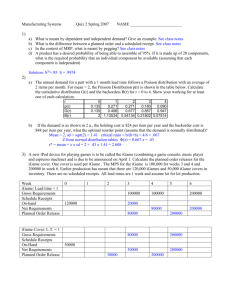
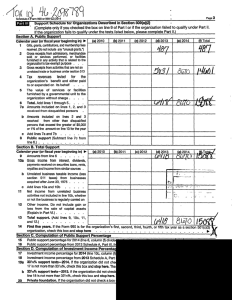
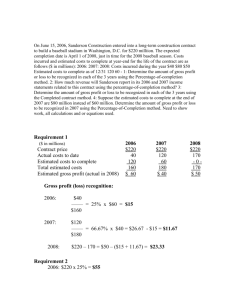
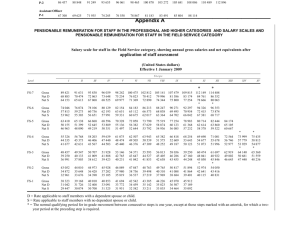
CHAPTER II NATIONAL TAXES Kinds of taxes under existing laws
advertisement

CHAPTER II NATIONAL TAXES Kinds of taxes under existing laws: 1. National taxes – those imposed by the National Government under the National Internal Revenue Code and other laws particularly the Tariff and Customs Code, 2. Local taxes – Those imposed by the local governments to meet particular needs under the Local Government Code, such as real property tax and community tax (formerly residence tax) KINDS/TYPES RELATED DEFINITIONS Income Tax Income (for tax purposes) means all wealth which flows into the taxpayer other than as a mere return on capital. Income tax is a tax on a person’s income, profits, and the like, realized in one taxable year imposed at a progressive or graduated rate. Gross income is all income but not including exempt income and income subject to final income tax. Taxable income is gross income less deductions allowed by law, including in the case of individuals, the allowable personal and additional exemptions. Deductions are items or amounts which the law allows to be deducted from gross income to arrive at a taxable income. Tax return is a sworn statement wherein the taxpayer states the facts as to the nature and extent of his tax liability for the taxable year. Head of the family is an individual who actually supports and maintain in one household, one or more individuals who are closely connected with him by blood relationship, by marriage or adoption. Recognized natural child is one born outside of wedlock between a man and wife, who, at the time of the conceptions of the child, were legally free to marry each other, and is recognized by one or both parents. NATURE AND PURPOSE Its nature is generally regarded as a privilege tax since a person earns an income and not a tax on property. Its purpose is to raise revenue. RATE AND BASES OF TAX Royalties – 10% Interest in bank deposits and other related income – 20% Prizes amounting to P10,000 or less – 20% Cash and property dividends – 6% to 8% Net capital gains from sale of stocks: P100,000 – 5% > P100,000 or excess – 10% Capital gains from sale of property – 6% EXEMPTIONS Winning of PSC and lotto Life insurance proceeds SSS/GSIS benefits Charitable activities Educational Sports and cultural competitions Prizes and awards PERSONS TO FILE Every resident, nonresident, resident aliens, and non resident aliens WHEN TO FILE On or before April 15 of each year, or in meritorious cases, within the extension that may be granted by the Commission er of Internal Revenue WHERE TO FILE Revenue district officer, revenue collection officer, or any authorized agent bank, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where such person has a legal residence. KINDS/TYPES RELATED DEFINITIONS Estate Tax Estate (inheritance) tax is a tax on the right of the deceased person to transmit his estate to his lawful heirs or beneficiaries. Net estate means gross estate less allowable deductions and specific exemptions. Specific exemptions are those which are declared by law as expressly exempt from the tax such as bequests to charitable institutions, subject to certain conditions. Allowable deductions consist of the amounts permitted by law to be deducted from the value of the gross estate. Donor’s Tax Donation is an act of liberality whereby a person disposes gratuitously of a thing or right in favor of another who accepts it. Donation is inter vivos if made between living persons, to take effect during the lifetime of the donor, and mortis causa, if made in the nature of testamentary disposition, that is, is shall take effect upon the death of the donor. Gift tax is a tax imposed on the transfer without consideration of property or money between two or more persons who are living at the time the transfer is made. Donor’s tax or the tax levied on the act of giving. Donee’s tax or the tax levied on the act of receiving. Net gift means the total amount of gifts less the allowable deduction and exemptions provided by law. NATURE AND PURPOSE It is not a direct tax on property, nor a capitation tax; that is, laid neither on the property nor on the transferor or the transferee. In other words, it is a privilege tax. It is a type of death taxes. It was imposed at high rates to help reduce undue concentration of wealth in society to which the receipt of inheritance is a contributing factor. The nature of gift tax is a privilege tax. The purpose of gift tax is intended to supplement the estate taxes by preventing their avoidance by those who gave away money and property in anticipation of death. It is also intended to prevent the avoidance of income tax through the device of splitting income from numerous donees. RATE AND BASES OF TAX Funeral, judicial, and medical expenses – 5% (if not exceeding P500,000) For losses, indebtedness, taxes, an amount equivalent to the fair market value of decedent’s family home not exceeding P1,000,000, and the amount of all transfers to or for the use of the Government or any political subdivisions are subjected in standard deductions as prescribed by law. EXEMPTIONS The first P200,000 value of the estate is exempted. PERSONS TO FILE Heirs or beneficiaries WHEN TO FILE If the gross estate exceeds P20,000, it must be filed within 6 months from the decedent’s death and the tax due thereon paid at the same time WHERE TO FILE Revenue district