next week. At last the dentist has placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. The students are reading the article about nervous system disorders now. Taras had investigated the symptoms of meningitis and encephalitis by 6 o’clock yesterday. Local anesthetics provide a patient with pain-free experience. A dentist will perform the process of cleansing patient’s teeth next time. Last week the dentist placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Doctors make their morning rounds every day. The skin performs the function of an important blood depot. Dr. Petrenko was delivering his lecture on Anatomy at this time on Tuesday. We did not discuss questions concerning maintence of veneers at our meeting yesterday. Has teeth whitening provided a white smile for you discoloured teeth? I am reading a very interesting article on advantages of dental implants now. The students haven’t finished their research work yet. The patient needs a dental crown to protect a severely worn down tooth. At 3 p.m. the teacher was checking the students’ test-papers on professional dental cleanings. The dentist will perform the procedure of teeth whitening next week. At last the dentist has placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Local anesthetics provide a patient with pain-free experience. Next week the dentist will place crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Root canal treatment provides desirable curing effect. The dentist has just performed the process of cleansing patient’s teeth. We are learning about the cases of dental implants failure. Tooth whitening hasn’t made dark teeth look whiter. Dentists place veneers mainly on front teeth. Will they be making veneers in the dental laboratory at this time tomorrow? After that the dentist recommended the patient the proper diet. My brother was cleansing the patient’s teeth at that time. The patient disinfects his retainer once a week. The professor will deliver a lecture on teeth whitening next Monday. The surgeon was still performing the operation at 7 p.m. The denturist has already instructed the patient how to take care of partial dentures. The dentist advised the patient to keep the dentures in place over night until the adjustment period is over. This endodontist is performing root treatment now. Researchers are investigating potential new materials for dental restorations. Will they make veneers in the dental laboratory tomorrow? The surgeons were performing the operation at this time on Monday. The dentist has just written out the prescription. The dentist will restore the tooth tomorrow. The nurse was sterilizing dental instruments when I came in. I am reading a very interesting article on advantages of dental implants now. The nurse checked the blood pressure of the patient before the operation. Will teeth whitening provide a white smile for your discoloured teeth? Трансформуйте наступні речення у активний стан: Will these drugs be tested for their adverse effect by the doctors? The information on chemical characteristics of plastics is being looked for by the students now. Half of the participants will be given a placebo instead of the drug by the doctors carrying on the experiment. Medicines you asked for have already been bought by my daughter. Cortison is often used by doctors for treating various inflammations. By 9 o’clock a.m. a cough mixture will have been compounded by the pharmacist. Herbal decoction will be brewed by my mother. By 12 o’clock the necessary medicines had been ordered by a pharmacy manager. Is this drug still being tested for its side effect by the doctors? The information on placebo effect wasn’t found by the students yesterday. Many medicinal plants were used for the prevention and curing of diseases by the ancient Slavs. Nowadays pharmacognosy is taught at pharmacy departments and pharmacy universities by specialized professionals. At the moment the importance of plants in modern farmacy and medicine is being discussed by the scientists. Hoofs, skin, horns and bones from animals are used in traditional medicine by the Chinease. Have these drugs been already tested for their adverse effect by the doctors? The information on chemical characteristics of plastics wasn’t found by the students yesterday. Have these drugs been already tested for their adverse effect by the doctors? The information on chemical characteristics of plastics wasn’t found by the students yesterday. My granny has been advised by her orthodontist to keep the dentures in place overnight. A temporary dental filling will be used by the dentist in this emergency dental treatment. The students were being taught by the teacher how to distinguish between different types of immunity during the