Chapter 4 Islam History
advertisement

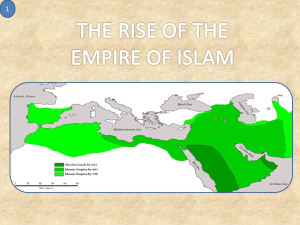
Exploring the Religions of Our World Chapter 4 Islam Chapter 4 Islam The Basics Mohammad God’s final messenger Islam “surrender” or “submission” Abraham ancestor to Jews, Christians, Muslims Allah “The God” Chapter 4 Islam Periods of Islamic History Page 135 Chapter 4 Islam History Islam has always existed, beginning with Adam the first man Muhammad: born in Mecca in about 570 CE first revelation from the Angel Gabriel who instructed him to be the messenger of Allah in 610 moved to Medina in 622 died in 632 Chapter 4 Islam History (continued) The first four caliphs : • Abu Bakr – first to succeed Muhammad • Umar – oversaw the expansion of Islam; appointed a committee of six to choose his successor • Uthman – a member of the Umayyah clan; was instrumental in the publication and distribution of the Qur’an • ‘Ali – Muhammad’s cousin Chapter 4 Islam History (continued) The Sunni Muslims and Shi’ah Muslims share fundamental beliefs and practices but are divided on who is to lead Muslims – why? Chronology of the division: 1. Uthman is assassinated 2. Ali succeeds him as caliph 3. Uthman’s cousin Mu’awiyah is also proclaimed caliph 4. following a series of battles, an arbitrator rules in favor of Mu’awiyah 5. ‘Ali is assassinated Chapter 4 Islam Chronology of division: (continued) 6. when ‘Ali’s son makes a claim to leadership, he and his family are massacred 7. Shi’ah Muslims see Husayn as a martyr and remain loyal to his family 8. The Sunni (the majority) accept the rule of the Umayyads 9. the Sunni support a caliphate and call their leaders caliph 10. the Shi’ah support an imamate and call their leaders Imam Chapter 4 Islam History (continued) Historical centers of Islam: Medina, Saudi Arabia Kufah, Iraq Damascus, Syria Baghdad, Iraq Chapter 4 Islam History (continued) Literature Philosophy Medicine Astronomy Mathematics Geography Chemistry Engineering Muslim scholarship sought to reconcile reason and faith which led to advances in: Chapter 4 Islam History (continued) The Nation of Islam W.D. Fard Muhammad – African-American who spoke against Christianity as a white man’s religion and called for the establishment of a separate, African-American homeland Elijah Muhammad – continued Fard’s message when he succeeded him, expanding the Nation of Islam to other cities Malcom X – leader in New York who challenged Elijah Muhammad’s leadership and message before being assassinated by rivals in 1965 Warith Din Muhammad – Elijah Muhammad’s son who succeeded in bringing most of the Nation of Islam into union with Sunni Islam Louis Farrakhan – led members of the Nation of Islam who opposed the more integrated ideology of Warith Din Muhammad Chapter 4 Islam Sacred Stories and Sacred Scriptures Qur’an Qur’an (Koran) most sacred book for Muslims a collection of the revelations Muhammad received directly from God contains God’s infallible words, uncorrupted by human intervention literally means “recitation” divided into 144 surahs Chapter 4 Islam Sacred Stories and Sacred Scriptures (continued) Sunnah Qur’an second authentic source of authority for Muslims contains Muhammad’s words and deeds as well as what he approved and prohibited it is Muhammad’s way of life it goes hand in hand with the Qur’an because one needs to fully understand and live as a Muslim Chapter 4 Islam Beliefs and Practices Belief in one God is the central belief of Muslims La ilaha ilia Allah wa Muhammadun rasul Allah There is no god but God, Muhammad is the Messenger of God. Chapter 4 Islam Beliefs and Practices (continued) Core Tenets Free will is an integral part of being human Muhammad is the “Messenger of God” God is very involved as a guide in human affairs God is the creator and sustainer of the universe God gives life and takes life away God is the judge of all and determines who will spend eternity in heaven or hell Divine providence God is all-: loving, powerful, knowing, merciful, present Chapter 4 Islam Beliefs and Practices (continued) Biblical prophets mentioned in the Qur’an: Adam Noah Qur’an Qur’an Abraham Moses The Aaron Christian Jacob and his sons Job Bible Jesus Beliefs and Practices (continued) The Five Pillars of Islam to Mecca Hajj (Pilgrimage) during Ramadan Sawn (Fasting) charity for the needy Zakah (Almsgiving) five times daily Salah (Prayer) There is no god but God, Muhammad is the Messenger of God Shahadah (Witnessing) Chapter 4 Islam Chapter 4 Islam Sacred Times prayer 5 times each day Eid al-Fitr (Festival of Breaking the Fast) Eid al-Adha (Festival of Sacrifice) Ashura (recalls the Exodus from Egypt) Chapter 4 Islam Sacred Places and Sacred Spaces Mosque (Masjid ) - a place of public worship Mecca, Saudi Arabia – the holiest city in Islam; birthplace of Muhammad and site of his first revelations Medina, Saudi Arabia – second holiest city; place to which Muhammad immigrated Jerusalem, Israel – the place of Muhammad’s “Night Journey”; place he ascended into heaven Karbala, Iraq – the site of the massacre of the ‘Ali and his companions and family Chapter 4 Islam Islam Through a Catholic Lens Similarities between Muslims and Catholics • • • • • • • • The worship of the one God The understanding of God as: living, subsistent, merciful, almighty, Creator The desire to submit to God’s decrees The veneration of Jesus as a prophet The invocation of the Virgin Mary The anticipation of the Day of Judgment The centrality of Family life Social concerns: prejudice, poverty, environment Chapter 4 Islam Islam Through a Catholic Lens (continued) Major Differences between Muslims and Catholics • Muslims do not believe in doctrine of the Holy Trinity • Muslims do not acknowledge Jesus’ divinity • Muslims do not believe Jesus suffered a human death by crucifixion Chapter 4 Islam Vocabulary Islam Muslim Allah Ka’bah Hijrah Caliphs Qur’an Imam Calligraphy Surahs hafiz Hadith Five pillars Shahadah Muezzin Salah Wudu Zakah Sawm Ramadan Hajj Ulama Mosque Adan