Persuasive Appeals - Moore Public Schools
advertisement

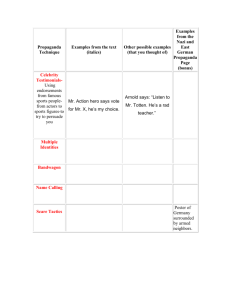
Persuasion Key Elements Persuasive Appeals- methods used to convince people to agree with a position- like using emotions, logic, urgency, or ethics. Claim-Stating your argument in a thesis. Example: Dark chocolate is a healthy snack because of its antioxidants. Persuasive Elements O counterargument: an argument opposed to your thesis, or part of your thesis. It expresses the view of a person who disagrees with your position. O propaganda: attempts to influence ideas or opinions dishonestly using faulty reasoning or other persuasive appeals O author’s bias: an inability or unwillingness of an author to look at all sides of an issue Propaganda= Faulty Reasoning O Faulty Reasoning- flawed thinking or thinking that has errors in it that lead to incorrect conclusions O Either/Or Fallacy- saying there are only two choices when there are actually more Propaganda= Faulty Reasoning O Transfer- connecting products to ideas that make the audience feel good but that don’t necessarily have much to do with the product. O Faulty Cause and Effect- believing that because one event came before another, the first event caused the second event to happen Legitimate Persuasion or Propaganda? (depends on the logic) O Bandwagon- talking about how many other people use a product or act a certain way, making the viewer want to be part of the “in crowd” (can either be legitimate persuasion or propaganda depending on the logic) O Repetition- repeating an idea or a phrase over and over so that it sticks in the viewer’s head Persuasion or Propaganda? O Testimonial- A famous or important person says that he/she uses a particular product, so the viewers and listeners should, too- regardless of whether the product is good. O Exaggeration- overstating a point Words Persuade O Denotation- the literal or dictionary meaning of a word O Connotation- thoughts, feelings, and mental pictures that a word brings to mind O (positive/negative) O Semantic Slanting- using words with very positive or negative connotation to describe something in order to convince an audience. O Slang- highly informal language that is not considered standard usage Logos- Logical/Rational Appeal Appeals to the head rather than the heart. Facts, numbers, and hard evidence can be very convincing. Example: A Snickers bar has 280 calories and 30 grams of sugar. That’s not very healthy. Ethos- Ethical Appeal Making readers trust the writer and believe that his/her position is the “right thing to do.” Examples- References to family, beliefs, character, people who the audience looks up to; this also includes proving oneself as a credible person Pathos- Emotional Appeal Getting people to feel happy, sad, or angry can help your argument. Example: Your donation might just get this puppy off the street and into a good home. Kairos- Appeal to Urgency Try to convince your audience that this issue is so important they must act now. Example: This is a one-time offer. You can’t get this price after today.