Unit 4 Review #2 KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

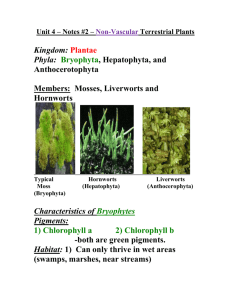
Unit 4 Review #2 1. Mosses belong to phylum BRYOPHYTA. 2. Most taxonomy systems throw mosses, liverworts (hepatophyta) and hornworts (anthocerotophyta) into this phylum. 3. Three reasons why bryophytes are still dependent on a moist environment are: - No waxy cuticle on epidermis to reduce water loss. - Sperm cells are flagellated and must swim in water to reach egg. - Non-vascular. They possess no transport tubules to move water and the products of photosynthesis around their plant body. 4. Bryophytes are very short plants as they must live near the ground close to water because they move water from cell to cell through osmosis. They are non-vascular. 5. You should know the difference between gametophyte generation and sporophyte generation in a moss, also the terms rhizoid, stalk and capsule. 6. Like all higher plants, mosses use chlorophyll “a” and chlorophyll “b”. 7. Haploid cells contain a nucleus that has only one of each chromosome type 1N Diploid cells contain a nucleus that has two of each chromosome type. 2 N 8. In humans the only haploid cells are the egg and sperm cells. In humans the rest of the cells are all diploid. 9. In a moss the haploid plant is the gametophyte generation. 10. In a moss the diploid plant is the sporophyte generation. 11. The part of the haploid gametophyte plant that produces sperm cells is the “ANTHERIDIUM”. 12. The part of the haploid gametophyte plant that produces egg cells is the “ARCHEGONIUM”. 13. The very first cell to form when an egg and a sperm unite is called a ZYGOTE and it is diploid. 14. From this diploid zygote, normal cell division (mitosis) takes place to give rise to a diploid plant known as the sporophyte. 15. Inside the capsule of the sporophyte diploid cells need to undergo reduction division (MEIOSIS) to form haploid cells known as haploid spores. 16. These haploid spores are properly called MEIOSPORES and they are dispersed to germinate out to give rise to the next haploid gametophyte (Protonema)plants. 17. All vascular plants belong to phylum Tracheophyta, but ferns belong to Subphylum PTERIDOPHYTA. 18. Trachea = PIPE Phyta = PLANT These are the “piped plants” 19. Because all Tracheophytes posses vascular bundles/pipes to transport water and the products of photosynthesis. 20. XYLEM is a vascular tissue that is responsible for forming tubules that transport water and dissolved minerals. Primarily made up of dead Tracheid cells and Vessel Element cells. 21. PHLOEM is a vascular tissue that is responsible for forming tubules that transport the products of photosynthesis. Phloem consists mostly of living Sieve Tube Elements and Companion cells. 22. Tracheid cells are hollow, rigid and dead. 23. Other than possessing vascular bundles for transportation, tracheophyte also possess a waxy cuticle and majority of tracheophytes produce seeds that are drought tolerant. 24. The ferns are the most abundant. 25. The creeping underground stem of a fern is known as the RHIZOME. 26. Leaf structures of ferns are called FRONDS. 27. The main generation of a fern is DIPLOID. The haploid gametophyte structure/generation (PROTHALLUS) is diminished. 28. Sori are the cluster-like structures of sporangia on the underside of a ferns leaflets. 29. Haploid fern spores germinate and grow into a haploid gametophyte known as the PROTHALLUS 30. Ferns are still somewhat dependent on standing water for a small part of their life cycle as they still rely on flagellate sperm cells rather than on air-borne pollen capsules like the higher tracheophytes. Also they lack seeds. 31. Archegonium of the prothallus produces EGGS. 32. Antheridium of the prothallus produces SPERM. 33. Frond sprouts are known as FIDDLE HEADS which are diploid. Adaptation for Living On Land 1. Water 2. Rigid xylem provide plants with the support they need to grow up against gravity to out-compete other plants in obtaining sunlight for photosynthesis. 3. Vascular plants transport water and minerals through their Xylem and they transport sugars for energy through their Phloem. 4. A cuticle is a waxy covering on the outside of the a plant’s epidermis that helps reduce water loss. 5. The biggest advancement that most land plants posses is the SEED. The seed contains an embryo that may remain dormant in drought periods for several years. This allows seed plants to inhabit drier environments.