Chapter 3 Culture's Influence on Perception

大学英语
跨文化交际
Chapter 3
Culture’s Influence on
Perception
黑龙江大学外语部
Quotation
Everyone thinks that all the bells echo his own thoughts.
— German proverb
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Learning Objectives
:
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Overview:
Human
Perception
A Basic
Model
Sensing
Perceiving
Chapter Outline
Culture’s Influence on Perception
Cross-cultural
Differences
In Sensation and
Perception
Physiological
Barriers to
Accurate
Perception
Sociological
Psychological
How to
Improve Your
Perceptual
Skills
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Lead-in Case:
Perception of War
Please read Case and then discuss the questions in pairs.
1. Why did Jim and Olga have very different attitudes towards starvation and war?
2. Give a brief analysis of their understandings of starvation and war.
3. What factors do you think influence the actual interaction between Jim and Olga?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Text A
Overview: Human Perception
Pre-reading Task:
Suppose you are an American farmer, a French engineer living in Paris, a Scottish country poet, a person living in tropical rain forest or a Chinese oversea student.
What do you think of the beautiful full moon on the traditional Chinese Mid-Autumn Day?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
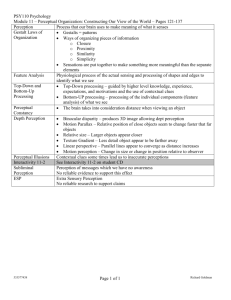
Discuss the model of human perception
Step 1:
Read “A Basic Model of Human
Perception” and then explain the following key words.
(1) Sensation
(2) Perception
(3) Selection
(4) Organization
(5) Interpretation
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Sensation: It is the neurological process by which people become aware of their environment. It refers to the initial detection of energy from the physical world.
感觉: 感觉是人们意识到周围环境的神经过程 , 是对物质世界的
第一察觉。
Perception: It is the process by which we become aware of objects, events, and especially people and their behavior through our various senses and involves higher-order cognition in the interpretation of the sensory information.
知觉:知觉是一种人们通过各种感觉来觉察事物、事件、人和人
的行为的过程。它是解释感觉信息更为高阶的认知过程。
Selection: It is a process in which we screen out what we need from all the stimuli and information around us.
选择 : 选择是从周围选择的刺激信息中筛选出所需要的信息的过程。
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Organization: It is the process during which we need to organize and impose structure on what we observe in a meaningful way.
组织: 组织是把从周围选择的刺激信息,以一种有意义的方式
整理,组合的过程。
Interpretation: It refers to attaching meaning to sense data and is synonymous with decoding.
释义:释义是赋予感觉信息意义的过程, 类似于解码过程。
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Step 2:
Discuss sensing
Discuss what we can sense and what we cannot sense in the daily life, and also analyze how we sense the outside world.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Step 3:
Discuss perceiving
Define perception after reading “perception” and finishing“ Blank Filling”.
(1) Perception refers to the process of the becoming aware of o______, e______, and p______, especially their b_____ through our senses.
(2) Our perceptions are only in a part of function of the outside world; in large measure they are a function of our own c_______, e_______, our d_______, our n_______ and our love and hatred.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
After-reading Check
Please do the analysis on Case 15 “Observations on a soldier” and then discuss the questions in groups.
( 1 ) How is the soldier described in the above conversation?
( 2 ) What stages of perception are reflected in the above conversation?
( 3 ) Could you describe the process in which Sherlock
Holmes and Mycroft perceived the stimuli around them?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Text B
Cross-cultural Differences in
Sensation and Perception
Pre-reading Task:
Please discuss the following statement and see what you can get from this statement in pairs: “We see what we choose to see and we hear what we choose to hear.”
There are so many stimuli around me.
I really need to think what I choose .
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Discuss Cultural Influence on
Sensation and Perception
Step 1:
Discuss physiological cross-cultural difference
Do the group work—divide the whole class into four groups; each group has one task to discuss one aspect of physiological cross-cultural difference, that is, conditions of physical environment, indirect environmental conditions, genetic differences and cultural differences in how people interact with their environment. After that, let each group leader to stand for each group to do the summary of the key points.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Physiological filters include the natural or genetic differences in how one sees, hears, smells, tastes, or feels.
According to some scholars, there are four explanations for intercultural differences in the perception of sensory stimuli.
(1) Conditions of the Physical Environment
(2) Indirect Environmental Conditions
(3) Genetic Differences
(4) Cultural Differences in How People Interact with
Their Environment
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Step 2:
Discuss sociological cross-cultural difference
Please read “cultural effect on sensing" and “Cultural
Effect on Perceiving” separately and summarize the key points .
Then share the key points with your classmates. You can have the classroom competition in groups to find more vivid examples about cultural influence on sensation and perception. In the end , you can find which group is the winner.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Sociological filters represent demographic data and one's membership in groups, including one's culture, microculture, and hometown. culture microculture hometown
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Step 3:
Discuss psychological cross-cultural difference
Do the activity “Expressing Opinions” and then analyze psychological cross-cultural difference.
Think Question: Do you think psychological elements can influence our sensation and perception?