whole lesson on Monday. The antibiotics have already been administered to the patients by doctors for combating an infection. My sister is being extracted a bad tooth by your father at the moment. The impressions have already been sent to the laboratory. The symptoms of asthma will be studied by the students next time. The problem of AIDS in our country is being discussed by the students at the moment. The patient has been advised by the dentist to keep the dentures in place overnight. He is being examined by the dentist now. Anaphylactic shock has been studied by this prominent scientist for two years already. They will be explained the use of the Present Perfect Tense by the teacher tomorrow. Amalgam fillings are commonly used by dentists nowadays. A permanent filling is being put by the dentist now. Allergic reactions haven’t been investigated by the students yet. The lungs are separated from the abdomen by the diaphragm. The student was being asked by the professor when I came. The patient has just been advised by the dentist to brush his teeth twice a day. A small post made of titanium is being inserted into the patient’s bone socket by the dentist now. Each alveolus is surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. This book was being read by him at this time yesterday. The symptoms of this disease will have been studied by the surgeon by the beginning of autumn. The impressions will be sent to the laboratory by the denturist tomorrow. Some sedative drug is being given to the patient by the dentist now. Peter is being examined by the doctor now. Operations are usually performed by the surgeon in the morning. The patient has been advised by the dentist to keep the dentures in place overnight. Veneers are mainly placed on front teeth. The interesting article about AIDS has already been written by our teacher. The student hasn’t been told about different nervous system tumors by teacher yet. Metabolic processes are regulated by the central nervous system. A small post is being inserted by the dentist at the moment. Teeth enamel discolouration was caused by chemical damage to teeth. The patient is being operated on the spinal cord by the famous surgeon now. New method of examining patients is being developed by scientists at the moment. Ann will have already been discharged from the hospital by the doctor by this time tomorrow. The patient’s state of the oral cavity will be improved by the stomatologist next week. His bad breath has been detected by his sister today. Brace breakage has been caused by eating tough-to-bite food. Jack is being performed a prophylactic check-up by the dentist at the moment. The secretory function of the skin is performed by the sweat and sebaceous glands. The patient’s lungs and heart have already been listened to by the therapeutist. Ann will be administered an injection by the doctor tomorrow. Wards are being cleaned and aired by the nurses now. These drugs were prescribed by the doctor. At the moment a very interesting article on deterioration of dental implants is being read by my father. A hole in the top or back of tooth is made by the dentist to get to the root. The patient will have been treated by this dental orthopedist by 5 p.m. tomorrow. Composite veneers were performed in a single visit to the dentist. A cobalt-chrome frame has been constructed around the remaining teeth. Many dental disorders are caused by poor hygiene. Temporary veneers will have been removed before the dentist installs them with dental cement. The patient has just been injected antibiotic by this pretty nurse. By evening the toothache will have been reduced by this new pill. Some natural teeth had been extracted by the dentist before he inserted immediate dentures. Veneers were invented by Charles Pincus in California. Jack is being examined by the dentist at the moment. Oral hygiene has never been observed by the patient adequately. My sister is being operated on by your father at the moment. Veneers are placed mainly on the front teeth. Veneers were permanently cemented to the teeth by the dentist yesterday. The drugs are being made by the pharmacist at the moment. The patient has just been advised by the dentist to brush his teeth twice a day. Amalgam filling had been put by the dentists by that time yesterday. The impressions will be sent to the laboratory by the denturist tomorrow. Some sedative drug is being given to the patient by the dentist now. Amalgam fillings are commonly used by the dentists nowadays. The impressions have already been sent to the laboratory. A permanent filling is being put by the dentist now. Absent teeth have already been substituted by bridgework. Veneers are mainly used to correct colour of the teeth. A small post made of titanium is being inserted into the patient’s bone socket by the dentist now. Veneers were invented by a dentist Charles Pincus. He is being examined by the dentist now. The patient has been advised to keep the dentures in place overnight until the adjustment period is over. Передайте наступні речення непрямою мовою: The doctor advised us, ‘Give the prescribed medicine to your baby more carefully’. The nurse said to me, ‘I have made some herbal tea for your cough’. The pharmacist asked the patient, ‘Did you use tinctures last year?’ The manager of the chemist’s said to me: “I regularly review up-to-date list of drugs and official standards for their manufacture”. My friend said: “I was preparing this information about drug categories, names and groups at 7 o’clock yesterday”. The physician said to the patient, “Don’t take these lollipops before meals”. The doctor said, “The results of your blood test show iron anemia”. The patient asked the physician, “Have you already diagnosed my disease?” The teacher said to the student, “Go to the library tomorrow and find an interesting information about this problem”. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the drug design and development from this article”. The patient asked his doctor, “Do placebos work upon everyone?” The elderly man said to his grandson, “Buy me some drugs for headache, please”. “In a year we shall test this candidate drug in people”, said our professor to us. The doctor asked, “Are you taking Tylenol for headache?” Our instructor said, “Learn definitions of effects and esthetics of placebo”. The nurse said to me, ‘I will make you a pain relieving injection in an hour’. The doctor asked us, ‘Have you given your baby the prescribed medicine today?’. The pharmacist said to the customer, ‘Buy this remedy, it is cheaper. ’ The researcher said, ‘Last month we received a new medicine effective in treatment of diabetes’. The doctor asked his patient, ‘Have you ever had similar symptoms?’. The teaching assistant said to Ann, ‘Give the definition of homeopathic medicine.’ The lecturer asked, ‘Why are so many students absent from the class today?’. The doctor advised us, ‘Don’t overuse this drug, it is dangerous’. The pharmacist said, ‘We will sell this medicine only with doctor’s prescription.’ “There will be a scientific TV program on the types of dental restorations tonight”, our teacher said to us. The doctor asked, “Do you smoke or drink any alcohol?” “I will keep the dentures in place overnight until the adjustment period is over”, said the patient. The doctor asked , “What side effects of this medicine have you had recently?” The student said, “I can't answer your question now, I don't remember everything about direct and indirect restorations. ” The doctor asked , “Are you taking any medicines at the moment?” The nurse said, “Don't worry. The dentist will be here to give you a hand.” She said, “Barbara has been a nurse for 20 years in this dental clinic and she is still working here” The nurse said, “Now, the doctor is doing everything possible to save your son”. The patient asked, “Shall I be discharged from the hospital tomorrow?” Mary said: “I’ll call the first aid station”. The doctor asked his assistant, “When did the lymph nodes in this patient swell?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Don’t be afraid and don’t cry”. The professor said to the students: “Many people experience serious long-term complications often resulting in autoimmune reactions”. The patient’s parents asked, “Will our son feel better soon after taking these drugs?” Sane said, “I’ve already talked to the doctor”. She asked, “How long do the active symptoms of this disease persist?” The doctor said, “Don’t enter the operating room!” The nurse said to the doctor, “I haven’t filled in the case history of this patient yet”. The doctor asked,” Did you have any allergic reactions before?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I gave that patient some sedative drugs last night”. The doctor said, ”Don’t use fluoride toothpaste for your teeth so often”. The dentist asked the patient,” When will you come to my office next time?” Tony asked the nurse, “Do you consider the pulse of the patient to be accelerated?” The patient said, “She didn’t expect to have complications after influenza”. Sam asked the nurse, “When will you give me an injection?” The doctor asked,” Do you feel numbness in this area?