History theme chart-1
advertisement
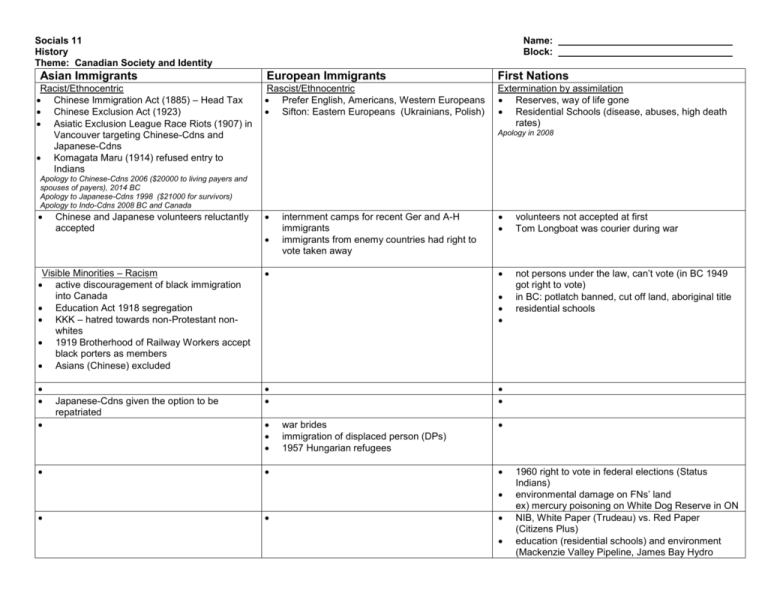
Socials 11 History Theme: Canadian Society and Identity Asian Immigrants Racist/Ethnocentric Chinese Immigration Act (1885) – Head Tax Chinese Exclusion Act (1923) Asiatic Exclusion League Race Riots (1907) in Vancouver targeting Chinese-Cdns and Japanese-Cdns Komagata Maru (1914) refused entry to Indians Name: Block: European Immigrants First Nations Rascist/Ethnocentric Prefer English, Americans, Western Europeans Sifton: Eastern Europeans (Ukrainians, Polish) Extermination by assimilation Reserves, way of life gone Residential Schools (disease, abuses, high death rates) Apology in 2008 Apology to Chinese-Cdns 2006 ($20000 to living payers and spouses of payers), 2014 BC Apology to Japanese-Cdns 1998 ($21000 for survivors) Apology to Indo-Cdns 2008 BC and Canada Chinese and Japanese volunteers reluctantly accepted Visible Minorities – Racism active discouragement of black immigration into Canada Education Act 1918 segregation KKK – hatred towards non-Protestant nonwhites 1919 Brotherhood of Railway Workers accept black porters as members Asians (Chinese) excluded Japanese-Cdns given the option to be repatriated internment camps for recent Ger and A-H immigrants immigrants from enemy countries had right to vote taken away volunteers not accepted at first Tom Longboat was courier during war not persons under the law, can’t vote (in BC 1949 got right to vote) in BC: potlatch banned, cut off land, aboriginal title residential schools war brides immigration of displaced person (DPs) 1957 Hungarian refugees 1960 right to vote in federal elections (Status Indians) environmental damage on FNs’ land ex) mercury poisoning on White Dog Reserve in ON NIB, White Paper (Trudeau) vs. Red Paper (Citizens Plus) education (residential schools) and environment (Mackenzie Valley Pipeline, James Bay Hydro Project) land claims (specific and comprehensive) 1990 Oka ($200M vs $5M) Nisga’a Treaty 1995 (since 1880s) – land, profits from fishery & hydro development, self-govt, policing and $$$ 1998 Delgamuluukw – Aboriginal title 1999 Nunavut 2008 Residential Schools apology June 2015 Truth and Reconciliation Report Theme: Canadian Society and Identity Farmers Workers “Last Best West” new immigrants to settle Prairies food produced for soldiers farmers are expanding farms they are good prices for their product anti-conscription because don’t want their men to leave farms Women Urbanization reminiscent of IR in GBR trade unions & strikes Victorian era suffragists (prohibition) nationalists vs imperialists Laurier (compromise) Manitoba Schools Question Boer War (1899) Naval Service Act (1910) factories are now manufacturing goods for war (shells, munitions, equipment etc…) war economy wages are high, unions tolerated anti-conscription because they are contributing to war effort at home Volunteer organizations (Red Cross) Serve as nurses (Bluebirds) worked in jobs traditionally held by men munitions factories MB 1916 received right to vote (1917 AB, SK; 1917 ON, BC) 1917 Wartime Elections Act 1918 right to vote in federal elections WCTU Agnes MacPhail 1921 Emily Murphy 1916 (Persons Case) Carine Wilson 1930 fashion reflects freedoms still paid less no loyalty to England (or Fr) low enlistment Vandoos (22nd Battlion) Henri Bourassa anti-conscription United Farmers’ Parties Don’t like National Policy, railway Progressive Party 1947 Oil AB 1962 SK passes Medical Care Quebec trade unions (Russian Rev) Western Labour Conference 1919: OBU 1919 WGS (higher wages, less hours, better working conditions, collective bargaining) Bloody Saturday 1966 CPP, Medicare 1960 birth control pill 1967 RC on Status of Women 1971 NAC Irene Murdoch, Rosemary Brown Duplessis (Great Darkness) Union Nationale – blame economic probs on Anglos, Church has power, traditional values (1948 Fleur de Lys) Jean Lesage (Quiet Rev) Liberal – separation of Church and state, education overhaul, modernize, equality for Francophones FLQ separatist terrorist organization Bi and Bi Commission Official Languages Act, new flag Expo 67 – DeGualles “Vivre Quebec Libre” 1967 PQ Rene Levesque October Crisis 1970 (FLQ) – WMA Bill 22 1976 PQ in power in QC – Bill 101 1980 referendum on sovereigntyassoc (60/40) 1982 Kitchen Compromise (patriation of Constitution) 1987 Meech Lake 1991 Bloc Quebecois – Lucien Bouchard 1992 Charlottetown Accord 1995 referendum on full sovereignty (50.6/49.4) Jacques Parizeau Clarity Act 2000 Jean Charest 2003 Socials 11 History Theme: Canadian Autonomy & International Involvement Independence 1867 Confederation Alaska Boundary Dispute (1903) WW1 – development of nationhood and identity Valcartier Vimy Ridge recognition at Paris Peace Conference w/ seat, but no vote 1922 Chanak Crisis 1923 Halibut Treaty 1926 King-Byng Crisis 1926 Balfour Report 1931 Statute of Westminster: British Commonwealth Sept 10, 1939 declaration of war King “This is not our War” (NORAD - under US) UN Cuba Vietnam (Pearson) Trudeau – Cuba, China, FIRA, aid to developing nations (Mulroney – Star Wars, Investment Canada, FTA, NAFTA) Canada’s role in WW1 HOME FRONT PM Borden (Conservative) “Ready Aye Ready” Laurier Sam Hughes and Shell Scandal, Ross Rifle, profiteering Imperial Munitions Board and Joseph Flavelle WMA volunteers Sir Thomas White and Income War Tax, Victory Bonds munitions factories convoys and merchant marine conscription (Military Service Act): Military Voters Act and Wartime Elections Act Union government Halifax disaster (1917) Spanish Influenza OVERSEAS high enlistment rates at beginning of war (35000) CEF: Ypres, Somme, Vimy Ridge, Passchendaele, 100 days Generals: Byng and Arthur Currie Paris Peace Conference, Treaty of Versailles ~424000 served overseas, ~60000 dead Name: Block: Canada’s role in WW2 HOME FRONT PM King promises “no conscription” not excited but enlistment is high TOTAL WAR (esp after spring 1940) WMA BCATP CD Howe (Min of Defense) NSS NRMA “Arsenal for Democracy” James Ilsley: Victory Bonds, Income Tax, rationing, WPTB convoys merchant marine role of women Conscription Crisis (1942 plebiscite) Ralston, McNaughton Japanese-Canadian interment and treatment of enemy aliens propaganda social programs OVERSEAS Battle of the Atlantic, Hong Kong, Dieppe, Italy (mouse holing), D-Day (Juno Beach), Liberation of northern Europe Battle of Britain Bomber Command ~370000 served overseas ~42000 dead Participation in world affairs British Foreign Office dictates foreign affairs for Canada Boer War: sent volunteers Naval Service Bill WW1 Paris Peace Conference, Treaty of Versailles contributions recognized with a seat but not a vote WW2 involvement in Eur and Asia UN – Korea, Suez Canal Crisis (Pearson), Somalia, Rwanda, Iraq/Kuwait Cuban Missile Crisis (Diefenbaker) Vietnam Cold War – Gouzenko Affair NATO, NORAD globalization Yugoslavia