Let ’ s go to see the movie “ Transformers II ” tonight, ok?
I don ’ t like it, for
I don ’ t like the original cartoons.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
The psychological filters refer to the psychological factors, including the attitudes, beliefs, and dispositions of the individual. attitudes beliefs dispositions of the individual.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
After-reading Check
Please do the analysis on Case 16 “Different
Responses to Noise” and then discuss the questions in groups.
(1) How did the German professor interpret the motor for the heating system?
(2) In what way did the Japanese professor interpret the motor for the heating system?
(3) Why did they make different responses to the same motor for the heating system?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Text C
Barriers to Accurate Perception in
Intercultural Communication
Pre-reading Task:
Form groups of four or five. Look at the following pictures and write down a few words for each picture to describe your perceptions about the following questions:
(1) What can you see in these pictures?
(2) What does everyone in the pictures look like?
(3) What are the people doing?
(4) What are their relationships to one another?
(5) Why are they doing so ?
And then share with your group members what you have written down. Try to discuss why you and your group members give different answers. What factors influence your perceptions of these pictures?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Discuss barriers to accurate perception in intercultural communication
Take all the barriers as the whole to conduct learning.
Do the analysis of the case 17 “What is Black?” in detail and then discuss what barriers we have at the very beginning.
What is Black?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(1) Ignoring Details
(2) Over-generalizing
(3) Holding on to Preconceptions and Stereotypes
(4) Imposing Consistency
(5) Preconnecting Causes and Effects
(6) Preferring Simple Explanations
(7) Ignoring Circumstances
(8) Crediting Irrelevant Information
(9) Focusing on the Negative
(10) Seeing Good or Bad
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(1) Ignoring Details
We give too much weight to information that is obvious and superficial. We tend to explain the motives for a person's actions on the basis of the most obvious information rather than on in-depth information we might have. When meeting someone new from another culture, we perceive his or her physical qualities: color of skin, body size and shape, age, sex, and other obvious physical characteristics. We focus on these qualities, because they are so vivid and available. In doing this, we are just ignoring some important details.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(2) Over-generalizing
We treat small amounts of information as if they were highly representative. This tendency also leads us to draw inaccurate, prejudicial conclusions. And also we can even get some general predictions about the people in a certain culture. But in doing this, we are over-generalizing as well.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(3) Holding on to Preconceptions and Stereotypes
We distort or ignore information that violates our expectations, preconceptions, or stereotypes. We see what we want to see, hear what we want to hear. Once we develop our impression on something, we have preconceptions about what we expect from another person. These preconceptions and stereotypes can be so strong that we will distort the way we process our perceptions in order to remain faithful to them.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(4) Imposing Consistency
We overestimate the consistency and constancy of others' behaviors. When we organize our perceptions, we also tend to ignore fluctuation in people’s behaviors, and see them as consistent. We believe that if someone acted a certain way one day, he or she will continue to act that way in the future. In fact, everyone's behavior varies from day to day.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(5) Preconnecting Causes and Effects
We rely on preexisting ideas about underlying causes and what we observe. We’ve already seen how preconceptions about a person can shape our attributions.
We also develop a particular type of preconception that reflects both our implicit personality theory and our personal constructs. We create beliefs about what particular causes are linked to what particular effects.
This keeps us from investigating and collecting additional information to explain an individual's action. To avoid imposing our own preconceptions on others, we must be ready to listen to alternative explanations.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(6) Preferring Simple Explanations
We prefer simple explanations to complex ones, for simple explanations tend to be more believable and easier to use in making sense of another's actions. But in reality our behaviors are affected by many factors.
Unfortunately, it takes a lot of efforts to understand what makes another person do what he or she does - more efforts than we are typically willing to give.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(7) Ignoring Circumstances
We diminish the effect of external circumstances on another's behavior. We also fail to compare one person's behavior with that of others under the same circumstances.
This tendency also represents our desire for simplification.
We are often unaware of the circumstances that affect others, and we do not want to take the trouble to investigate them.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(8) Crediting Irrelevant Information
We treat irrelevant information as if it were relevant. In truth, most exchanges are filled with irrelevant information, and it requires skill and experience to separate the irrelevant information from information that really does help explain another's actions.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(9) Focusing on the Negative
We give more weight to negative information than to positive information, We seem to recognize this bias and compensate for it when we first meet someone by sharing only positive information about ourselves. One piece of negative information can have a disproportionate effect on our impressions and negate the effect of several positive pieces of information.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(10) Seeing Good or Bad
We distort our attributions to match our like or dislike for someone. You would attribute the behavior to an internal cause. You relieve your friend of responsibility by attributing his or her action to external causes. And also, if someone we like does something positive, we attribute it to his or her personality, but when those we dislike do something positive, we attribute it to external reasons or to some darker motivation.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
After-reading check
Do the interview to explore the deep ideas about the barriers to accurate intercultural perception.
And then have interview any classmate according to the table and exchange some information with the classmate, then he or she can know his or her barriers to accurate perception.
First Impressions
Name
Star Sign
College
Major
Hometown
Music preferences
Sport preferences
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
My Barriers to Accurate Perception
________________________
________________________
________________________________
________________________________
________________________________
________________________________
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Text D
How to Improve Your Perceptual
Skills in Intercultural
Communication
Pre-reading Task:
Think about your own preconceptions about cause-and-effect relationships. For each of the following, think about what your first explanation of cause would be :
(1)A person not calling back after a first date.
(2)An American waiter giving you lousy service.
(3)Your car not being repaired after you paid a high service fee.
(4)A teacher’s being late for class.
(5)A child who beats up other kids.
(6)A student who copies test answers from the student next to him.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
And then generate as many explanations for each behavior as you can. Discuss in groups on how you can be sure of which explanation is correct and which one is incorrect and also how to improve your perceptual skills in intercultural communication.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Discuss how to improve your perceptual skills in intercultural communication
Take all the skills as the whole to conduct learning.
Read “How to improve Your Perceptual Skills in
Intercultural Communication” and then discuss what we can benefit from each skill separately.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(1) Increase Your Understanding of the Perceptual Process
(2) Increase Your Observational Acuity
(3) Recognize the Elements to Which You Attribute
Meaning
(4) Check Your Perceptions
(5) Increase Your Awareness of Perceptual Inaccuracies and
Compensate for Them
(6) Increase Your Awareness of Others’ Perceptions of you
(7) Develop Social Decentering, Empathy, and Other-
Orientation
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(1) Increase Your Understanding of the Perceptual Process
You need to understand the process through which you make sense of the world and other people. Don't take your conclusions about others for granted. Question your perceptions and analyze the process through which you arrive at perceptual conclusions. And use your knowledge of the perceptual process to sharpen your own perceptions and conclusions.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(2) Increase Your Observational
Acuity
You can increase the amount of information that you process from your senses by consciously attending to the input. When you interact with others, try to identify one new thing each time to focus on and observe. Each observation will provide information that potentially can improve the quality of your interactions. Try to notice as much detail as possible, but keep the entire picture in view.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(3) Recognize the Elements to
Which You Attribute Meaning
The perception process involves attributing meaning to what we perceive. We do this so automatically that we often fail to realize that we have attributed meaning to something. Therefore, we also fail to recognize the effect it might have on what we do and say. Try to become aware of the stimuli to which you attribute meaning. Take an inventory of your own perceptual tendencies. When you become more aware of what you attend to and when you are attributing meaning, you can then decide whether you are giving proper weight to the elements you perceive.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(4) Check Your Perceptions
You can check out the accuracy of your perceptions and attributions indirectly and directly. Indirect perception checking involves seeking additional information through passive perception to either confirm or refute your interpretations. Direct perception checking involves asking straight out whether your interpretations of a perception are correct. This is often not easy to do for several reasons: we don't like to admit uncertainty or suspicions to others; we might not trust that they will respond honestly; if our interpretations are wrong, we might suffer embarrassment or anger. But asking someone to confirm a perception shows that you are committed to understanding his or her behavior.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(5) Increase Your Awareness of
Perceptual Inaccuracies and
Compensate for Them
As you read through the list of distorting factors above, some of them should have struck a familiar chord . Keep in mind which distortions tend to color your perceptions of others and be aware of their effect. For example, if you know you are likely to interpret the behavior of people you don’t like in a negative way, regardless of their intentions, then you can question your interpretations and correct them if necessary .
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(6) Increase Your Awareness of
Others’ Perceptions of You
The best athletes don't avoid hearing criticisms and observations from their coaches. Instead, they seek out as much feedback as they can about what they are doing right and wrong. Olympic training often involves the use of videotaped replays and computer analysis so that athletes can see themselves as others see them and use that perspective to improve their performance. It is difficult to be objective about our own behavior, so feedback from others can help us with our selfperceptions. The strongest relationships are those in which the partners are both willing to share and be receptive to the perceptions of the other.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
(7) Develop Social Decentering,
Empathy, and Other-Orientation
Effective interpersonal perception depends upon our ability to understand where others are coming from, to get inside their heads, to see things from their perspective.
We have already introduced the importance of social decentering and empathy in interpersonal communication.
They enable us to increase our understanding of others, and they improve our ability to predict and adapt, to increase our communication effectiveness, and to achieve our interpersonal goals. To improve your ability to decenter (to focus on the thoughts of others), strive for two key goals: (1) gather as much knowledge about the circumstances that are affecting the other person as possible; and (2) gather as much knowledge about the other person as possible.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
After-reading Check:
Please do the analysis on Case 18“Are Perceptions
Always Right?” and then discuss the questions in groups.
(1) How does the process of perception work in this conversation?
(2) What are the barriers to accurate perception in intercultural communication shown in this conversation?
(3) What kinds of skills are needed to improve one’s perceptual skills in intercultural communication or to avoid the barriers mentioned above?
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Assignments
Do the Checklist and Assessment.
Do the rest exercises and activities in “After-reading
Check” of each text.
Review what has been learned and preview the next chapter.
Chapter 3 Culture’s Influence on Perception
Thank you
!