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I have given that patient some sedative drugs”. The doctor said, ”Brush and floss your teeth more carefully”. The dentist asked the patient,” When did you have your tooth extracted?” The traumatologist asked her, “Pull up the sleeve so that I can look at the wound”. The teacher explained us, “A person with HIV can remain well for over a decade”. She asked, “Is the immune system of premature infants fully developed?” Olga’s relatives were told, “Olga’s condition has improved greatly since last week”. The doctor said, ”You will feel numbness in a minute”. The nurse asked the dentist, ”Why have you administered antibiotics”. The doctor said, ”Don’t move”. The dentist asked the patient, ”Do you have any allergic reactions?” The student asked, “When will neurologic examination be performed?” The doctor said to me, “Don’t take off the plaster cast for a week”. She said, “Antituberculosis vaccination is administered to all the babies in maternity homes”. The patient said, “My dentures have been ill fitting for quite some time” He said, “Two days ago we watched the endodontist removing the pulp”. “If I feel better, I shall attend the lecture in Anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The lecturer said, “Learn the procedure of simple tooth extraction in detail”. The student asked, “Are innate and learned immunity independent of each other?” The teacher said, “We’ll study the diseases of the nervous system next week”. The patient asked the doctor, “What drugs are usually taken to reduce fever?” The doctor said to him, “Don’t forget to have your chest examined once a year”. Describing his general state the patient said: “I suffered from severe headaches, cough, and had trouble sleeping”. The denturist said, “Yesterday I fabricated maxillary denture for your grandfather”. “Do you prefer composite resin or ceramic filling for your front tooth?” the dentist asked his patient. The lecturer said: “You’ll have to know in detail three types of neurons”. The nurse asked the doctor, “Why has the blood pressure fallen?” He asked, “Are they performing magnetic resonance imaging now?” The doctor asked, ”Do you feel numbness in this area?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I have given this patient some sedative drugs”. The lecturer said, “Learn the structure of the nervous system in detail”. “Have you already interviewed the patient to obtain his medical history?” the professor asked the student. The doctor said to the patient, ”You will feel numbness in a minute”. The dentist asked the patient, ”Have you ever had any allergic reactions?” “Don’t speak loud, the patient is sleeping after the medical procedure”, the doctor said to him. The doctor said, ”Don’t use fluoride toothpaste for your teeth so often”. The dentist asked the patient, ”When will you come to my office next time?” “What was muscle atrophy caused by?” asked the nurse. I said to the doctor, “This patient suffers from severe headaches”. The teacher said, “In a week we are having practice in the polyclinic”. He asked, “When will you perform tooth extraction?” “If I feel better, I’ll attend the lecture in anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the structure of the CNS from this book”. The dentist asked, “Do you feel numbness?” My sister said to me: “Don’t speak loud, mother is sleeping after the procedure of tooth extraction”. The teacher said, “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. He asked, “Did you order special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The patient asked the doctor, “When will you perform the spinal tap?” The laryngologist said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. “Write three sentences in passive voice”, our teacher said to us. The doctor asked, “Did you take any drugs yesterday?” “My sister will become an orthodontist”, he said. Then she said, “Brush your teeth thoroughly but not too vigorously”. The patient complained, “I have been suffering from severe halitosis for over a year”. The maxillofacial surgeon said to me, “Make a panoramic X-ray tomorrow”. The mother said to her son, “The dentist has prescribed you this toothpowder to maintain oral hygiene”. “When will you like to have your appointment?” the dentist asked Tom. The nurse said to us. “There is no dentist here, in the office. He has just left. He’ll come back tomorrow”. The lecturer said, “Learn the procedure of ultrasonic teeth cleaning in detail.” The patient said,” My dentures have been ill-fitting for quite some time”. ”The dentist had left the office before I came”, the nurse said to us. He said, “We have already watched the endodontist removing the pulp.” The professor asked, “Did you like your practice at the dental clinic?” “If I feel better, I shall attend the lecture in Anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The doctor asked, “Do you smoke or drink any alcohol?” The patient said, “My dentures have been ill-fitting for quite some time. What shall I do?” He said, “Two days ago we watched the