FTCE K-6 SciencE Exam
advertisement

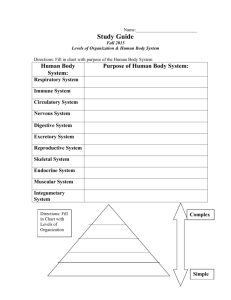
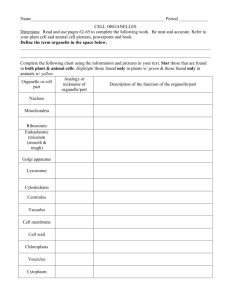
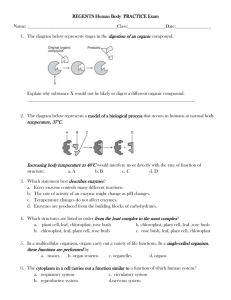
FTCE K-6 EXAM Subtest 3: Science GENERAL EXAM KNOWLEDGE Competency # of Questions 1 Knowledge of Effective Science Instruction About 11 2 Knowledge of the Nature of Science About 10 3 Knowledge of Physical Sciences About 11 4 Knowledge of Earth and Space About 10 5 Knowledge of Life Science About 13 GENERAL EXAM KNOWLEDGE QUESTION TYPES Complete the statement Example – water can turn from liquid to gas by evaporating or ___________ a. Condensing b. Pouring c. Boiling d. Freezing Which of the following Example – which of the following is translucent a. A car windshield b. A convex mirror c. A frosted lightbulb d. A concrete block Negative questions Example - which is not found in the electromagnetic spectrum? a. X-rays b. Infrared light c. FM radio waves d. Sound waves Questions that include graphs, tables, or reading passages Example – which conclusion can be drawn from the following chart? a. Adding 7 ml of water provided the most growth. b. The more water a plant received, the taller the plant grew. c. The more sunlight a plant received, the taller the plant grew. d. For each ml of water added, the plant grew 1 inch. There are three levels of question difficulty. Easy Average Rigorous WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT EFFECTIVE SCIENCE INSTRUCTION Instructional Strategies To Know • 5 E’s Engage, explore, explain, elaborate or extend, evaluate • Inquiry Method Student centered Emphasizes how we come to know rather than what we know Construct knowledge through active involvement Starts with a problem • POE Predict, observe, explain • Hands on Science Activities • Project based Learning WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT EFFECTIVE SCIENCE INSTRUCTION Ways to assess in science • Diagnostic assessments • Formative assessments • Summative assessments • Traditional assessments • Performance based assessments Differentiation in science instruction • English language learners (ELL) • Students with exceptionalities Preconceptions and misconceptions WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT THE NATURE OF SCIENCE Science Processes • Basic Process Skills (k-4) • Integrated Process Skills (3-6) Scientific Method • Question • Hypothesis • Variables (independent, dependent, controlled) • Experimental Design • Data Collection • Analysis of Results Lab Safety and Procedures • Teaching Safety Procedures • Teaching Proper Usage of Equipment WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT THE CONTENT OF SCIENCE • PHYSICAL SCIENCE • EARTH SCIENCE • LIFE SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCE • Properties of matter • Types of matter • Phase changes • Temperature, heat, and heat transfer • Forces • Light • Electricity • Types of energy • Balanced and unbalanced forces ALL ABOUT MATTER Physical Properties PHYSICAL VS. CHEMICAL CHANGES Physical changes do not result in a change in substance Chemical changes (reactions) result in new substances Let’s Practice - Physical or Chemical? • Water condenses on a cold glass • Breaking glass • A rusting nail • An ice cube melting • Sugar dissolving in water • Baking soda mixed with vinegar • Burning a piece of paper CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER Phases of matter • Solid, liquid, gas Phase changes • What are these? • How do they work? Temperature, heat, and heat transfer • Are heat and temperature the same? • How does heat move? • Radiation, convection, and conduction MAY THE FORCE BE WITH YOU • What is a force? • How do you know a force is acting on an object? • What kinds of forces are there? Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • What happens when forces are balanced? • What happens when forces are unbalanced? TYPES OF ENERGY Type Important Ideas Mechanical Potential and Kinetic Light Light Passage (opaque, translucent, transparent) Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction, and Absorption Magnetic Magnets, Opposites Attract, Likes Repel Nuclear Dividing, Combining, or Collision of Nuclei Sound Travels in mechanical waves through materials Chemical Breaking of chemical bonds into heat and light (combustion, burning, explosions) Electrical Circuits, Conductors, Insulators, Movement of Electrons, Static Electricity Thermal Manifests itself as heat EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE Geologic Formations • Result from geologic processes that are either constructive or destructive Rocks and Minerals • Minerals make up rocks • Characteristics of Minerals • Igneous, Metamorphic, Sedimentary • Rock Cycle Water, Air, and Land • Water Cycle • Cloud Formation • Interaction of Water and Soil Heat Transfer • Radiation, Convection, Conduction EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE Planets Celestial Bodies • Comets, Asteroids, Stars, Moon • Phases of the Moon • Eclipses Space History What is the reason for seasons? LIFE SCIENCE Living and non-living things • What makes something alive? Cells • Cell Parts Prokaryotes • Single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or organelles Eukaryotes • Have a nucleus, cell walls or cell membranes, and other organelles Heredity, evolution, and natural selection PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A toy car is stationary at the top of an inclined ramp. What type of energy is demonstrated? (Easy) a. Electrical b. Potential c. Solar d. Kinetic PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A toy car is stationary at the top of an inclined ramp. What type of energy is demonstrated? (Easy) a. Electrical b. Potential c. Solar d. Kinetic PRACTICE QUESTIONS 2. An object’s ability to float depends on its ______? (Average) a. Size b. Temperature c. Insulation d. Density PRACTICE QUESTIONS 2. An object’s ability to float depends on its ______? (Average) a. Size b. Temperature c. Insulation d. Density PRACTICE QUESTIONS 3. Which statement explains why the sun appears to rise and set each day? (Rigorous) a. Earth rotates b. Sun rotates c. Sun revolves around the Earth d. Earth revolves around the Sun PRACTICE QUESTIONS 3. Which statement explains why the sun appears to rise and set each day? (Rigorous) a. Earth rotates b. Sun rotates c. Sun revolves around the Earth d. Earth revolves around the Sun PRACTICE QUESTIONS 4. Everything in our world is made up of _____? (Easy) a. Matter b. Cells c. Grams d. Molecules PRACTICE QUESTIONS 4. Everything in our world is made up of _____? (Easy) a. Matter b. Cells c. Grams d. Molecules PRACTICE QUESTIONS 5. Dr. O. was baking a cake. She noticed that the ingredients that she was using were being turned into different substances. This is an example of a _____? (Rigorous) a. Physical property b. Chemical property c. Physical change d. Chemical change PRACTICE QUESTIONS 5. Dr. O. was baking a cake. She noticed that the ingredients that she was using were being turned into different substances. This is an example of a _____? (Rigorous) a. Physical property b. Chemical property c. Physical change d. Chemical change PRACTICE QUESTIONS 6. Materials through which electric charges easily flow are ________? (Easy) a. Conductors b. Insulators c. Neutrons d. Ions PRACTICE QUESTIONS 6. Materials through which electric charges easily flow are ________? (Easy) a. Conductors b. Insulators c. Neutrons d. Ions PRACTICE QUESTIONS 7. When is a hypothesis formed? (Easy) a. Before data is collected b. After data is collected c. After data is analyzed d. After the results are described PRACTICE QUESTIONS 7. When is a hypothesis formed? (Easy) a. Before data is collected b. After data is collected c. After data is analyzed d. After the results are described PRACTICE QUESTIONS 8. Identify the correct sequence of organization of living things from lower to higher order: (Rigorous) a. Cell, Organelle, Organ, Tissue, System, Organism b. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organelle, System, Organism c. Organelle, Cell, Tissue, Organ, System, Organism d. Organelle, Tissue, Cell, Organ, System, Organism PRACTICE QUESTIONS 8. Identify the correct sequence of organization of living things from lower to higher order: (Rigorous) a. Cell, Organelle, Organ, Tissue, System, Organism b. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organelle, System, Organism c. Organelle, Cell, Tissue, Organ, System, Organism d. Organelle, Tissue, Cell, Organ, System, Organism PRACTICE QUESTIONS 9. Explain the proper technique for smelling a substance. (Average) PRACTICE QUESTIONS 9. Explain the proper technique for smelling a substance. (Average) Hold the substance at arms length and gently waft it. PRACTICE QUESTIONS 10. Which of the following is not an appropriate formative assessment for evaluating student performance in an activity? (Average) a. Unit exam b. Journal entry c. Student presentation d. Student video PRACTICE QUESTIONS 10. Which of the following is not an appropriate formative assessment for evaluating student performance in an activity? (Average) a. Unit exam b. Journal entry c. Student presentation d. Student video RESOURCES • Florida Department of Education FTCE website http://www.fl.nesinc.com/testpage.Asp?Test=060 • National Science Teachers Association http://www.nsta.org/ • CliffsNotes FTCE: Elementary K-6 http://www.scribd.com/doc/26446600/CliffsNotes-FTCE-Elementary-Education-K-6 • Quizlet Flashcards - Science https://quizlet.com/subject/FTCE-k%252D6-science/ • Content Module - Science http://www.fl-pda.org/independent/courses/elementary/science/unitObj.htm