officer, revenue collection officer, or any authorized agent bank, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the decedent was residing at the time of his death. Donor or donee Donor’s tax must be files within 30 days after the gift is made and the tax thereon paid at the same time. Revenue district officer, revenue collection officer, or any authorized agent bank, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the donor was residing at the time of the donation. Where the decedents was married, only ½ forms part of the gross estate for the other ½ belong to the surviving spouse. Donor’s tax is computed upon the basis of total net gifts during the calendar year, in accordance with the schedule provided by law. Net gifts of the amount of P100,000 or less are exempted. KINDS/TYPES RELATED DEFINITIONS Value-Added Tax Value-added tax (VAT) is a percentage tax imposed on every sale, barter, exchange, or lease of goods of or properties or sale of services in the course of trade or business, and on every importation of goods, whether or not in the course of trade or business, based on the gross selling price or value, or the gross receipts, payable by the seller, thereferor, lessor, or importer. NATURE AND PURPOSE VAT is a privilege tax used to raise revenue. Percentage Taxes EXEMPTIONS Sales of goods and services – 10% of the gross selling price or gross value in money of the goods or properties sold or barter. No exemptions PERSONS TO FILE Taxpayer WHEN TO FILE The quarterly VAT return must be filed within 25 days following the end of each quarter. Taxpayers The quarterly VAT return must be filed within 25 days following the end of each quarter. Importation of goods – 10% of the total value used by the Bureau of Customs Sale of services – 10% of the gross receipts derived by any person engaged in the performance of services. Gross selling price is the total amount of money or its equivalent or its equivalent which the purchaser pays or is obligated to pay the seller. Gross receipts means the total amount of money or its equivalent representing the contract price or fee for the service performed or to be performed for another person. Percentage taxes are based on certain percentage of the gross selling price or gross value in money of goods sold, bartered, exchange, or imported, or gross receipts or earning derived by a person engaged in the sales of services. RATE AND BASES OF TAX VAT (output tax) is computed by multiplying the total amount indicated in the VAT invoice or receipts by 1/11 which amount is deemed to include already the 10% VAT. Percentage taxes are used to raise revenue. Small businesses (<P550,000 annual income) – 3% of gross quarterly sales or receipts. Domestic carriers by land, air or water – 3% of gross receipts. International carriers – 3% of gross quarterly sales or receipts. Franchise holders or grantees (<P10M of annual gross receipts) – 3% of gross of receipts. Senders of overseas messages – 10% of the amount paid for the service. Bank and non-bank financial intermediaries – for <5 years is 5%, 1% if >5 years. Royalties, rentals on property, and other gross income and net trading games – 5% of gross receipts. Life insurance companies – 5% of gross premium collected. Agent foreign insurance companies – 10% of the total premium received. Proprietors, lessees, or operators of amusement places – 15%, 18%, or 30% of gross receipts. Winner in horse races – 10%of the winnings or dividends. Sellers of shares of stocks – 0.5%, 4%, 2%, and 1% of gross selling price or gross value of the shares. Overseas communication tax – 10% of the amount paid or receipts. As prescribed by law WHERE TO FILE Revenue district officer, revenue collection officer, or any authorized agent bank, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the taxpayer is registered as a VAT registered person or required to register. Revenue district officer, revenue collection officer, or any authorized agent bank, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the business or principal place of business of the taxpayer is located. KINDS/TYPES Excise Tax RELATED DEFINITIONS Excise taxes are taxes imposed on certain specified goods manufactured or produced in the Philippines for domestic sale or consumption or for any other disposition and on goods imported into the Philippines. NATURE AND PURPOSE Naturally, excise tax is taxes on property. Documentary Stamp Tax Custom Duties Custom duties are taxes levied by a government on the importation or exportation of goods in or out of the country. Tariff means a book of rates, a schedule of fees imposed on goods imported into a country. EXEMPTIONS Goods manufactured or produced in the Philippines, goods imported from foreign countries, alcohol products, tobacco products, petroleum products, and automobiles, non-essential goods such as jewelry, pearls, perfume, and vessels for pleasure or sports, and mineral products. As prescribed by law It is a privilege tax for the purpose of raising revenue and not to invalidate the contract. Original issue of shares of stocks, sales, agreements, bonds and alike, certificates of profits, debt instruments, bills of exchange or drafts, insurance policies, certificates, warehouse profits, bill of ladings or receipts, proxies and power of attorney, lease, mortgages, pledges, deeds of sale, charter parties and assignment or renewal of certain instruments. For government revenue Dumping duty an amount lower than their home market price. Insurance policies or annuities to members of fraternal