endodontist removing the pulp”. Перекладіть наступні речення англійською мовою: Я не можу говорити з тобою по телефону. Мій брат щойно обпік стегно, тому швидка везе нас в опікове відділення міської лікарні. Кардіолог проведе повний медичний огляд пацієнта, зробить електрокардіограму та поставить діагноз до кінця наступного тижня. Хірург щойно закінчив операцію на зап’ясті і щиколотці, які є короткими кістками. Коли лікар оглядав моє обличчя, медсестра готувала інструменти для огляду ротової порожнини. Учора лікар взяв у пацієнта зразок слини для аналізу. Медсестра буде провітрювати палати завтра з 10 до 12. Гастроентеролог обстежив пряму кишку пацієнта за допомогою проктоскопу до цього часу вчора. Лаборант зробить аналіз шлункового соку до того, як хворий покине палату. Я повинна здати реферат про різновиди раку ротової порожнини 21 травня. Поглянь: цей пацієнт має у роті прикусний валик. Коли пацієнт пив гарячу каву, то відчув сильний зубний біль. Він ще не протер спиртом шкіру навколо опіку. Після того, як травматолог виявив сколіоз, лікар зробив рентген, щоб підтвердити діагноз. Медсестра провітрить палату до того часу, коли я повернуся. Інфекція гепатиту може поширюватись під час особистого контакту з хворим. Травматолог щойно оглянув дитину з обмороженням кінцівки. Медсестра приготувала систему для переливання крові до того, як прийшов лікар. Учора лікар взяв у пацієнта зразок слини на аналіз. Серцевий м’яз працює близько 1/3 часу всього життя. Цей стоматолог був упевнений, що його пацієнт не дотримується гігієни порожнини рота. Існує кілька типів білих кров’яних тілець, серед яких гранулоцити й агранулоцити. Ви коли-небудь застосовували розчин новокаїну при опіках? Після того, як лікар провів повний медичний огляд пацієнта, він призначив ці ліки у формі внутрішньом’язевих ін’єкцій. Вчора вона ходила в найближчу аптеку, щоб купити ліки від зубного болю. Лікар проводить профілактичні процедури, тому не турбуйте його зараз. Для запобігання карієсу мій син зменшив вживання цукру. Хірург підійде до вас пізніше, бо він щойно закінчив операцію на серці і зараз дуже втомлений. Лікар виписав рецепт хворому, що скаржився на біль у шлунку до того, як медсестра увійшла до кабінету. Гастроентеролог зробить гастроскопію завтра до 5 години. Почекайте лікаря в коридорі. Він має прийти через 15 хвилин. Я добре пережувала їжу перед тим, як ковтнула її. У науковій медичній літературі є багато інформації щодо доцільності використання серповидного зонду у стоматологічній практиці. Вірус, що фільтрується можливо виявити лише за допомогою електронного мікроскопа. Після того, як лікар зробив біопсію кісткового мозку, він визначив тип лейкемії. Ми переглянемо цю наукову телепередачу про методи лікування захворювань шлунка до наступного заняття. Стоматолог пломбуватиме ваш зуб завтра з 10 до 10.30. Не розмовляйте так голосно. Пацієнт може почути вас. Над стоматологічним кріслом є світильник і комп’ютерний монітор. Хірург завершив операцію по видаленню жовчного міхура за допомогою лапороскопа ще до обіду. Марта вже знайшла таблетки від болю в м’язах і суглобах, які їй приписав лікар. Вона сьогодні купила їх в аптеці, що знаходиться біля її будинку. Коли пацієнт пив гарячу каву, то відчув сильний зубний біль. Вона шукала таблетки два дні, а сьогодні купила їх в аптеці. Стоматолог пломбуватиме ваш зуб завтра з 10 до 10.30. Лікар призначить ці ліки у формі внутрішньом’язевих ін’єкцій або орально після їжі після того, як проведе повний медичний огляд пацієнта. Лаборант зробить аналіз шлункового соку ще до того, як лікар попросить його про це. При жовтяниці жовч не здатна проходити в кишечник. Коли лікар оглядав моє обличчя, медсестра готувала інструменти для огляду ротової порожнини. Учора лікар взяв у пацієнта зразок слини для аналізу. Медсестра буде провітрювати палати завтра з 10 до 12. Чи могла б я дізнатися про результат аналізу крові цієї пацієнтки? Медсестра провітрить палату до того часу, коли я повернуся? Лікарі можуть направити вас в інфекційну лікарню при найменшій підозрі гепатиту. Температура крові може бути різною у різних органах і частинах тіла. Черговий лікар проведе ранковий обхід до 10 години ранку. Мати може передати гепатит В своїй дитині під час народження. Пацієнтові слід здати кров на загальний аналіз сьогодні. Вона повернеться з міжнародної конференції лікарів-гастроентерологів до кінця тижня? Він вже п’ять років вивчав властивості мінералів, коли його перша стаття була опублікована. Студенти запитали викладача, чи плацебо все ще використовуються зараз. Біль при гострому запаленні жовчного міхура може бути нестерпним. Лише білі кров’яні тільця здатні боротися з інфекцією. Лікар сказав, що ці гомеопатичні ліки не викликають побічних реакцій. Я вже півроку з’ясовую причину своєї алергії, і ніяк не можу з’ясувати. Лікар випише рецепт хворому, що скаржиться на біль в шлунку, до того, як медсестра увійде у палату. У людини з гострим холециститом можуть бути серйозні ускладнення. При найменшій кровотечі слід звернутися до лікаря. Фармацевт сказав, що він уже зробив настій та відвар з кульбаби. Покупці уже півгодини чекають на ліки від артриту та пневмонії. Після того, як старша медсестра дозволить нам зайти у палату, ми дізнаємось про самопочуття Андрія. Кровотеча може супроводжувати таке захворювання, як цироз печінки. Студенти-медики повинні серйозно ставитися до їх майбутньої професії, оскільки їм прийдеться мати справу зі здоров’ям і життям пацієнтів. Я не можу розмовляти з тобою по телефону. Моя сестра щойно обпекла долоню, тому ми зараз їдемо в опікове відділення обласної лікарні. Властивості нових заспокійливих препаратів вже вивчили та перевірили клінічно у цьому дослідному інституті. Ми не зможемо піти сьогодні у кіно, бо маємо прочитати і перекласти текст про побічні дії ліків. Бабуся спитала онука, чи він вже купив таблетки від кашлю, виписані лікарем. Наукова конференція з фармакоепідеміології триває вже третій день. Вони збудували нову лікарню до першого серпня. Сподіваємось, що вони встигнуть завезти все необхідне обладнання до першого вересня. Свербіж також може бути присутнім при гострому вірусному гепатиті. Ти повернув Степану підручник з терапії, який ти позичив у нього, щоб прочитати параграф про хвороби серця? Учасники дослідницької групи повідомили, що новий препарат тестується на контрольній групі тварин уже два місяці. «Вам слід дотримуватися строгої дієти і приймати гомеопатичні препарати» – порекомендував лікар пацієнту. Студенти вже прочитали та переклали цей текст. Зараз вони виконують граматичні вправи. Вони виконають усі завдання до кінця пари. Перед операцією хірург повинен одягнути стерильний халат і рукавички. Ви часто приймаєте якісь ліки, коли у вас болить спина? – Ні, але сьогодні біль сильніший, і я щойно прийняв знеболювальний засіб. Студент опрацював тему “Травна система і травлення”, до того як повернув посібник з терапії у бібліотеку. Якщо ми матимемо вільний час, ми переглянемо цю наукову телепередачу про методи лікування захворювань шлунка ще до наступного заняття. Вoна вже п’ять років вивчає властивості та дію гомеопатичних препаратів. Студентам пояснили процес розробки, виготовлення та випробування нових препаратів. – Ви коли-небудь були за кордоном? – Так, я їздив цього року до Сполучених Штатів на міжнародну конференцію, присвячену профілактиці остеопорозу й артриту. Лікар Петренко зробив ранковий обхід до 10 години. Пацієнт повинен знати, що робити у випадку алергічної реакції на ліки. Студенти вивчають назви ліків протягом всіх років навчання в університеті. Якщо я швидко знайду хірургічне відділення, я побачу брата ще до того, як лікарі заберуть його на операцію. Лікар ще не закінчив операцію із заміни ушкодженого суглоба на штучний, а родичі пацієнта уже зібралися в холі з квітами. Проктолог обстежив пряму кишку пацієнта за допомогою проктоскопа до цього часу вчора. Вони складуть іспит з англійської мови до другої години в четвер? – Де медсестра? Я можу з нею поговорити? – Вона вже пішла. – Не може бути. Я щойно бачила її в третій палаті. Гастроентеролог був впевнений, що пацієнт не здав шлунковий сік на аналіз. Цей професор або терапевт, або хірург, але я точно знаю, що він працює в обласній клінічній лікарні. Я накладаю тугу пов’язку на стопу з того часу, як я розтягнув зв’язки. Я відчуваю такий сильний біль, що не можу ходити. Після того, як дільничний лікар оглянув його ротову порожнину, язик і горло, він попросив медсестру виписати хворому рецепт. У нього не було ні температури, ні інших симптомів, проте він почувався погано. Скільки разів на цьому тижні ти робив процедури, які тобі порадив лікар для зміцнення м’язової системи? – Цього тижня я лише двічі ходив на електрофорез, але робив вправи щодня. Ти повернув Сергію підручник з внутрішніх хвороб, який ти позичив у нього, щоб прочитати параграф про розлади шлунково-кишкового тракту? Медсестра зараз або допомагає лікарю у приймальному покої, або ставить крапельницю пацієнтові з восьмої палати. – Ви бачили його останнім часом? – Так, я зустрів його сьогодні біля міської лікарні. Він цього місяця зламав руку. Я добре пережувала їжу перед тим, як ковтнула її. Хвороба Боткіна може вражати людей різних вікових груп. Сьогодні вранці вона ходила в аптеку купити мазь від болю в спині. Після того, як я почала приймати панкреатин та інші ліки під час кожного прийому їжі, у мене зникли шлункові коліти й покращилось засвоєння білків, жирів, вуглеводів та інших поживних речовин. При переливанні крові інфекція гепатиту В може потрапити в організм людини.