societies; certificates of oath administered by government officials; affidavits of poor person; and certificates of assessed value <P200.00 Non imported goods Specific tax or one imposed and based on weight, volume capacity, length, number, or any other physical unit of measurement. Ad valorem tax or one imposed and based on the selling price and other specified value of the article. Documentary stamp tax is a tax on documents, instruments, and papers evidencing the acceptance, assignment, sale or transfer of an obligation, right or property incident thereto. RATE AND BASES OF TAX Countervailing duty is equal to the ascertained or estimated amount of the bounty or subsidy given. Marking duty imposed on imported articles and containers which have not been properly marked in any official language in the Philippines. Retaliatory or discriminatory duty is imposed upon articles of foreign country which discriminates against Philippines commerce. PERSONS TO FILE Taxpayers WHEN TO FILE Before the removal of domestic products from the place of production or before the release of the custom house. Person who issue the document and person to whom it is issued. 10 days after the close of the month when the taxable document was signed, issued, accepted or transferred. Taxpayers Before the removal of custom duties before the release of the custom house. WHERE TO FILE Revenue collection officer, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the taxpayer has his/its legal residence or principal place of business. Revenue collection officer, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the taxpayer has his/its legal residence or principal place of business. Revenue collection officer, or duly authorized treasurer of the city or municipality where the taxpayer has his/its legal residence or principal place of business. KINDS/TYPES RELATED DEFINITIONS Travel Tax Travel tax was imposed to a particular travel. NATURE AND PURPOSE To provide adequate funds for government programs. RATE AND BASES OF TAX P2,700 – on passengers traveling under first class passage. P1,620 – on passengers traveling under economy class passage. P1,350 (1st class) and P810 (for economy class) persons 2-12 years old, accredited Filipino journalist, those authorized by the President for national interest. Energy Tax Motor Vehicle User’s Charge Energy tax is imposed on energy (electric, fuel and alike) consumption. Motor vehicle user’s charge is imposed on motor vehicle. To conserve energy and promote efficient utilization thereof. To provide and ensure the adequate maintenance of national and provincial roads through sufficient funding for the purpose. On aircraft – based on weight EXEMPTIONS Foreign diplomatic and consular officials, crew members of ships; airplanes flying international routes; infants below 2 years old; Filipino OFW, UNO officials, nonresident Filipino citizens; bonafide students with government approved scholarships As prescribed by law. PERSONS TO FILE All Filipino citizens; permanent resident aliens; and nonimmigrant aliens. WHEN TO FILE Upon leaving the country WHERE TO FILE Immigration All consumers Upon payment of consumed energy. Accredited agencies or collectors Owner of the vehicle Upon registration Land Transportation Office On watercraft – based on length Electric power consumption – based on kilowatt hour (KWH) Private passenger vehicles – 25% (1st year); 50% (2nd year); 75% (3rd year); and 100% (4th year onwards) Sports utility vehicles – 15% Motorcycles with sidecars shall not pay more than P300 No exemptions COMPUTATION OF THE INDIVIDUAL INCOME TAX For resident citizens, non-resident citizens and overseas contract workers, resident aliens, and non-resident aliens: Gross income from all sources (within and/or outside the Philippines) Less: Allowable itemized deductions (or 10% Optional Standard Deductions (OSD) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------= Net income from all sources Less: Deductions -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------= Taxable income Less: Exemptions -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------= Amount of income tax due and payable Graduated tax rate since 2008 (Republic Act 9504 – Tax Relief for Minimum Wage Earners Act): Over Over Over Over Over Not over P50, 000 P50,000 P70,000 P140,000 P250,000 P500,000 but not over but not over but not over but not over but not over P70,000 P140,000 P250,000 P500,000 Tax Exempted P2,500 + 15% of the excess over P30,000 P8,500 + 20% of the excess over P70,000 P22,500 + 25% of the excess over P140,000 P50,000 + 30% of the excess over P250,000 P125,000 + 34% of the excess over P500,000 Amounts of personal and additional exemptions allowable to individuals: 1. 2. 3. 4. P20,000 – for single individual or married individual judicially decreed as legally separated with no qualified dependents. P32,000 – for each married individuals (husband or wife); or a total of P64,000 in case both spouses earn income. P25,000 – for unmarried individuals who is “head of the family” depending upon him or her support. P25,000 – for each “recognized natural child” and siblings but not exceeding 4 dependents may be claimed by one of the spouses in the case of married individual. Therefore, a family with four children will have a maximum exemption of P200,000. It is a substantial increase from the previous P96,000 per family with four children. In theory, a family with four children earning exactly or below P200,000 per year will not be subject to income tax. Sample Computation: